Objective:
- Few studies look at the geographical distribution of these environmental pressures and impacts
Case:
Methodology:
- MRIO approach
- Environmental indicators
Data Source: partial open
- Extended multiregional input-output table: EXIOBASE
- GDP: World Bank
- World Economic Outlook
- Population: United Nations
Findings:
- 66-77% of GHG emissions happened within the EU, while the remaining 23-24% happened outside its borders
- land use and biodiversity loss from land use show roughly a 50-50 split with shares increasing in the EU
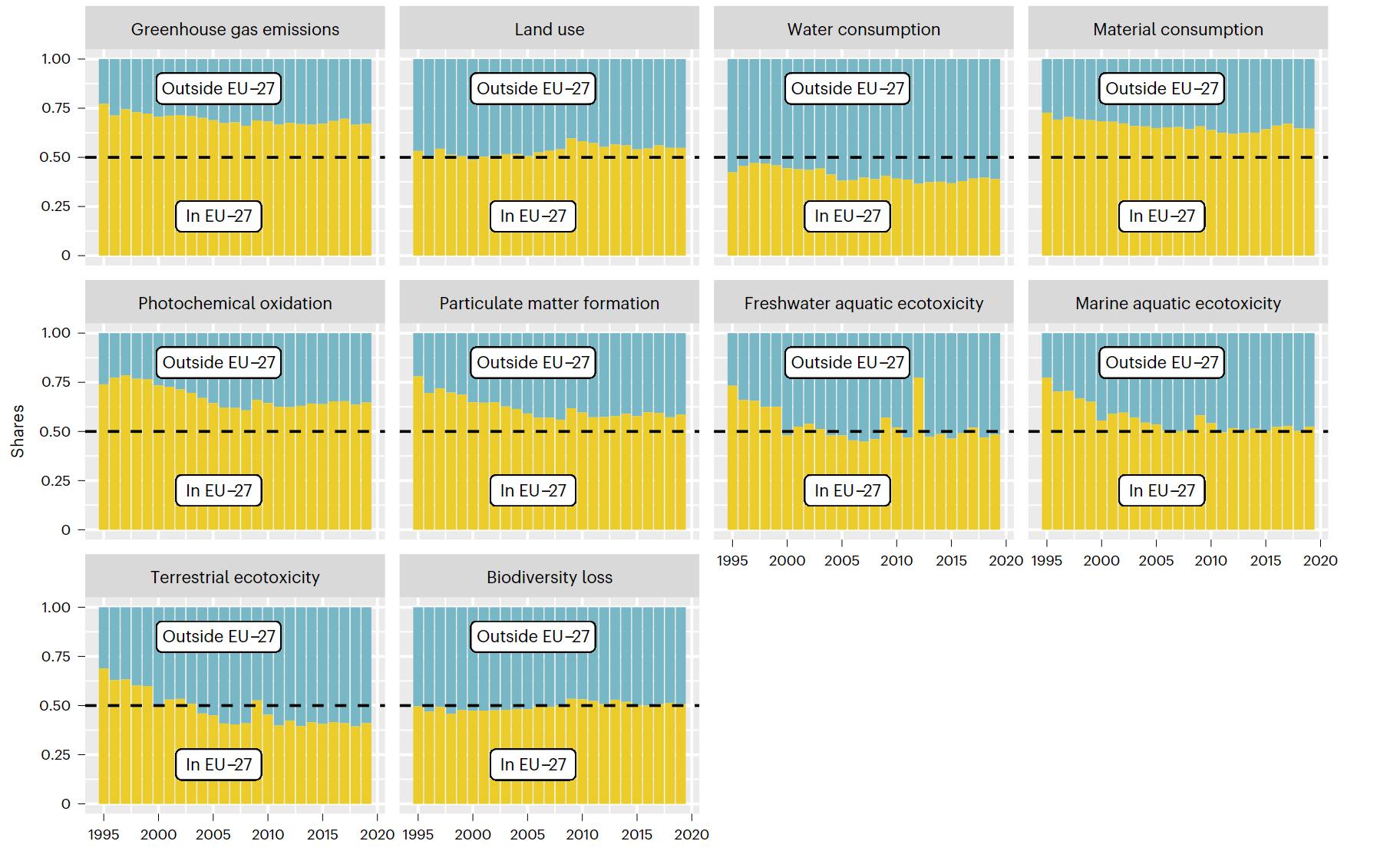
- Various impacts across countries and sectors
- Consumption of food was the highest contributor to land use and biodiversity loss
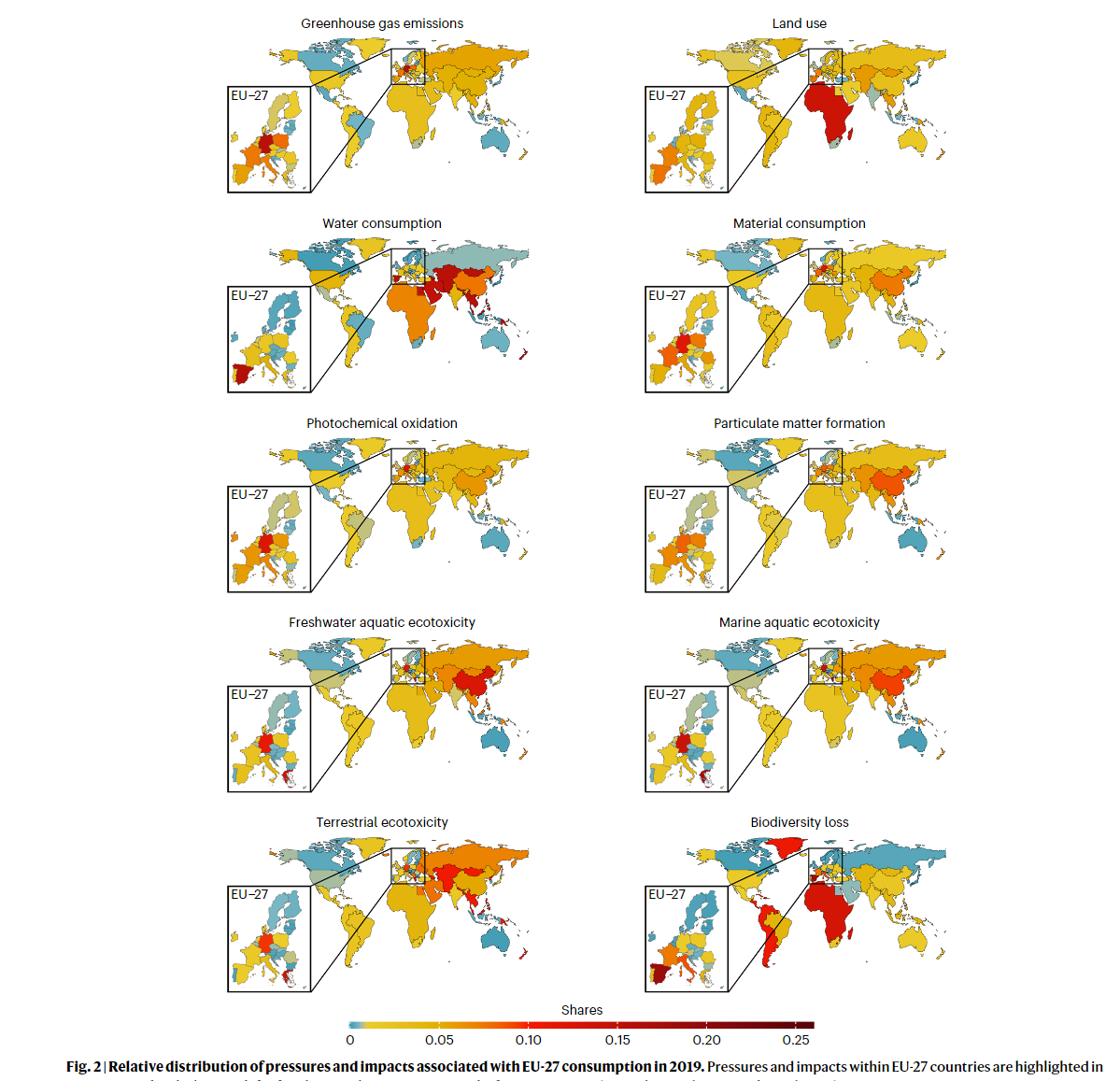
- Five envrionmental pressures decreased but other five increased
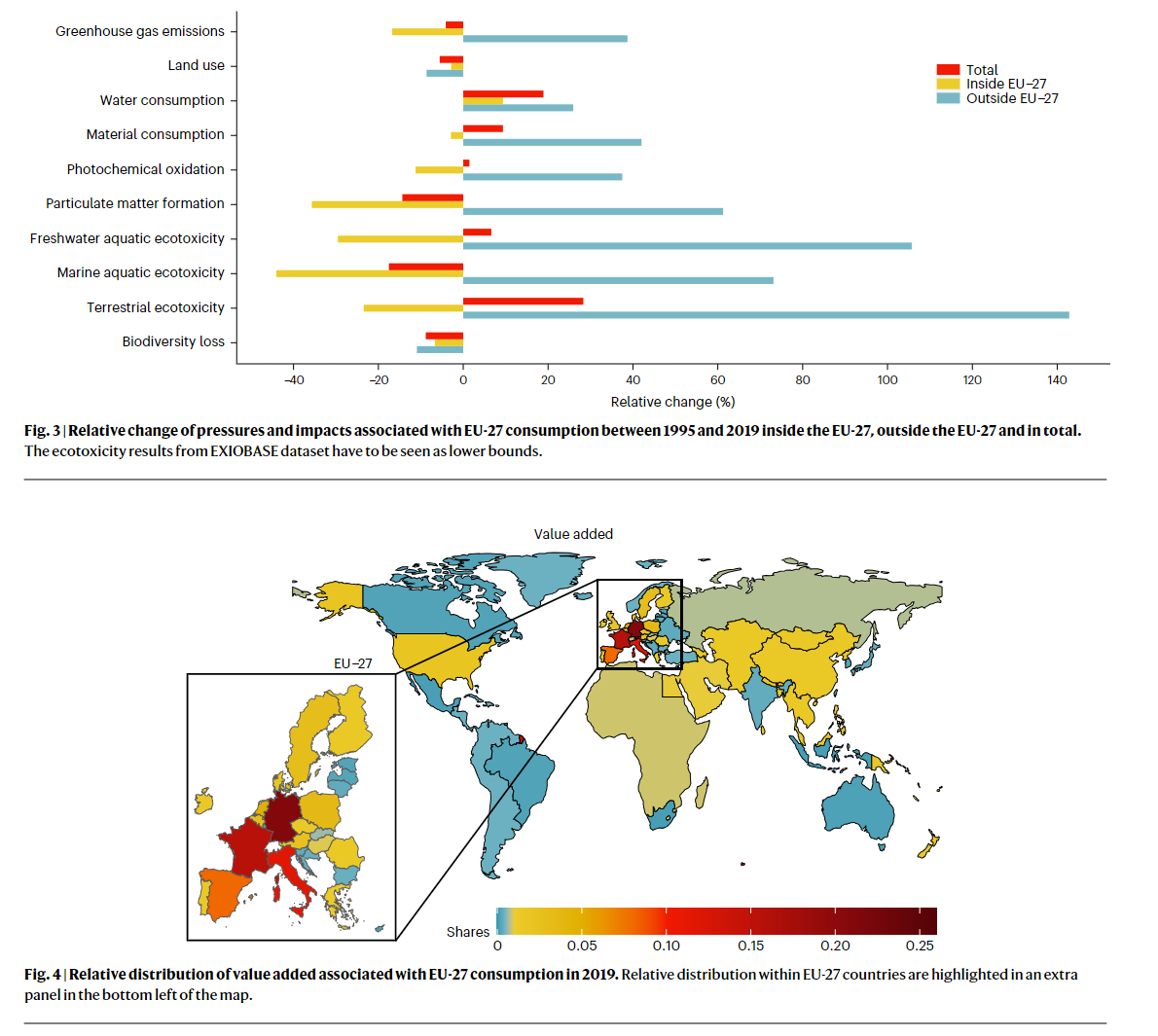
- EU consumption is connected to high GHG emissions in Russia and countries in the ROW Asia and Pacific region
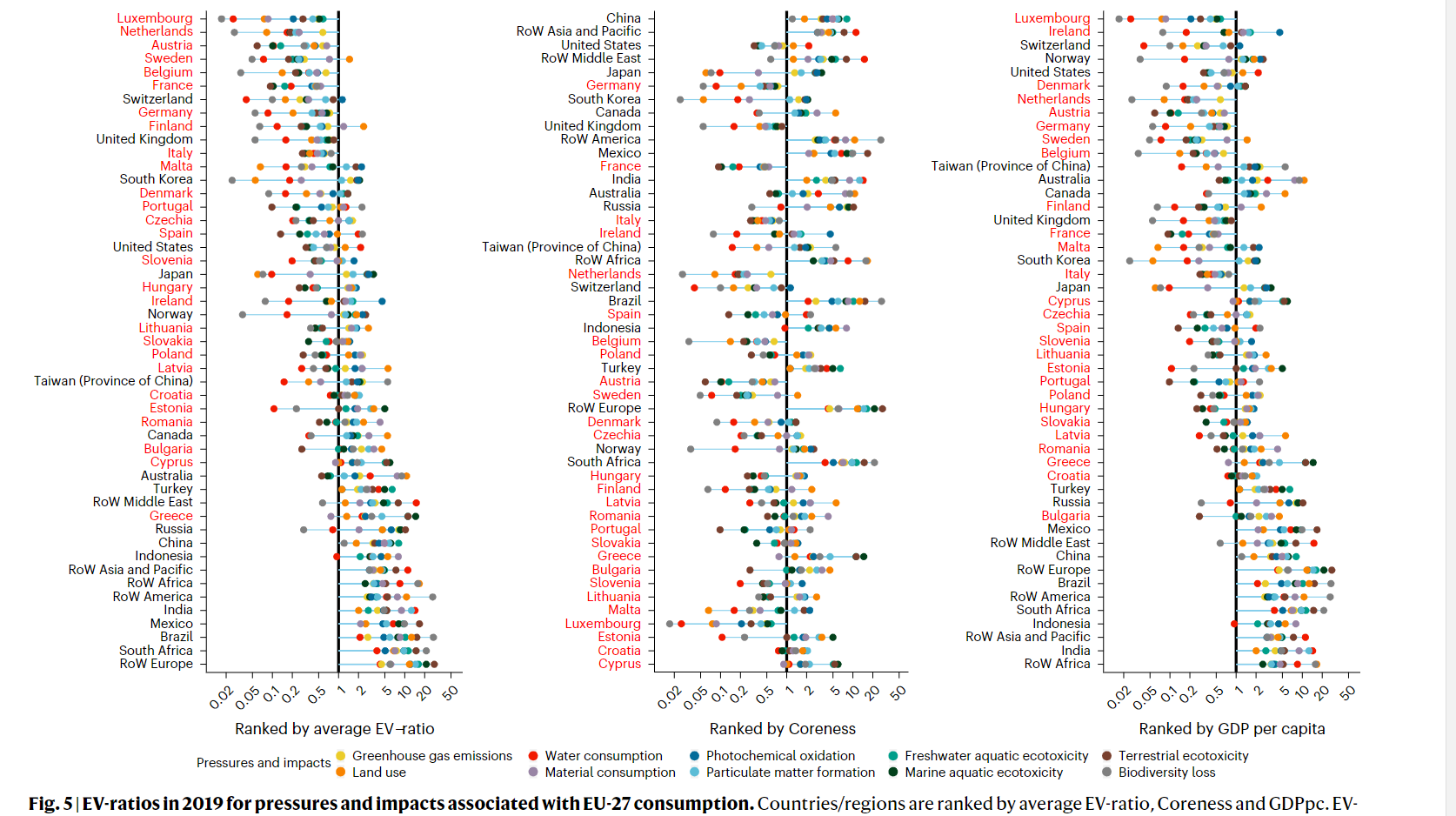
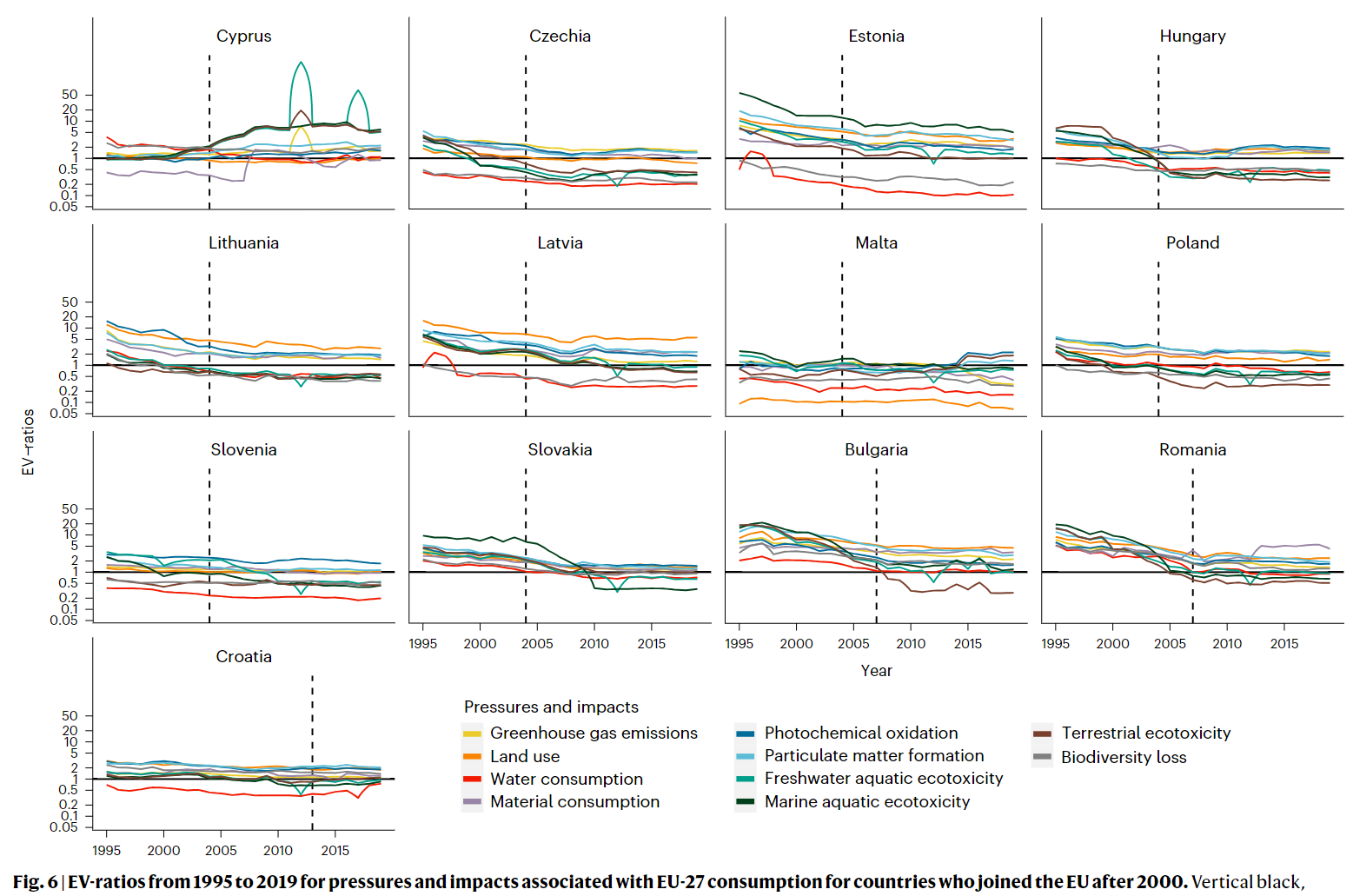
- EV ratios associated with EU consumption are more beneficial for most member countries than for non-EU countries and regions
- EU consumption induced higher environmental pressures and impacts per value added in the ROW Europe region than others
Coding Reference:





