Objective:
- Provide a detailed worldwide representation of how people are organized around urban centers in city-regions
Case:
Methodology:
- Assumption:
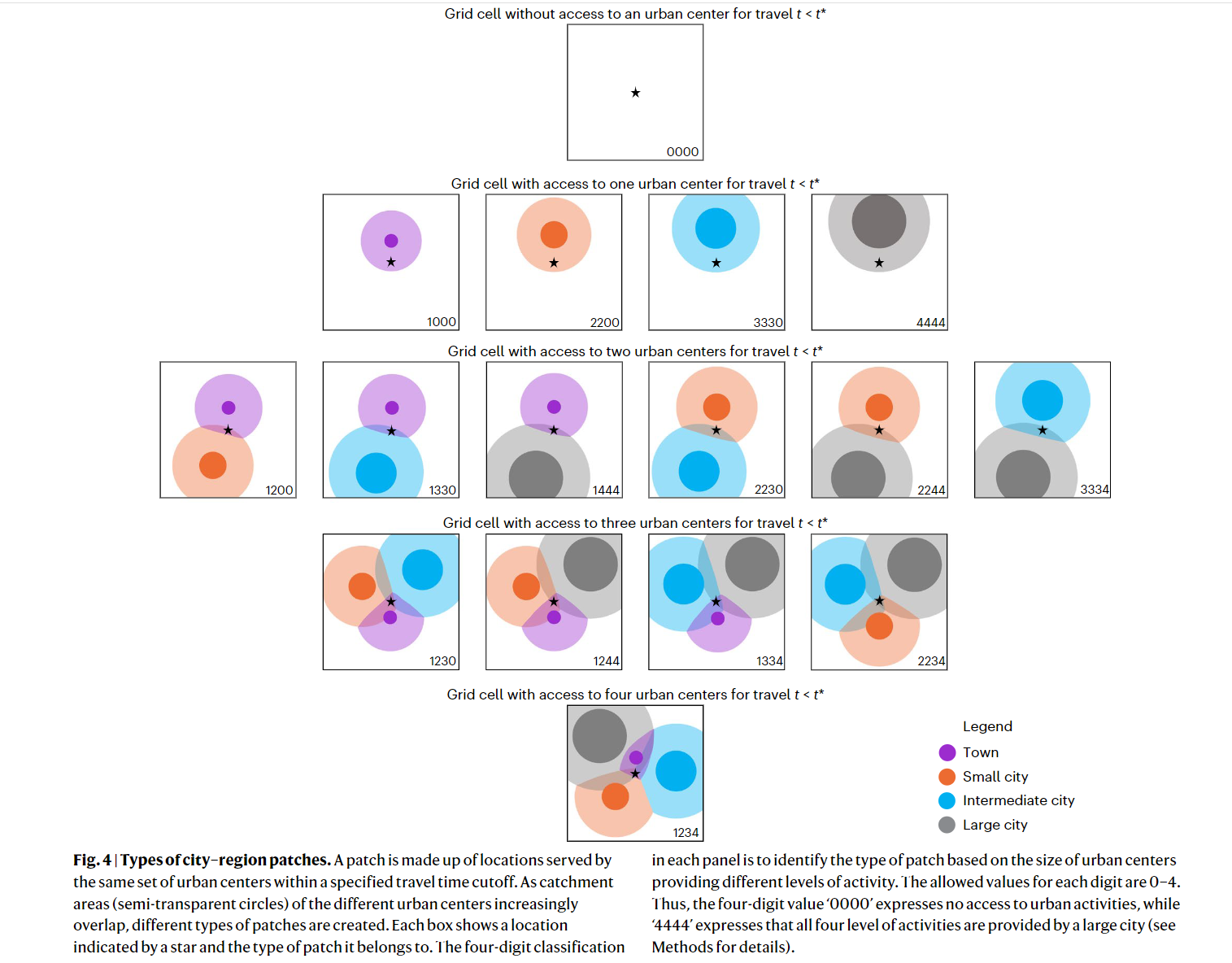
- Towns: between 20,000 and 50,000 people provide basic activites
- Small cities: between 50,000 and 250,000 people
- Intermediate cities: between 250,000 and 1 million
- Large cities: more than 1 million
- catchment area based on 1 h travel represents daily commuting potential
Data Source
- Grid population: GHSL
- Travel time: Weiss et al. (2018)
- Boundary: GADM
Findings:
- 18,619 towns, 9,440 small cities, 1,538 intermediate cities and 482 large cities
- Four catergories of primary city-regions
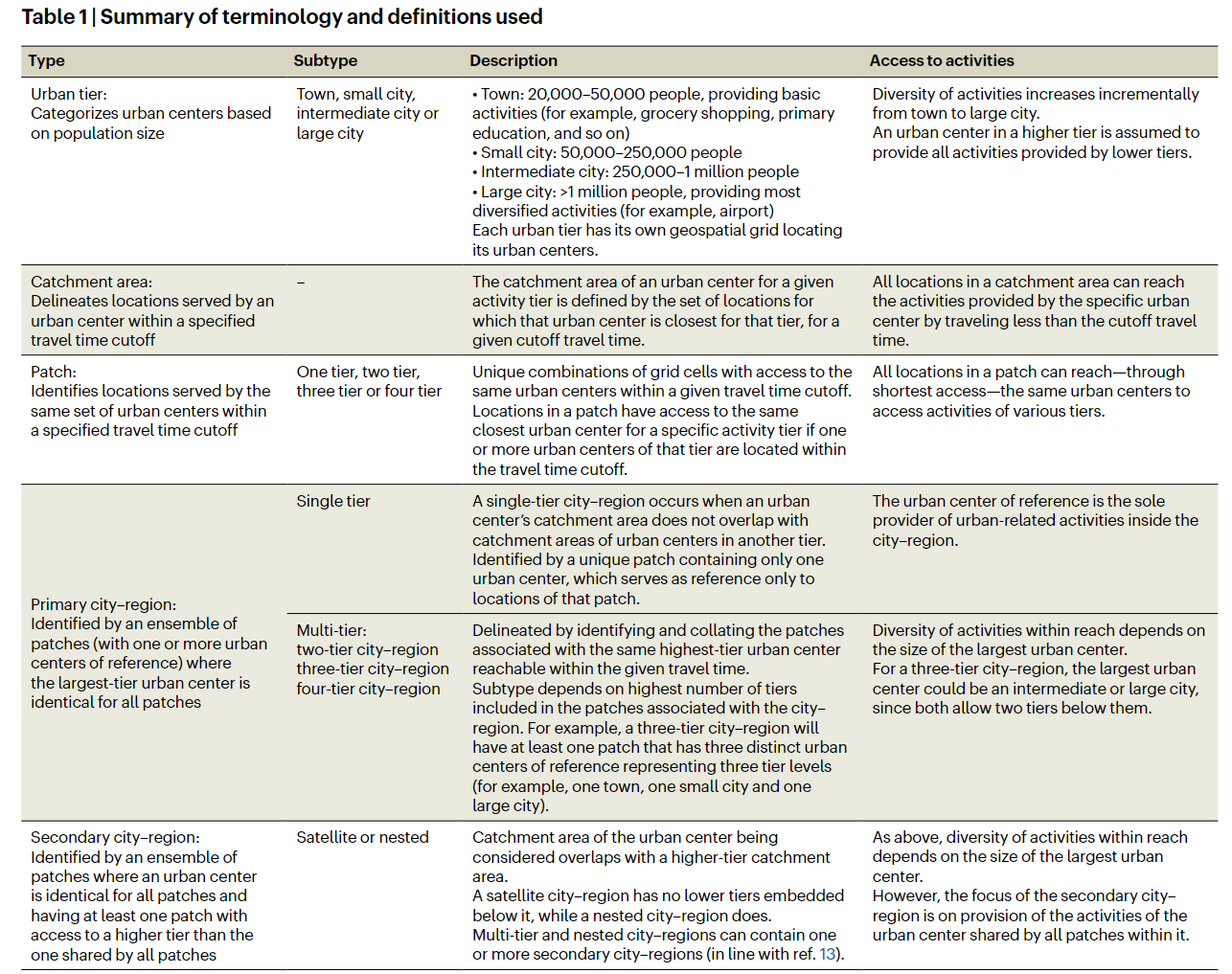
- 4,210 primary and 25,869 secondary city-regions
- 1,524 are single tier and 2,686 are multi-tier, with 1,751 being two-tier systems; 627 and 308 city-regions with three and four urban tiers, respectively
- The smaller the populatio nof an urban center, the more probable that urban center is to be part of a higher-tier city-region
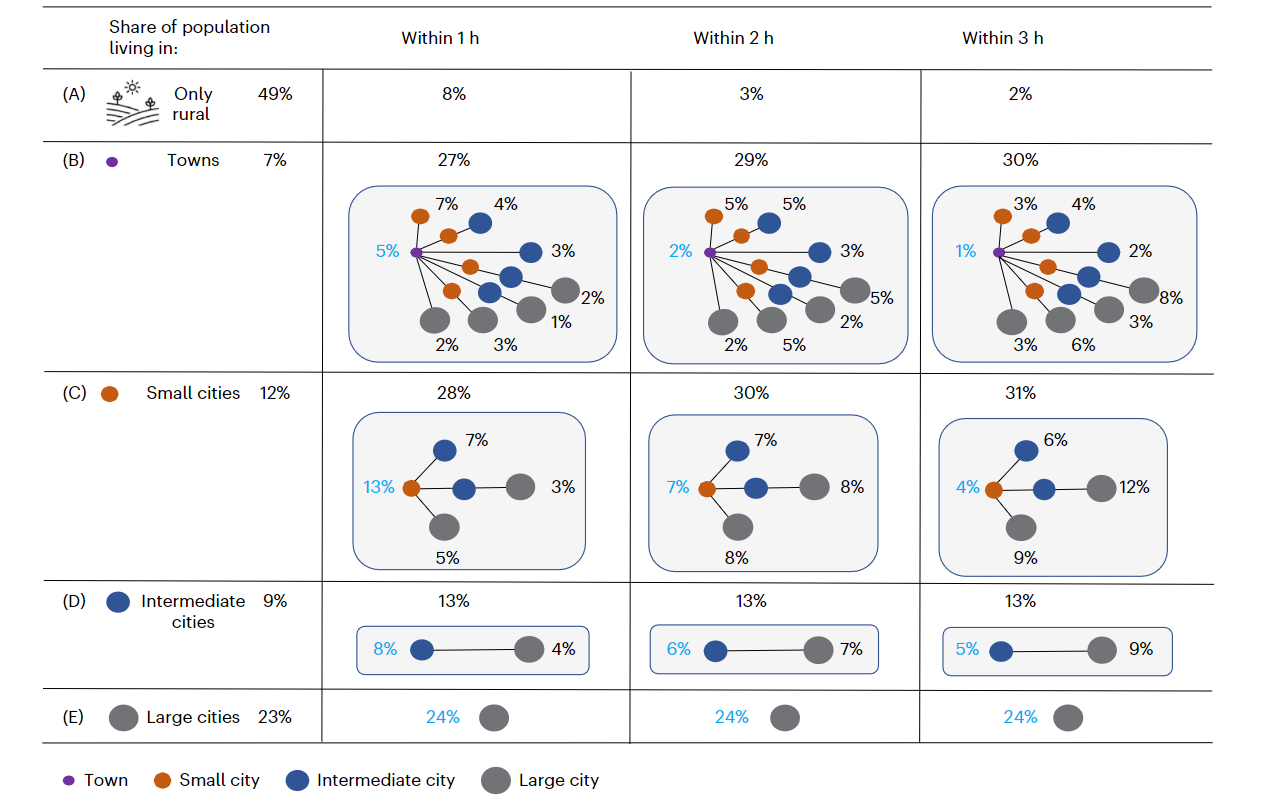
- 5% of the world’s population lives within 1 h from a town with no other urban center in the same vicinity; conversely, 7% live within 1 h from a town and a small city, with teh town being the closest, while 4% live closest to a town but can also access a small and an intermediate city within 1 h travel time
- A almost half of the world’s population lives outside an urban center (more than 20,000 people); only 8% have to travel more than 1 h to access an urban center, implying 92% of people live within a commuting distance of an urban center
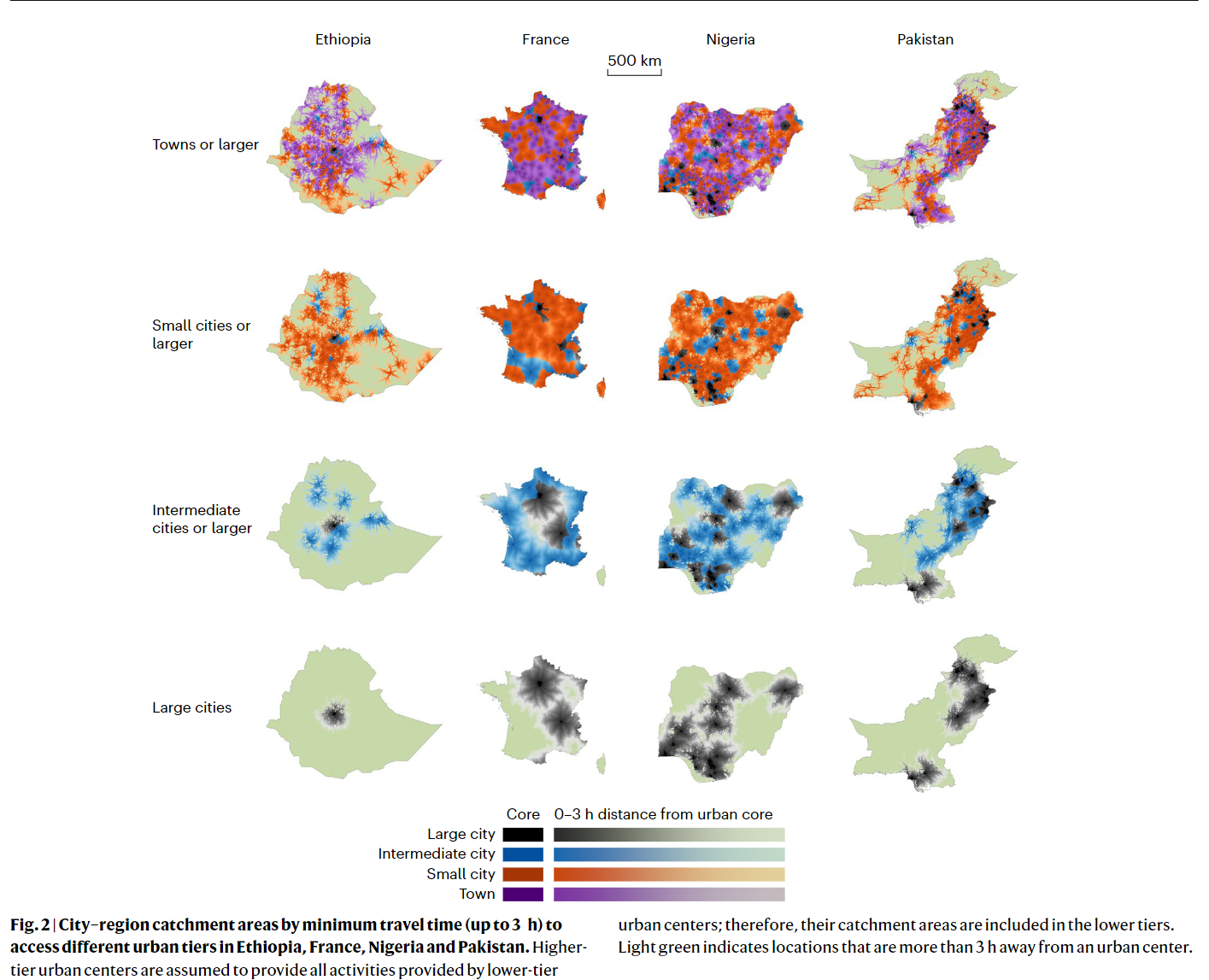
- 41% had physical access to multiple tiers within 1 h and 57% and 64% within 2 h and 3 h
- 28% of the world’s population is part of two-tier city-regions, and 13% of three tier or four tier
- two-thirds of the global population has easier access to small or intermediate cities than to large ones
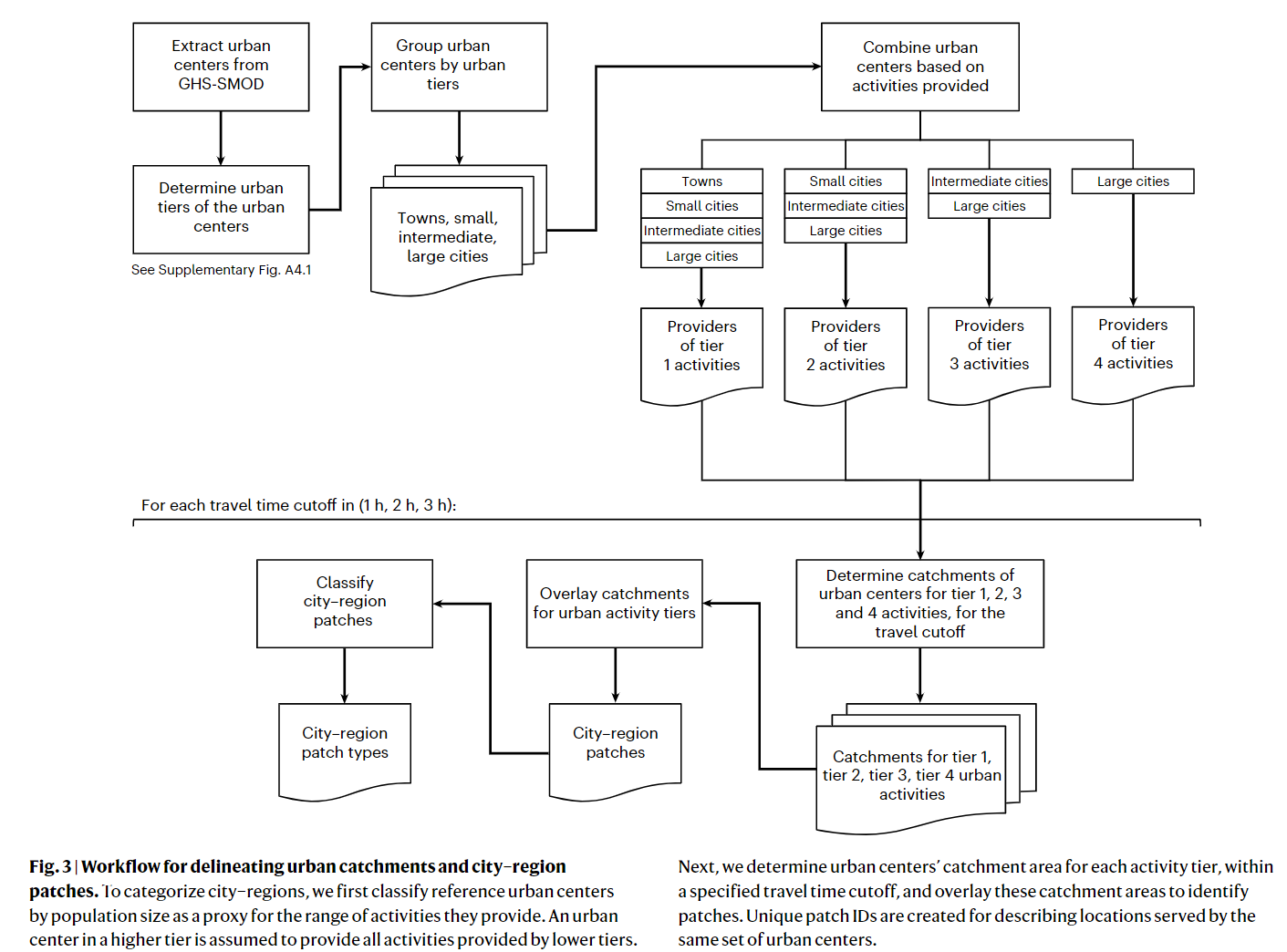
Coding Reference:





