Objective:
- Simulate the carbon reduction potential of 21 lifestyle changes on household direct energy use and other final consumption and upstream emissions along the entire global supply chain
Case:
Methodology:
Data Source
- MRIO: GTAP
- Expenditure database: WBGCD
Findings:
- Higher expenditures translate into higher carbon footprints among household deciles
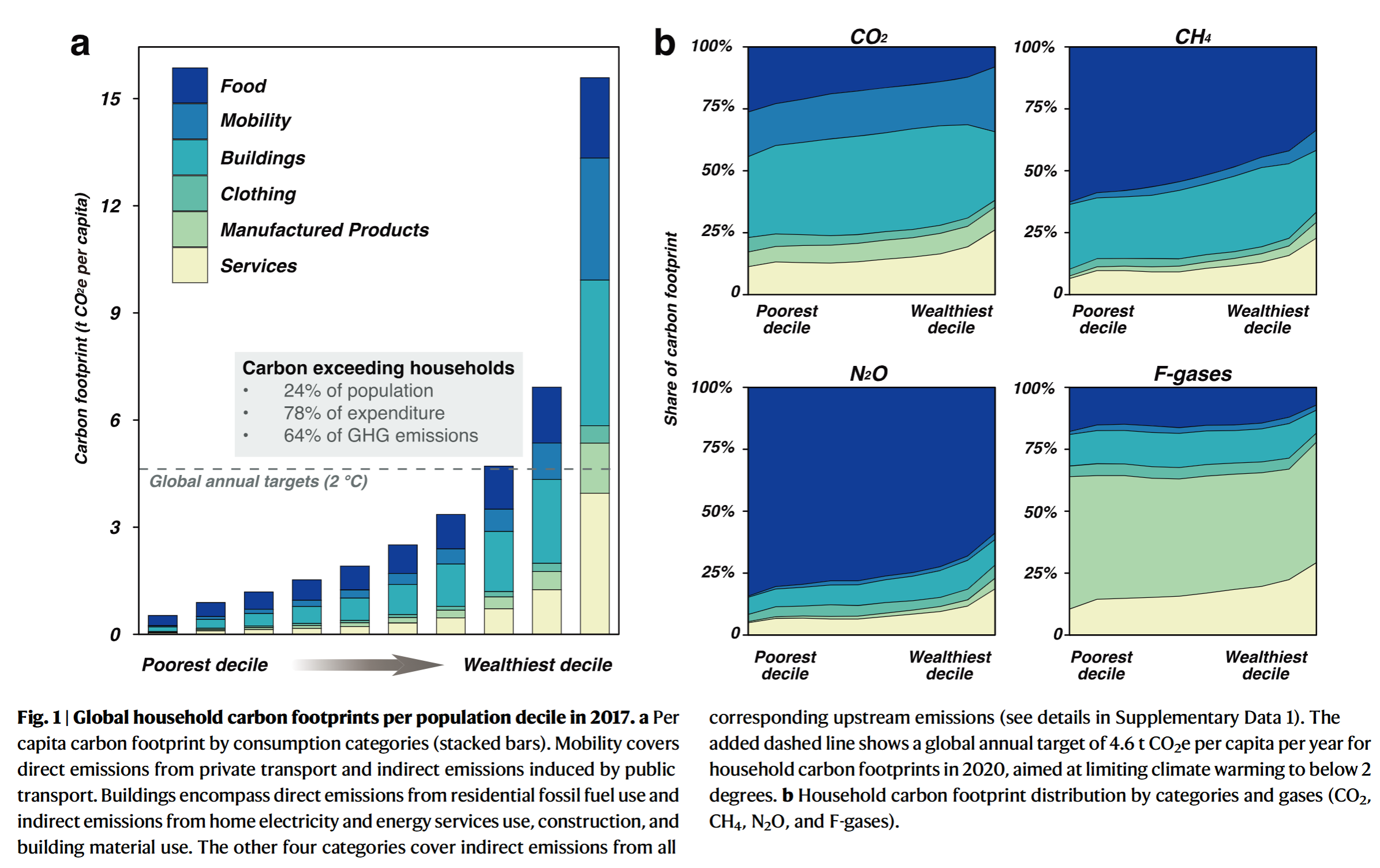
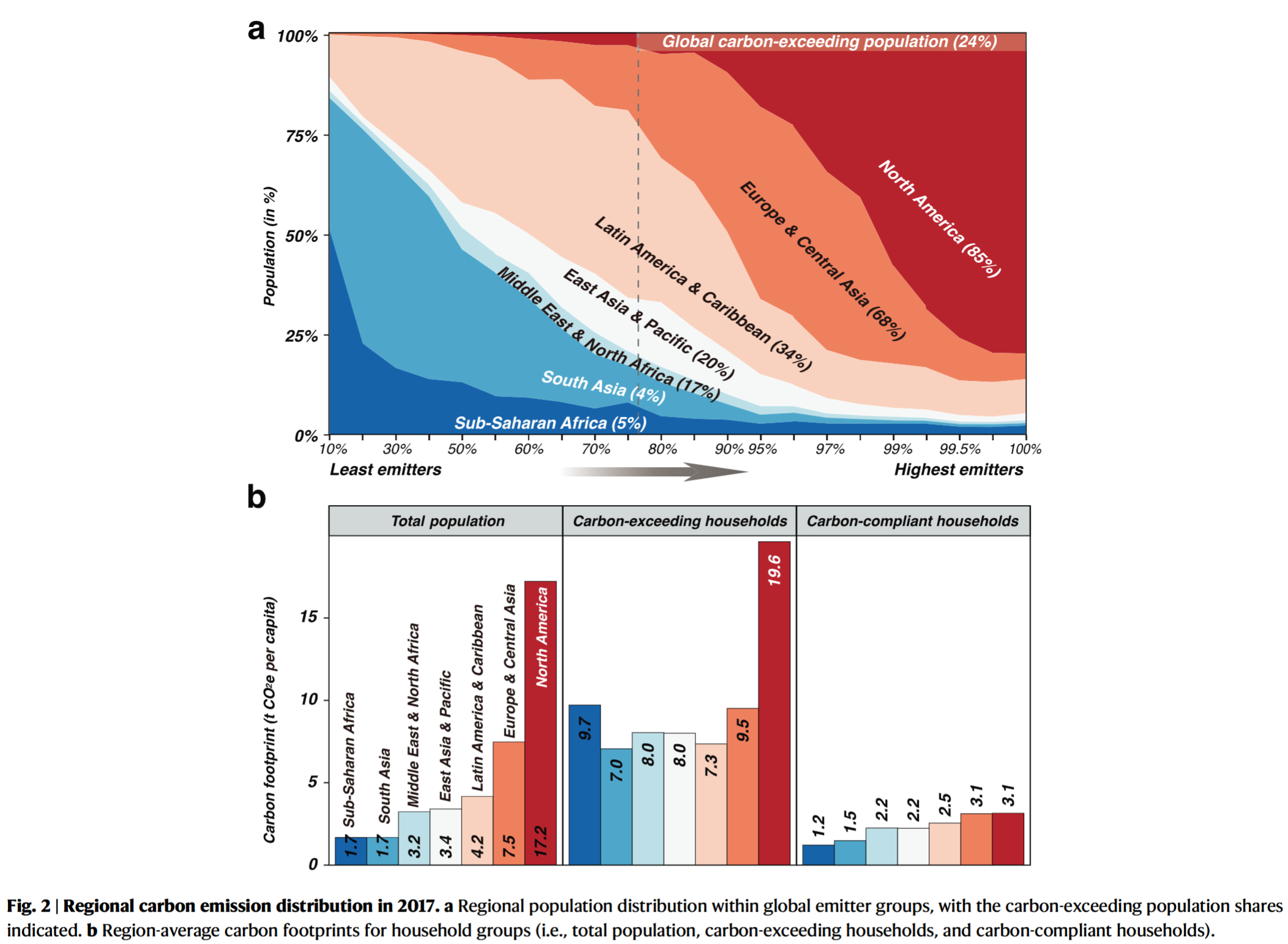
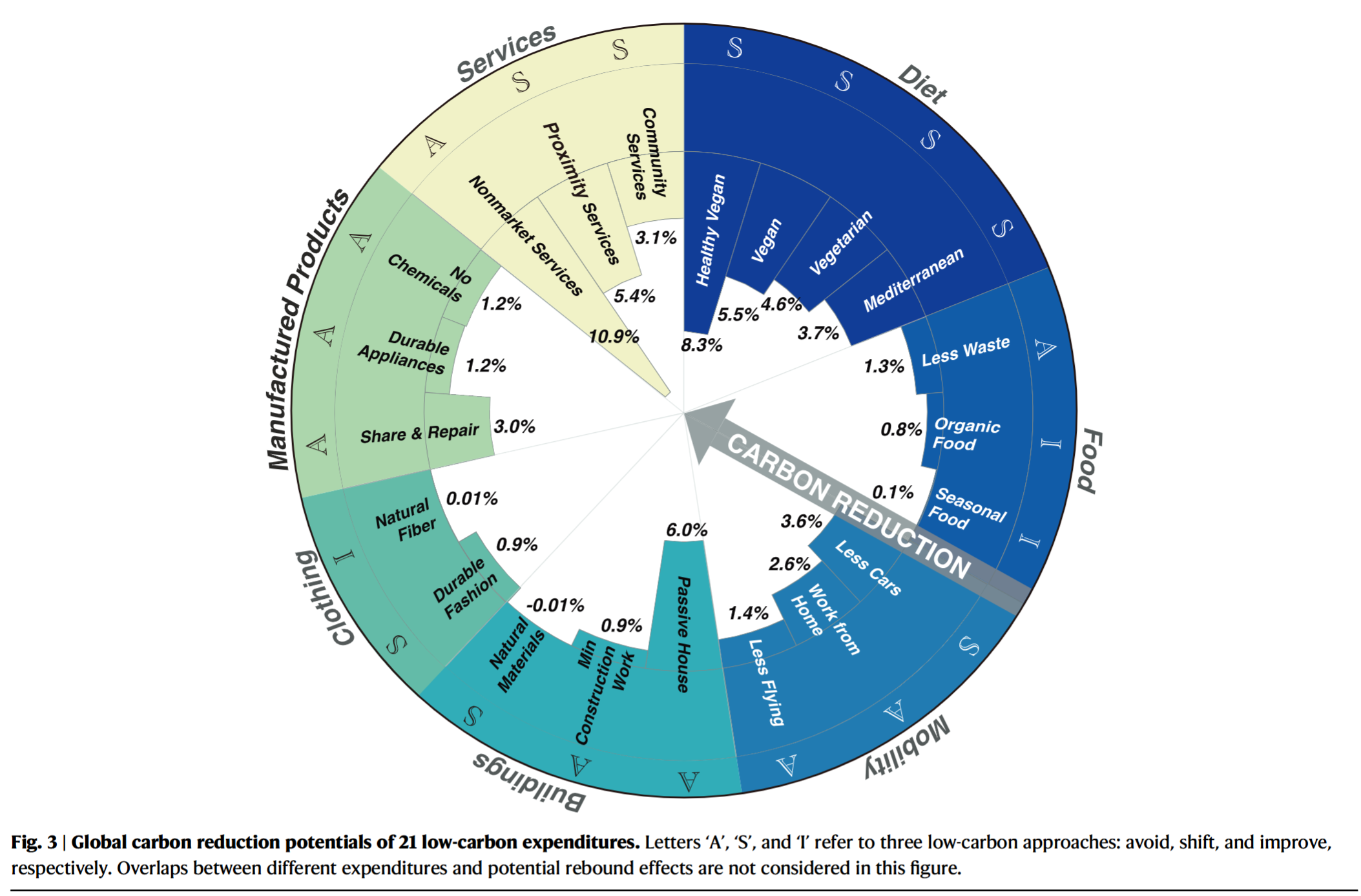
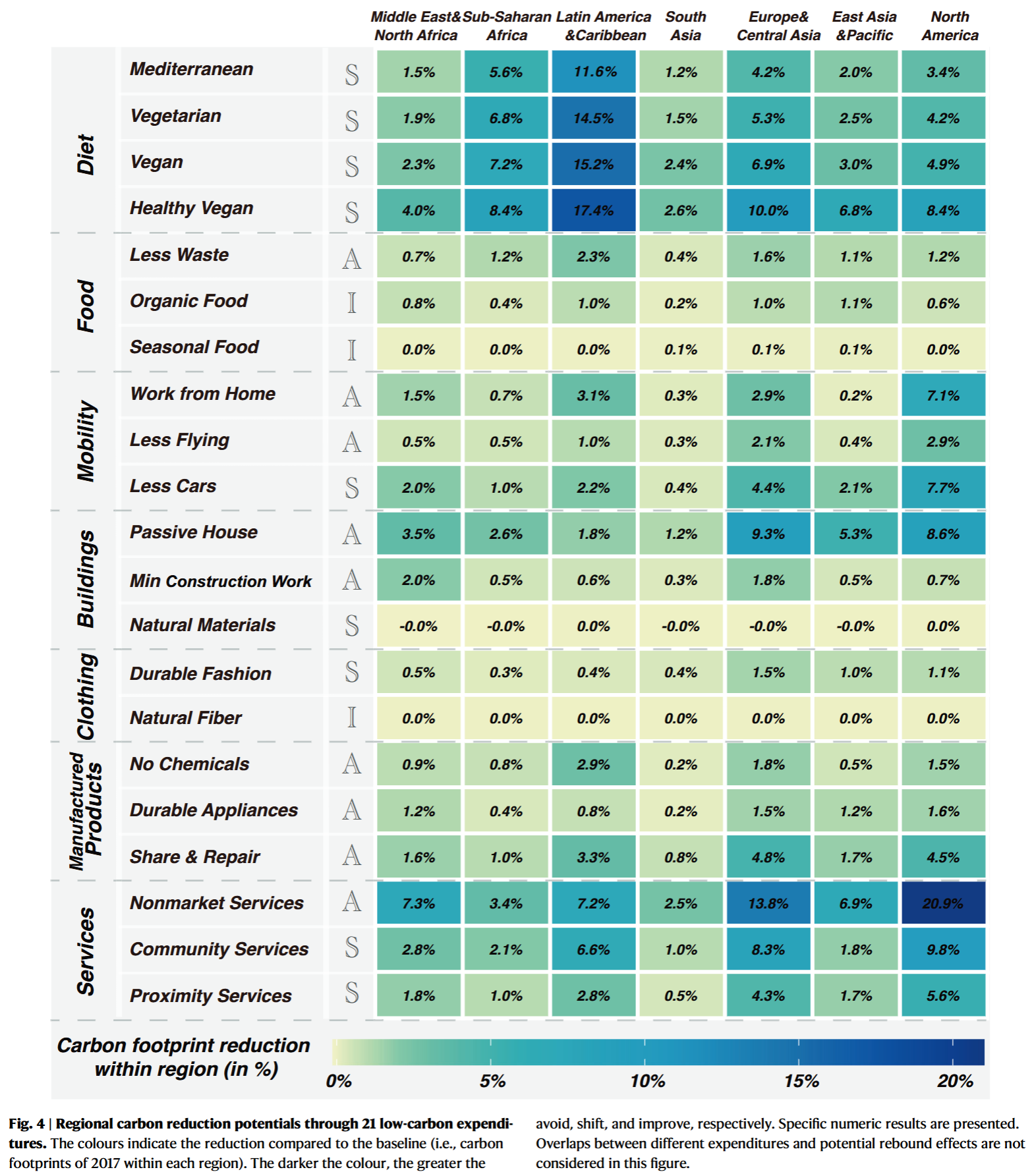
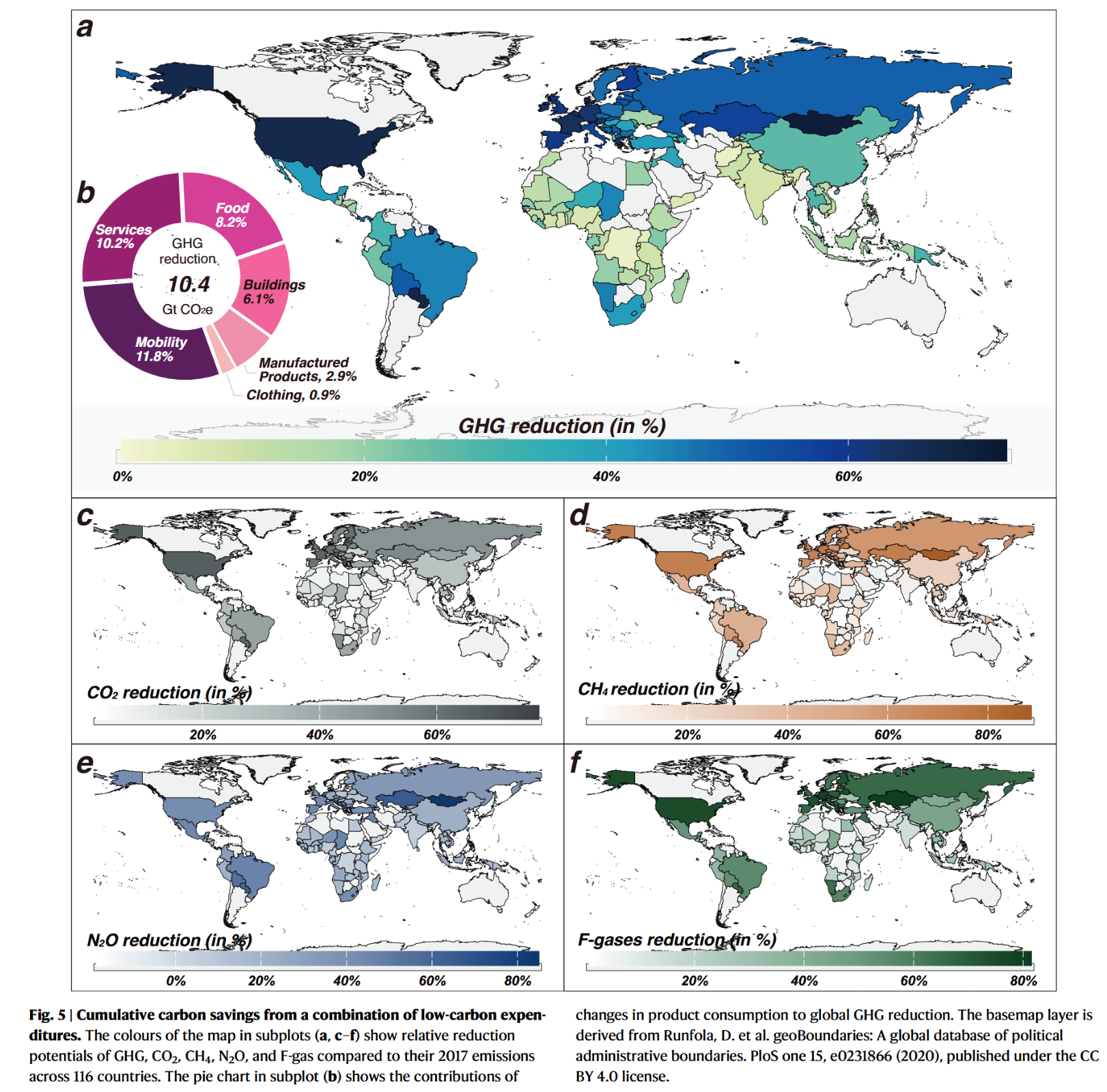
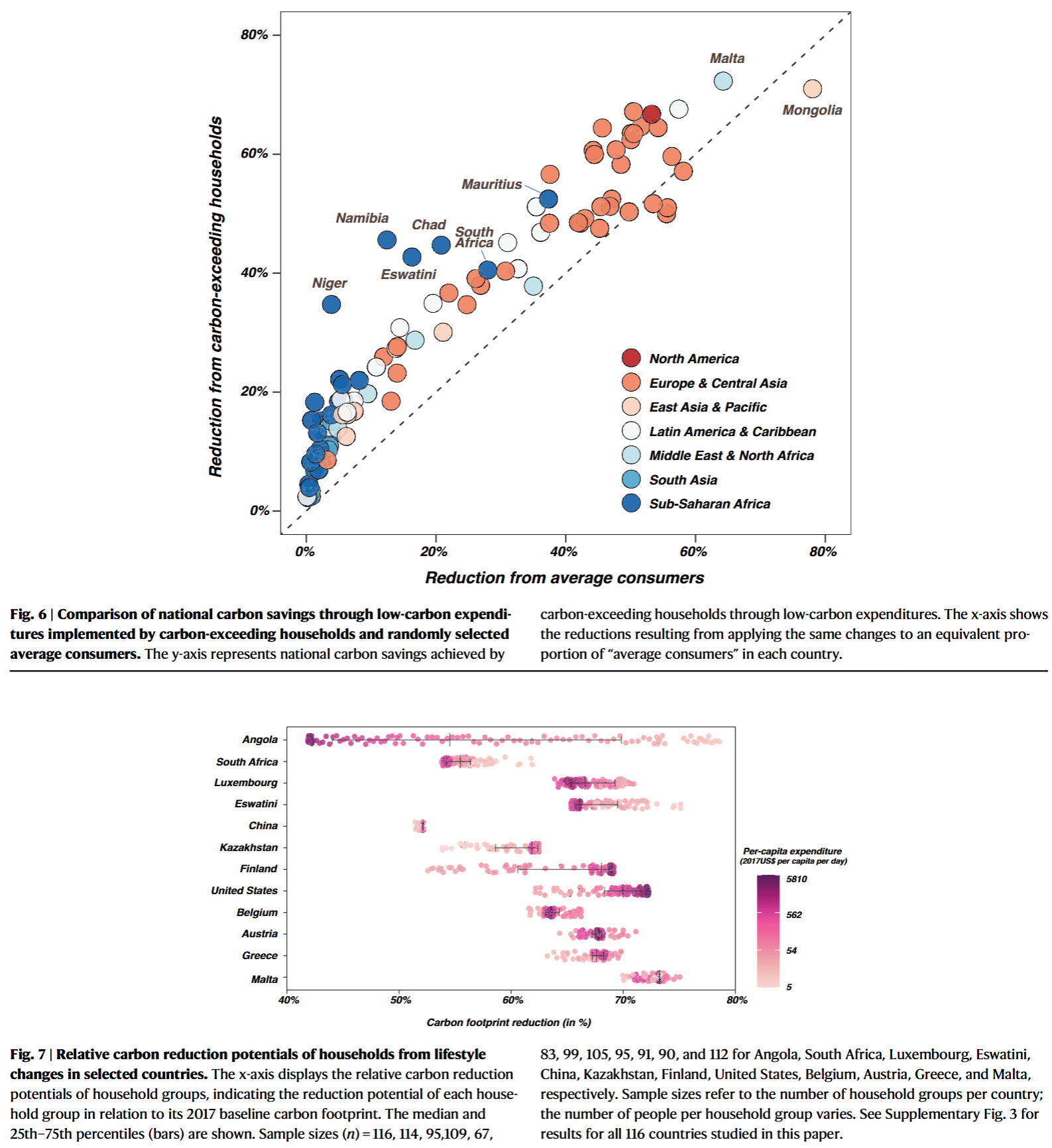
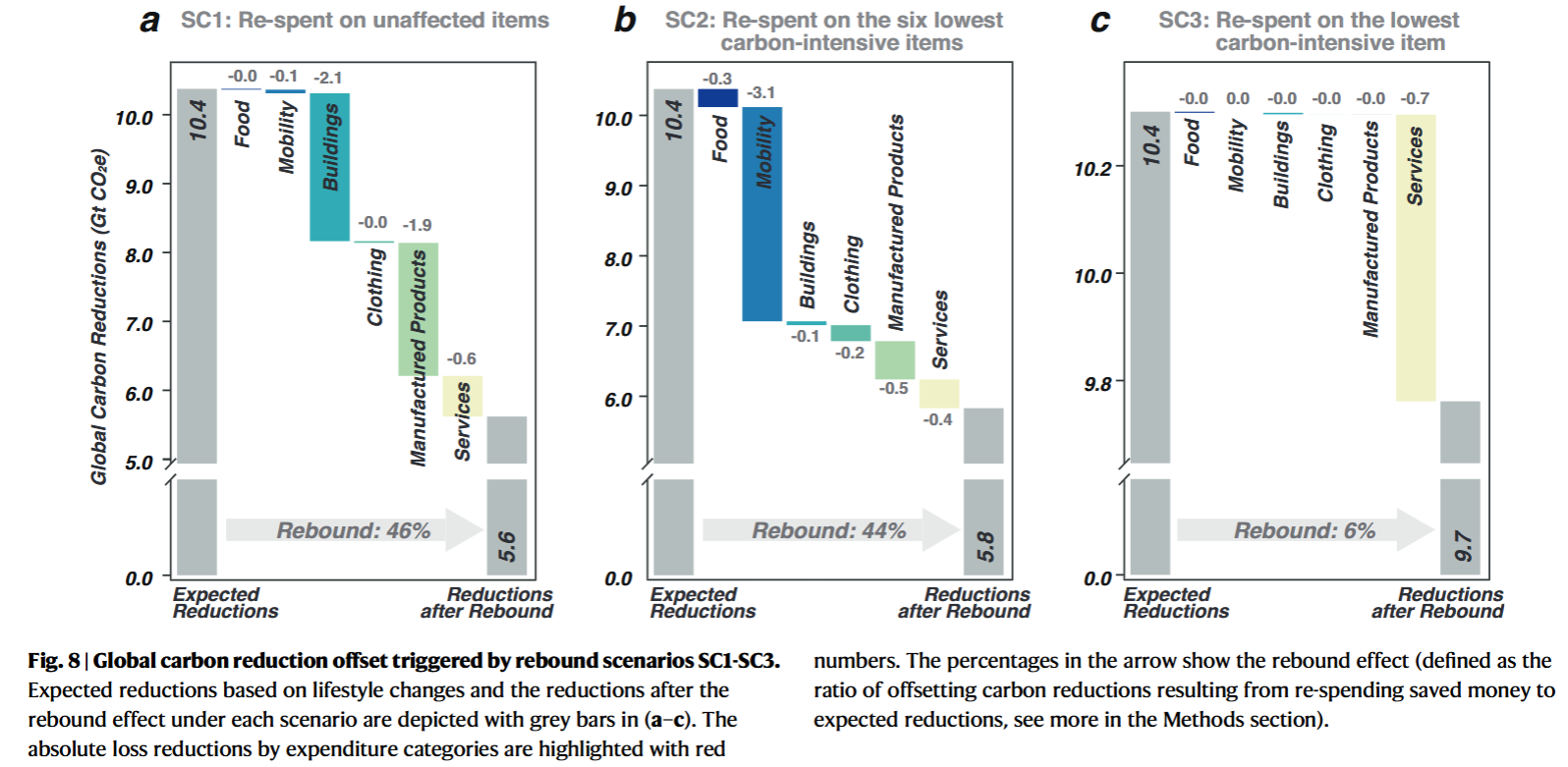
- Implementing a combination of low-carbon lifestyles in 23.7% of the top-emitting population could potentially result in a 40.1% reduction in household consumption-based GHG emissions
Coding Reference:







