Objective:
- There is little concensus concerning the direction and the extent to which these factors influence migration
Case:
Methodology:
- Regression: $M_{ct} = \alpha + E_{ct}\beta +C_{ct}\gamma +\theta_c +\tau_t + \epsilon_{ct}$
- $\beta_{stan,im} = \mu_m + D_{im}\delta +\mu_{im}$
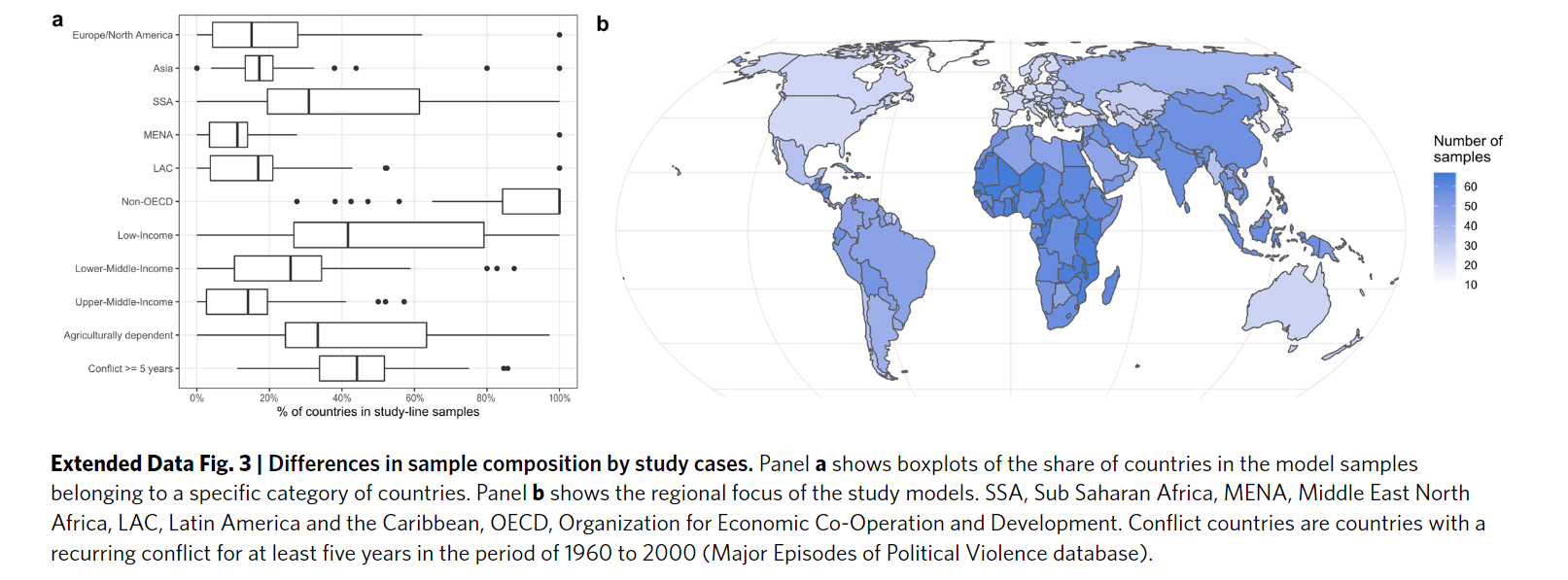
Data Source
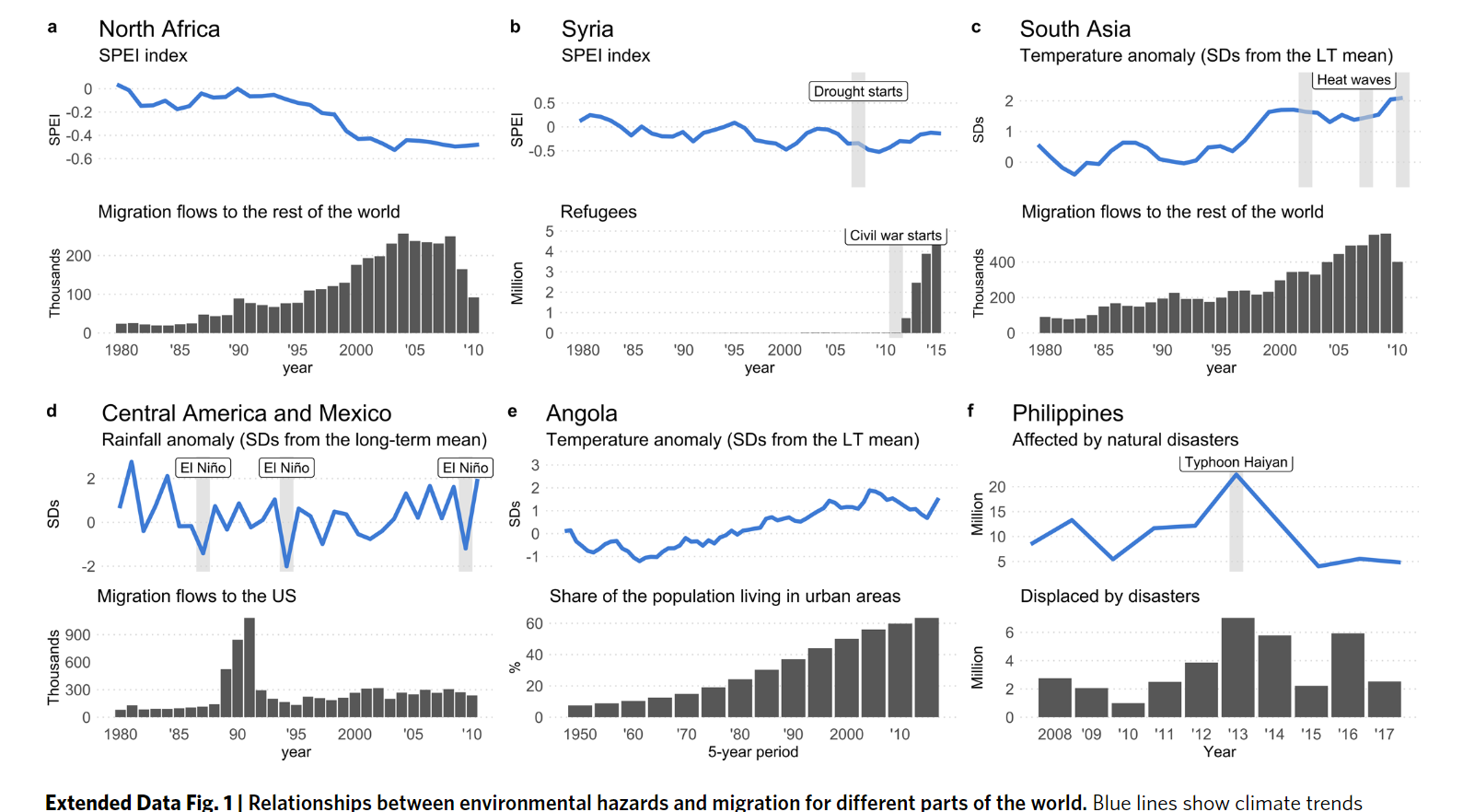
Findings:
- 27 of the 30 considered studies come to the conclusion that environmental factors are a relevant migrantion driver
- Environmental conditions can either directly influence migration decisions or indirectly by affecting other migration drivers
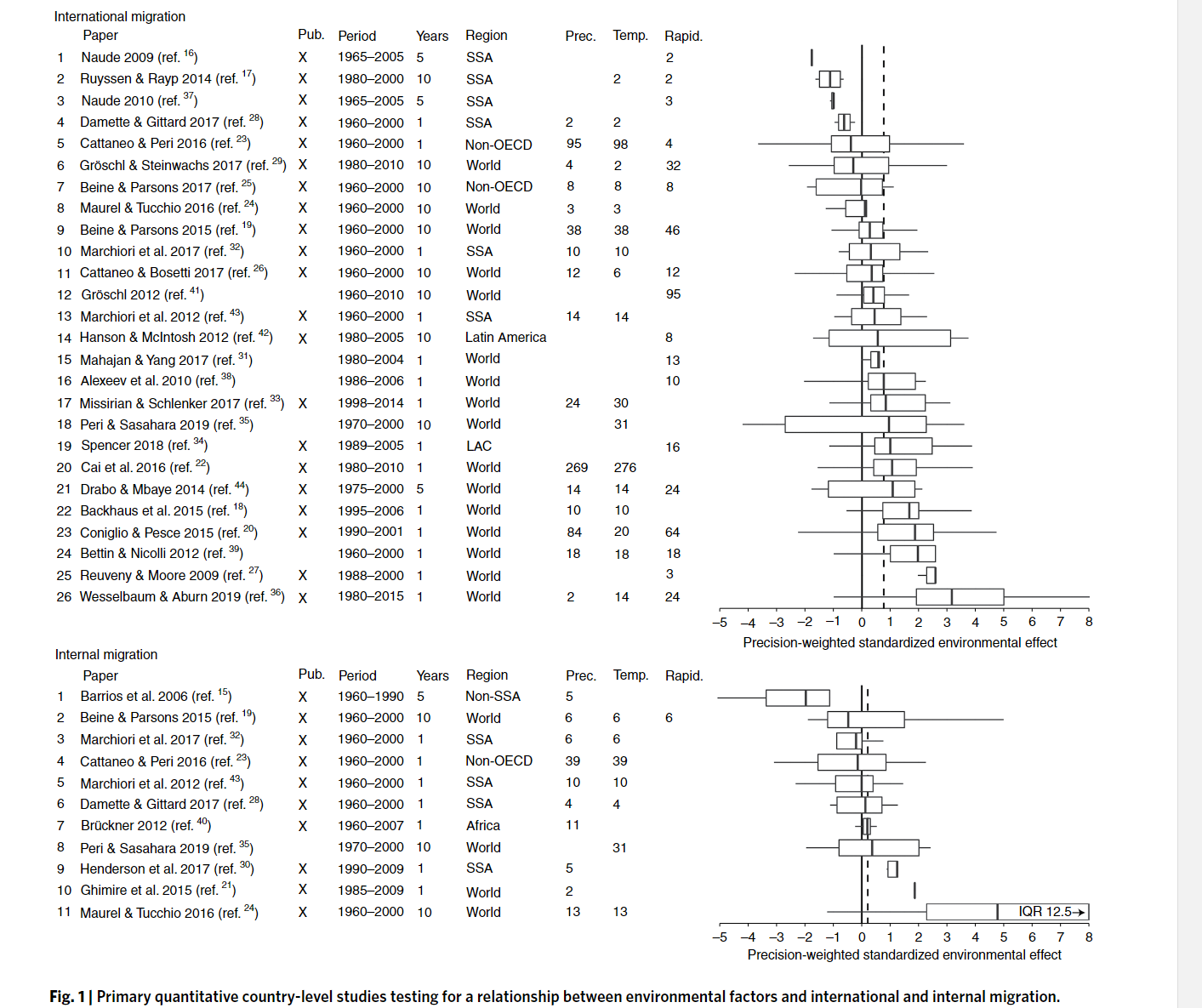
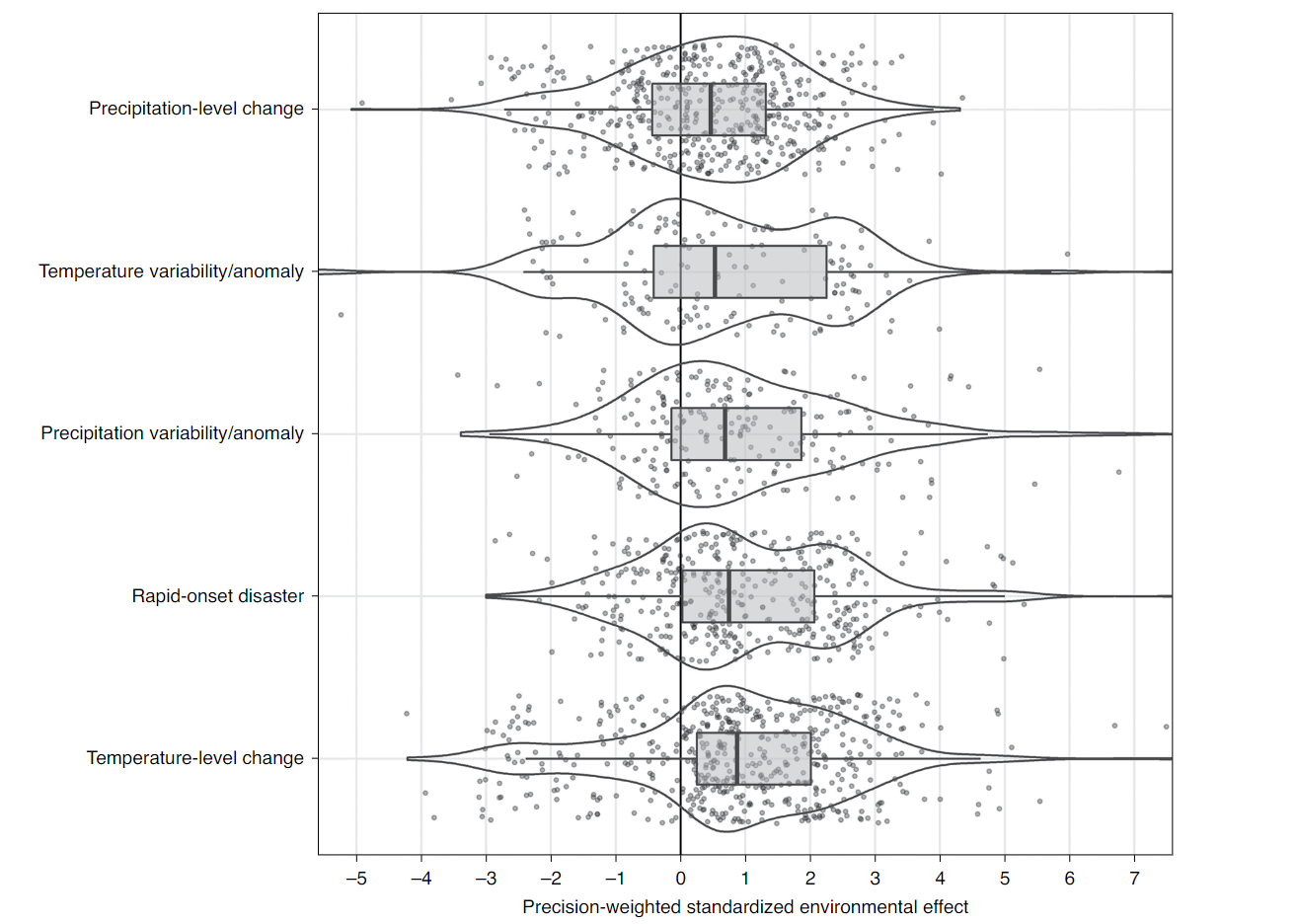
- a one standard deviation change in the environmental conditions leads to an increase in migration by 0.021 standard deviation
- While changes in the level of precipitation tend to have only a small impact on migration, changes in variability and anomalies of rainfall usually show a significantly positive impact
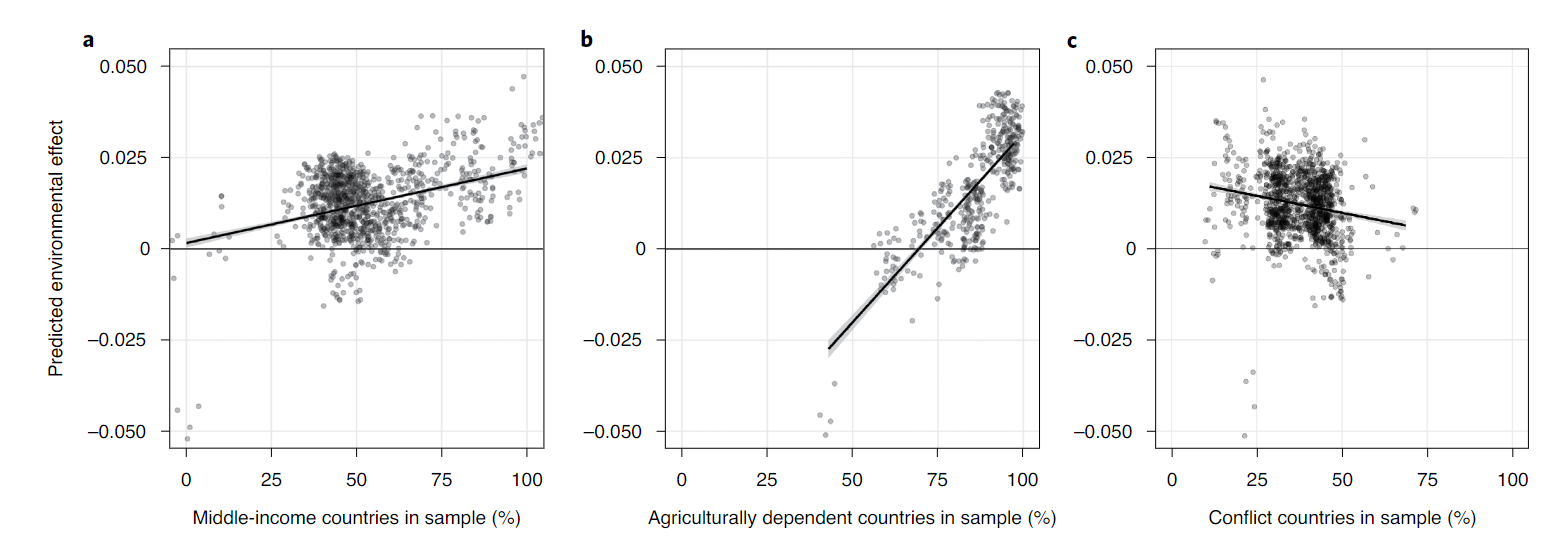
- Considering global migrant, larger environmental effects for internal migration than for estimates
- Considering international migrant, the effects are largest for the models assessing migration to low- or middle- income country destinations
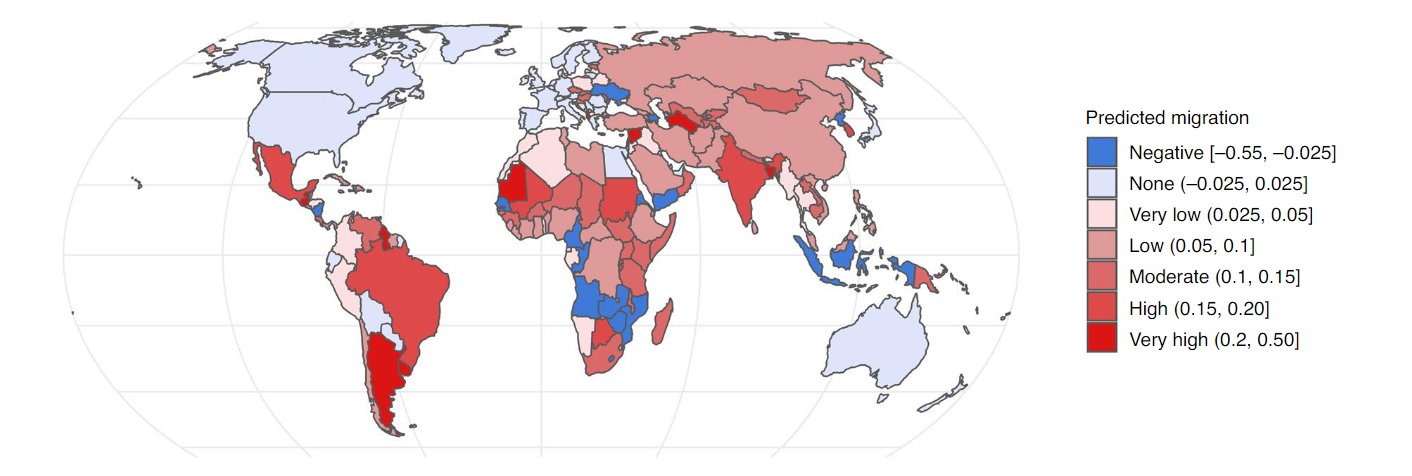
Coding Reference:






