Objective:
- Examine whether participants substitute attributes in the direction and magnitude of their true correlation with emissions
Case:
Methodology:
- Tau value: normally distributed, indicating participants were no differ than chance
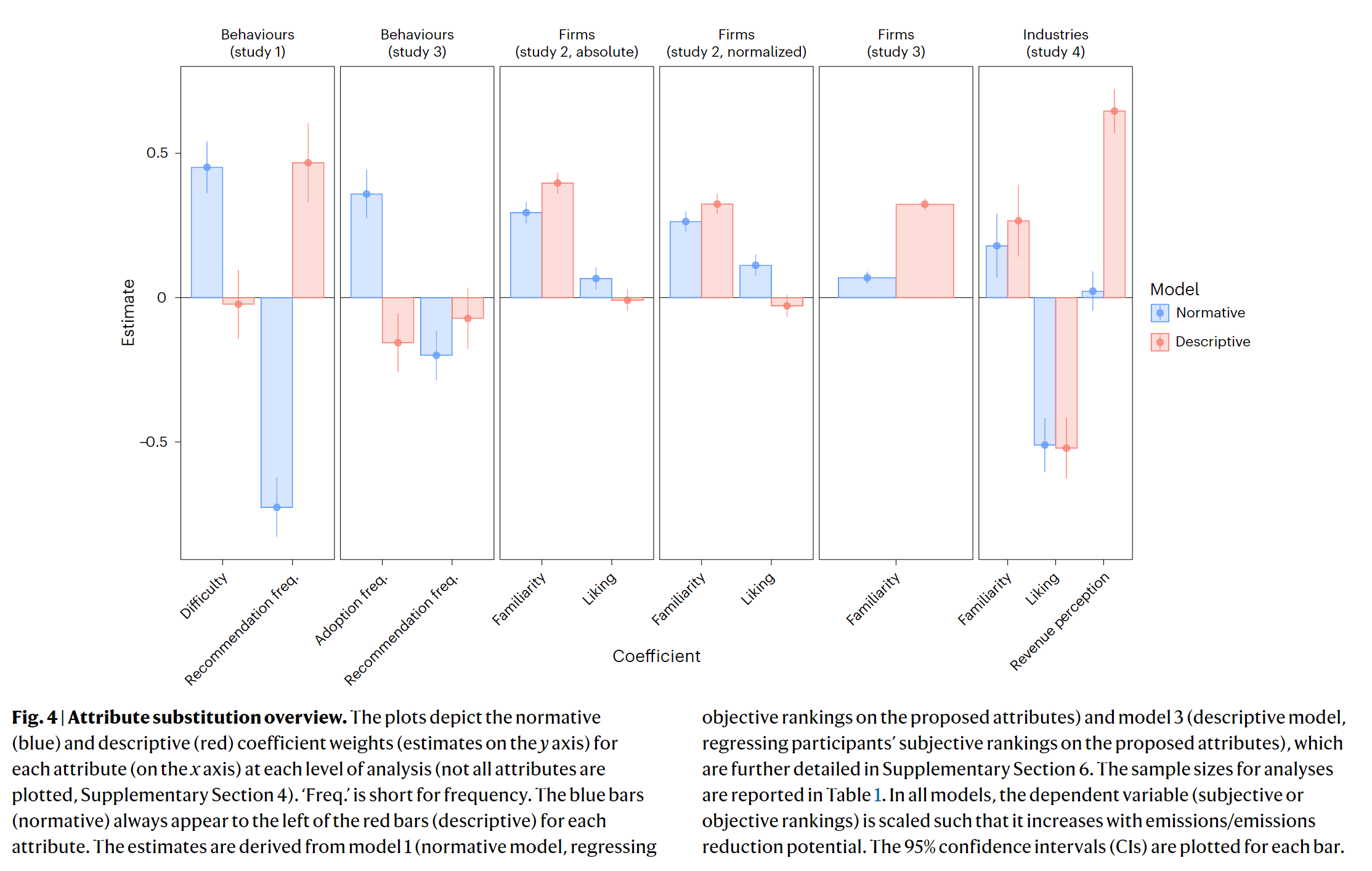
- Lens model
- Normative regression predicts the actual, objective rank of items
- A descriptive regression predicts the ranks estimated by participants
- Robustness: ordinal logistic model
Data Source
Findings:
- Despite the oppotunity to double one’s compensation, incentive compatibility had no significant effect on emissions
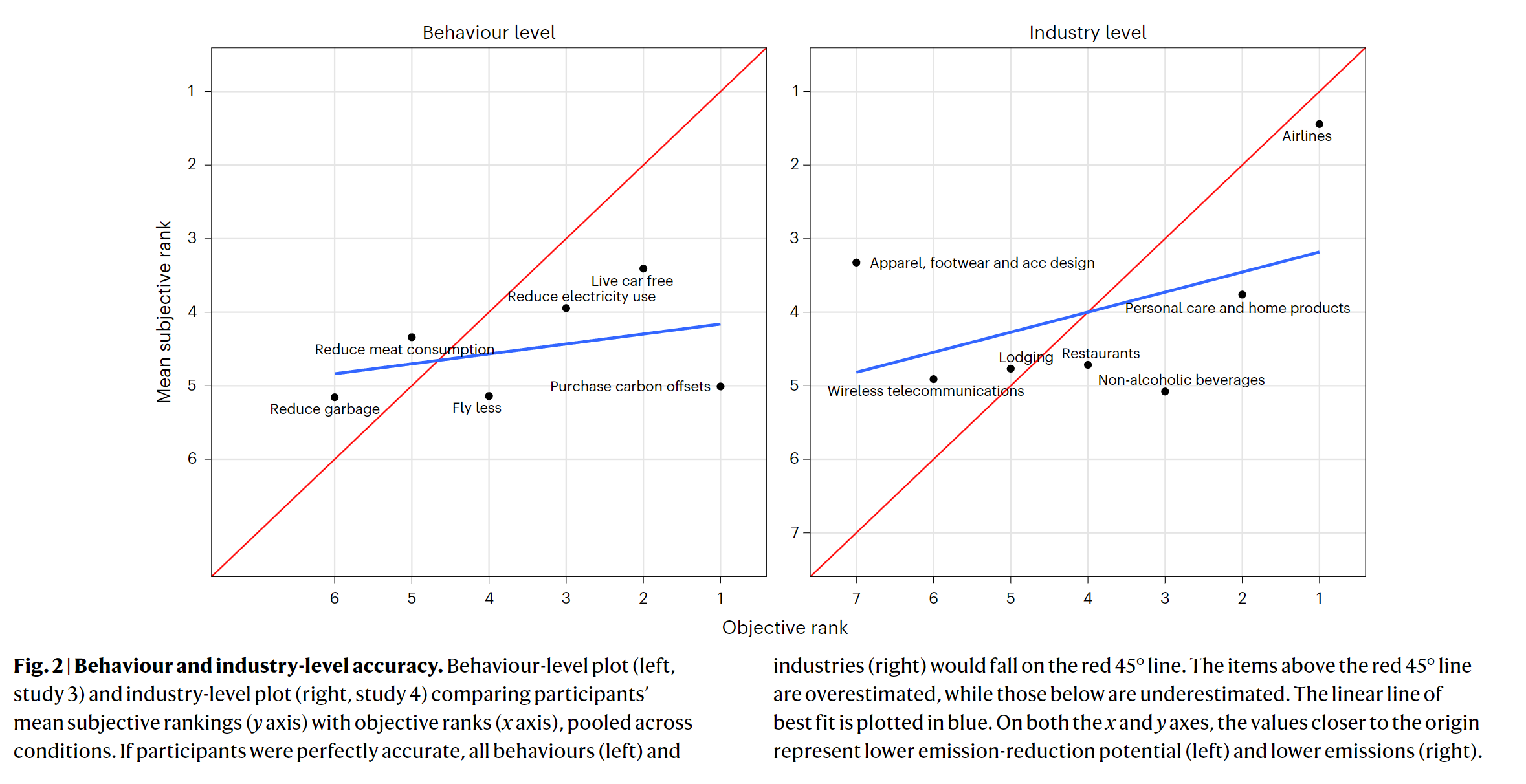
- Larger firms emit more. Participants maight be more accurate in industries compared to firms since greater tau value.
- Consumers lack the necessary carbon competence to accurately estimate the emissions associated with various behaviors, firms and industries.
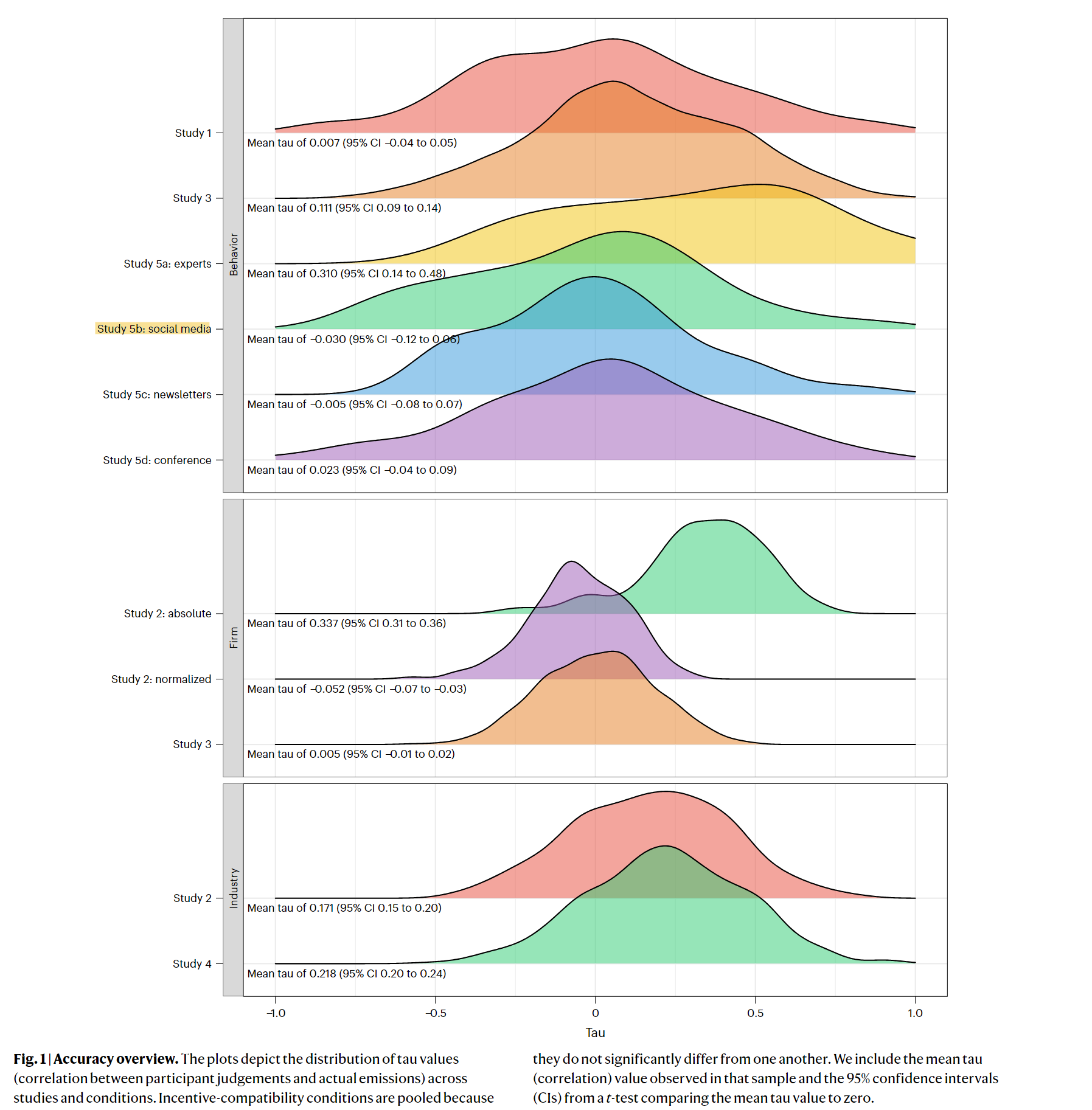
- Attribute substitution does occur. Certain attributes are over- or under-weighted. Some attributes are interpreted in the wrong direction.
- Subjective and objective ranking were significantly related to some of the attributes
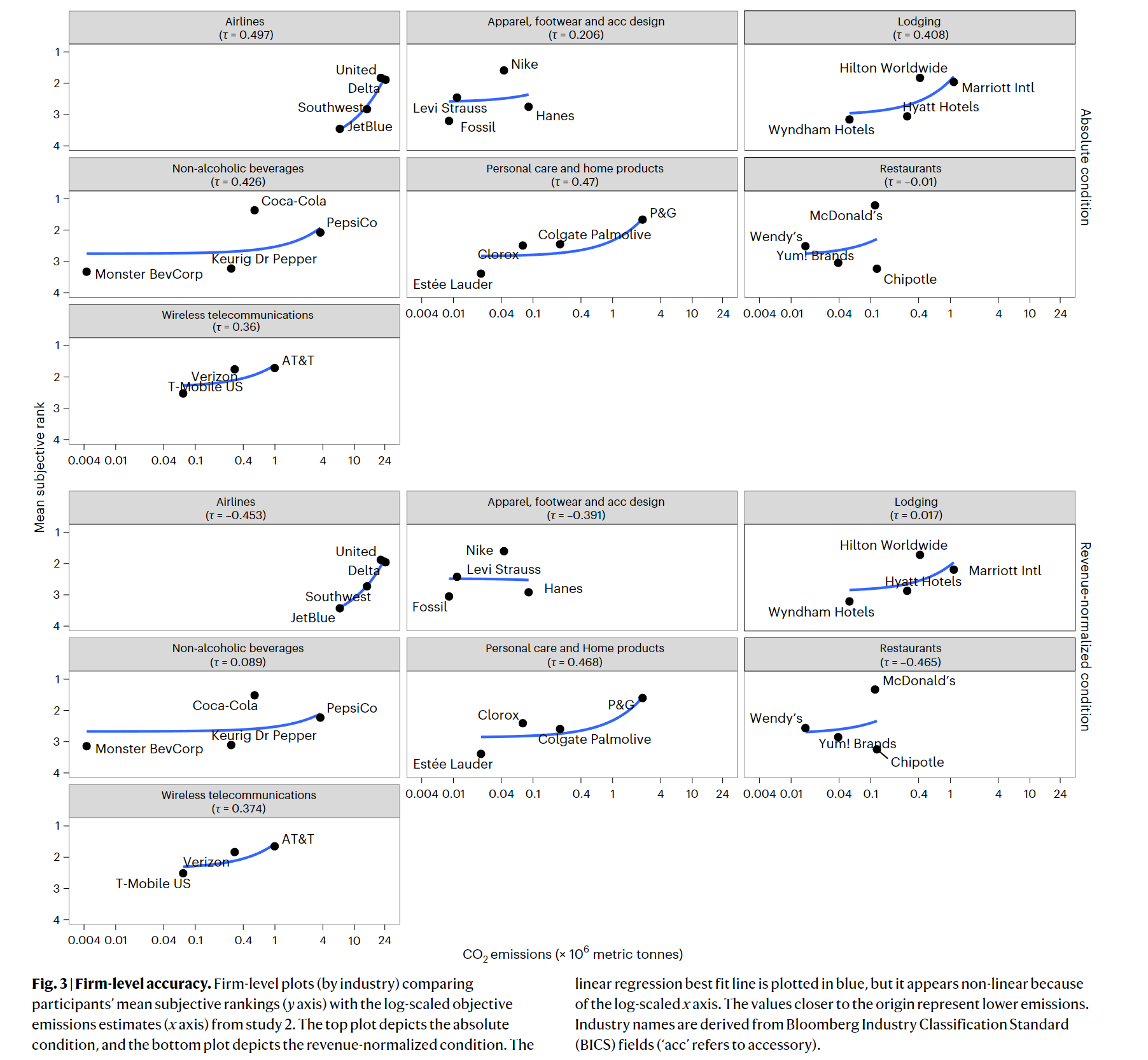
- The familarity with and linking of a given firm influence emission judgements, with a more subjective ranking.
- Exports significantly outperformed the general population
Coding Reference:





