Objective:
- Introduce an approach to implement and answer the reverse causal question of what reduced CO2 emission ? in the EU road transport sector between 1995 and 2008 by first detecting substantial changes in emissios relative to a control group using machine learning and subsequently attributing them to likely causes such as single or interacting policy interventions
Case:
Methodology:
- Familiar two-way fixed effects:
- $log(CO2{it}) = \alpha_i + \phi_t + \sum_j \sum_s \tau{j,s} l_{i=j} + x^{'} \beta +\epsilon_{i,t}$
- Sparse model
- Carbon emission in road sector: EDGAR
- GDP and population: World Bank
Findings:
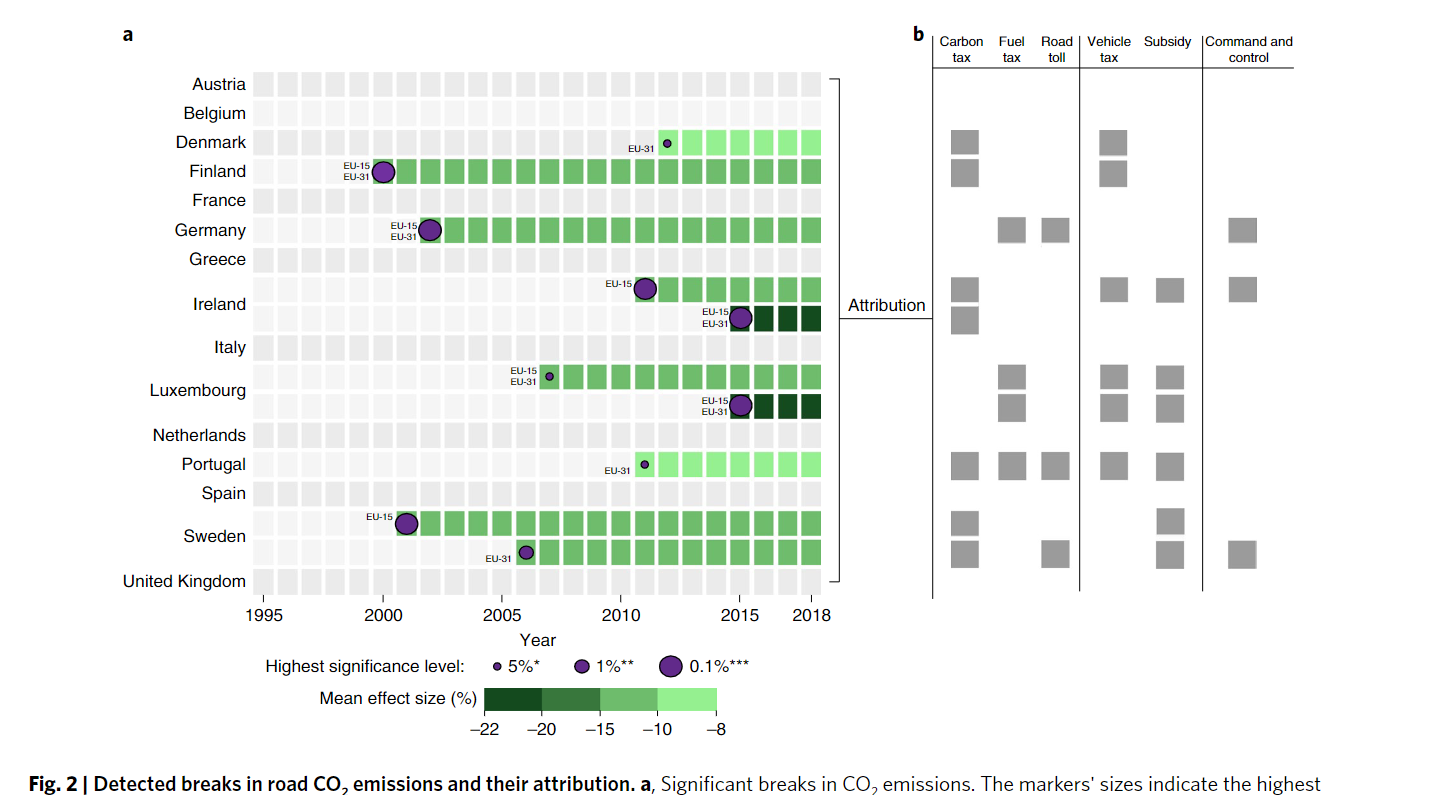
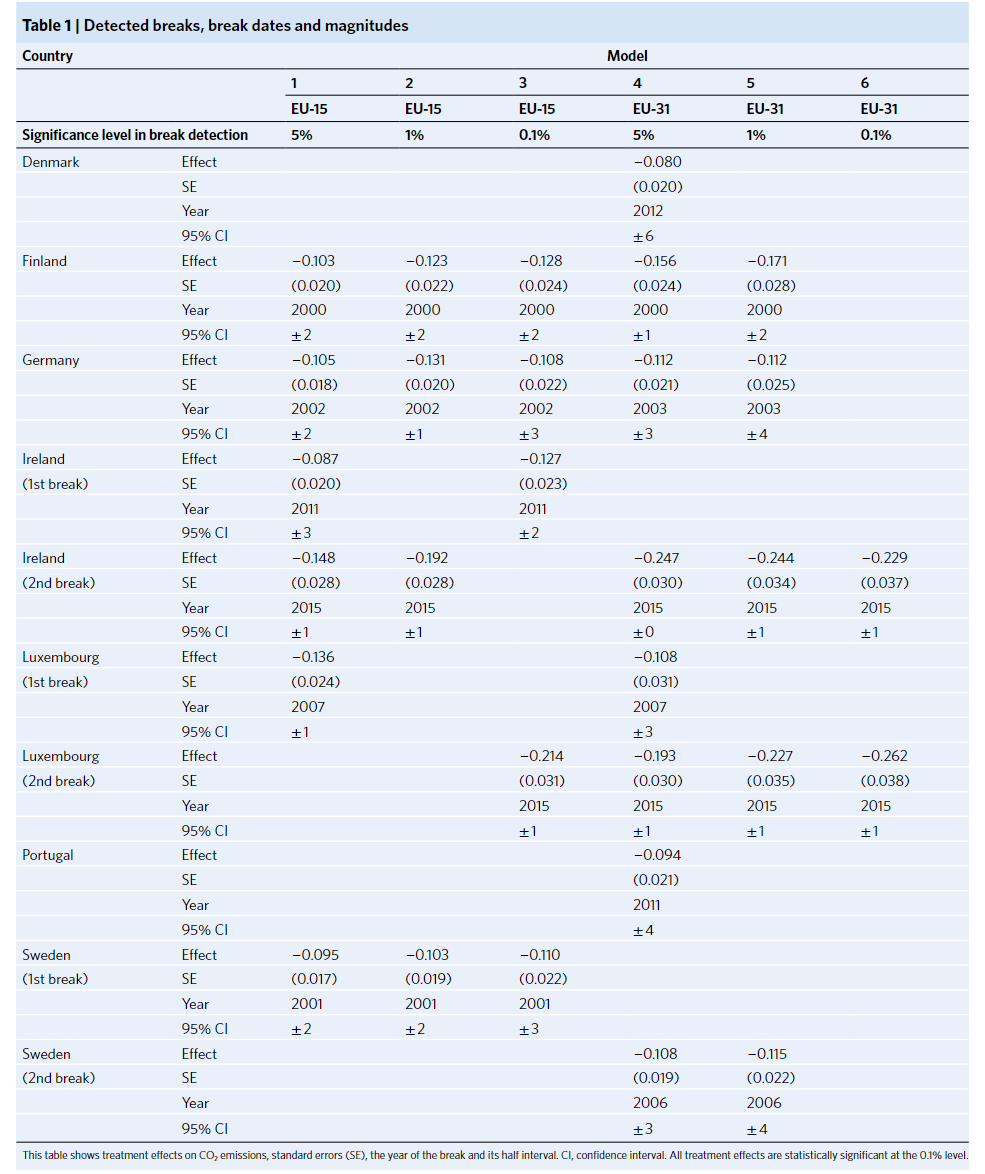
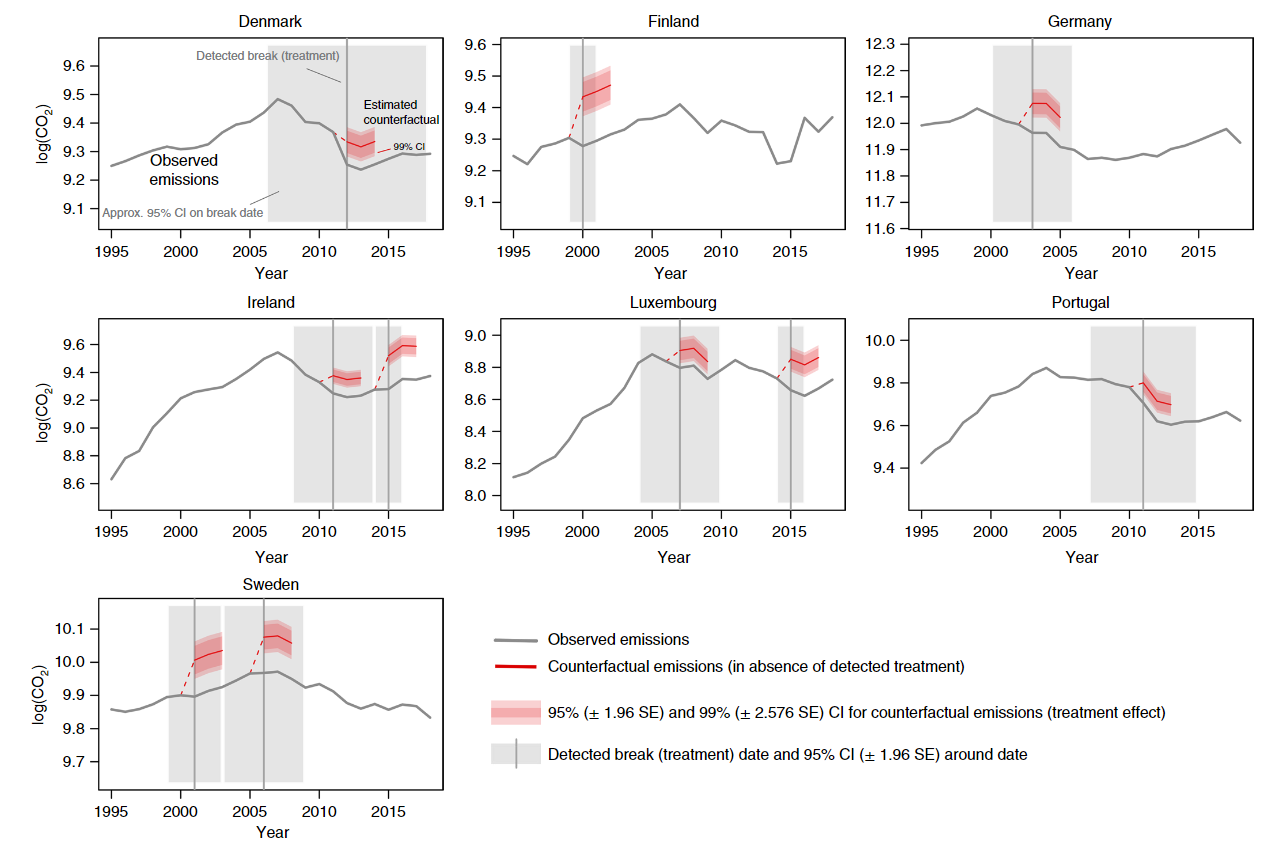
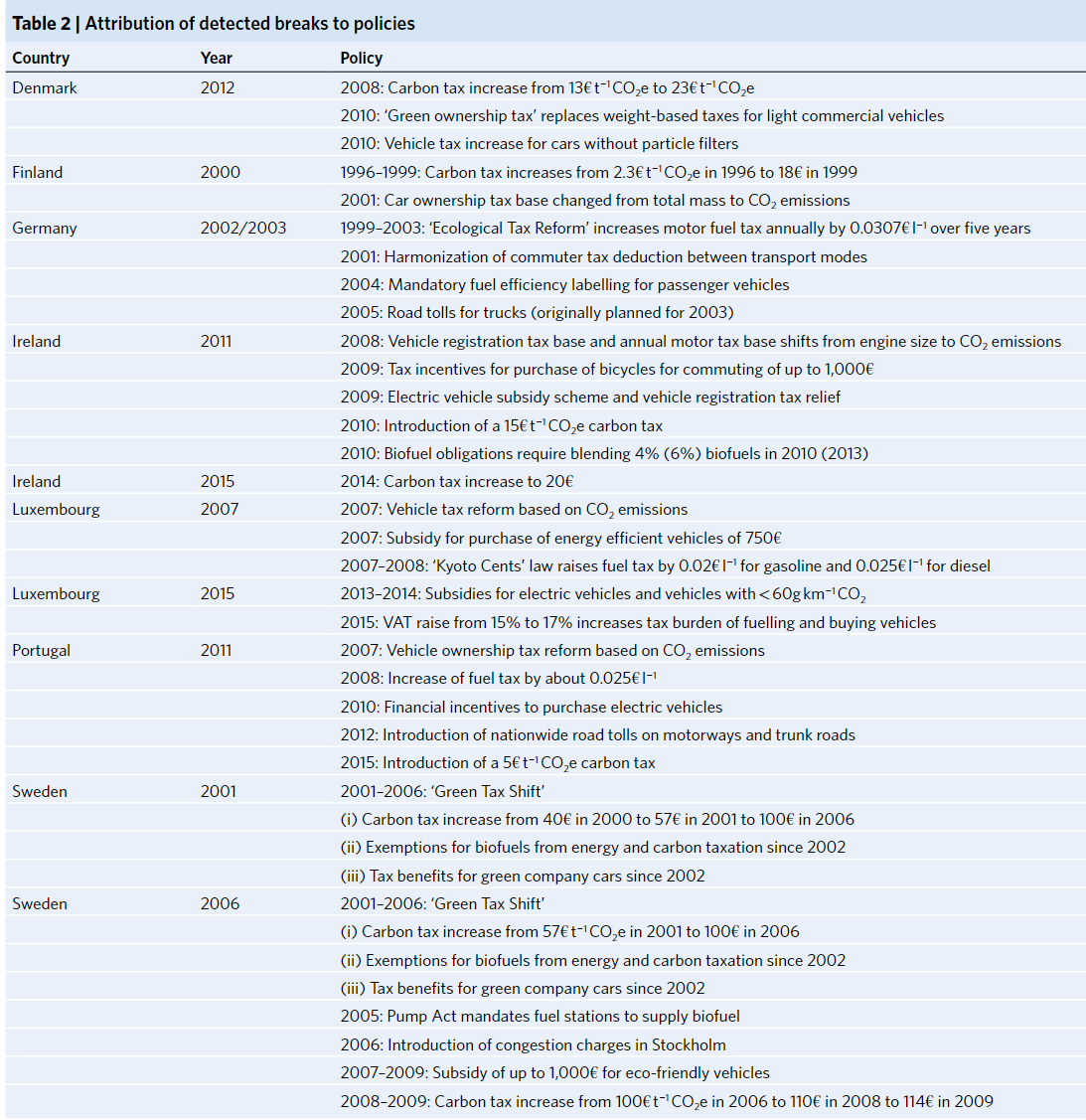
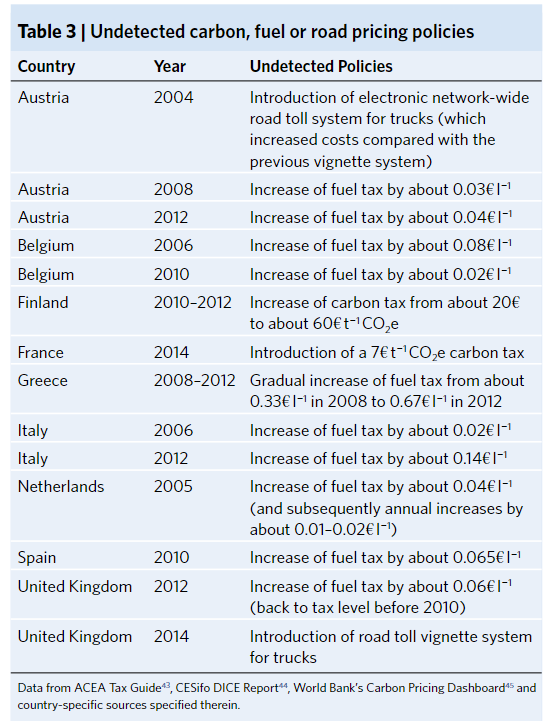
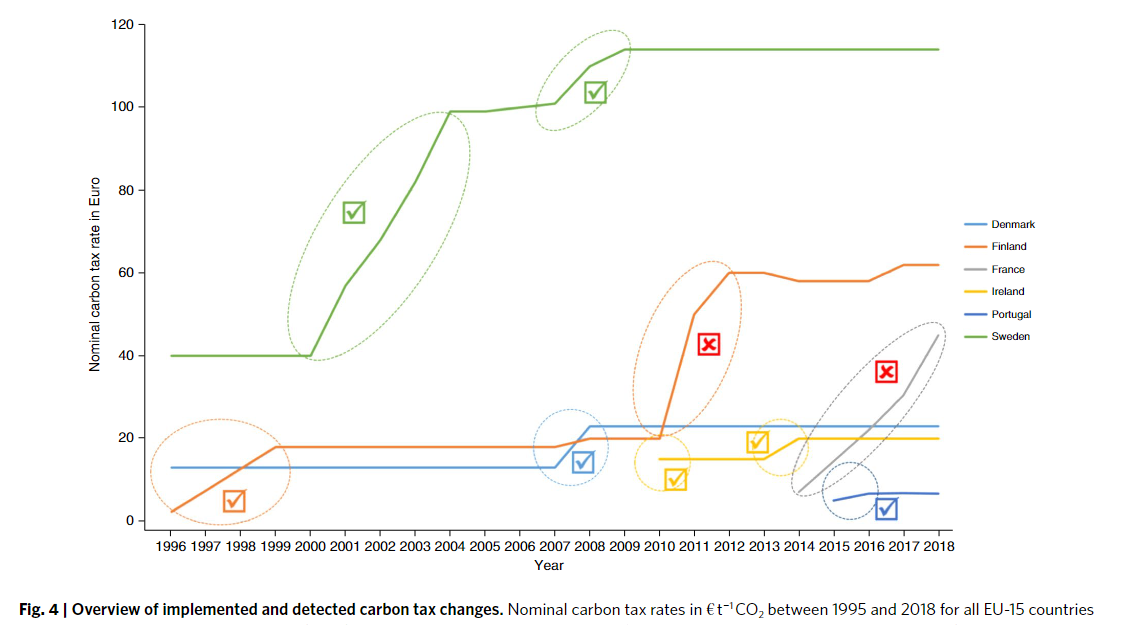
- Ten successful interventions with emissions reductions between 1995 and 2018 and attribute all detected emissions reductions to policy mixes
- Carbon pricing is a critical element of effective policy packages
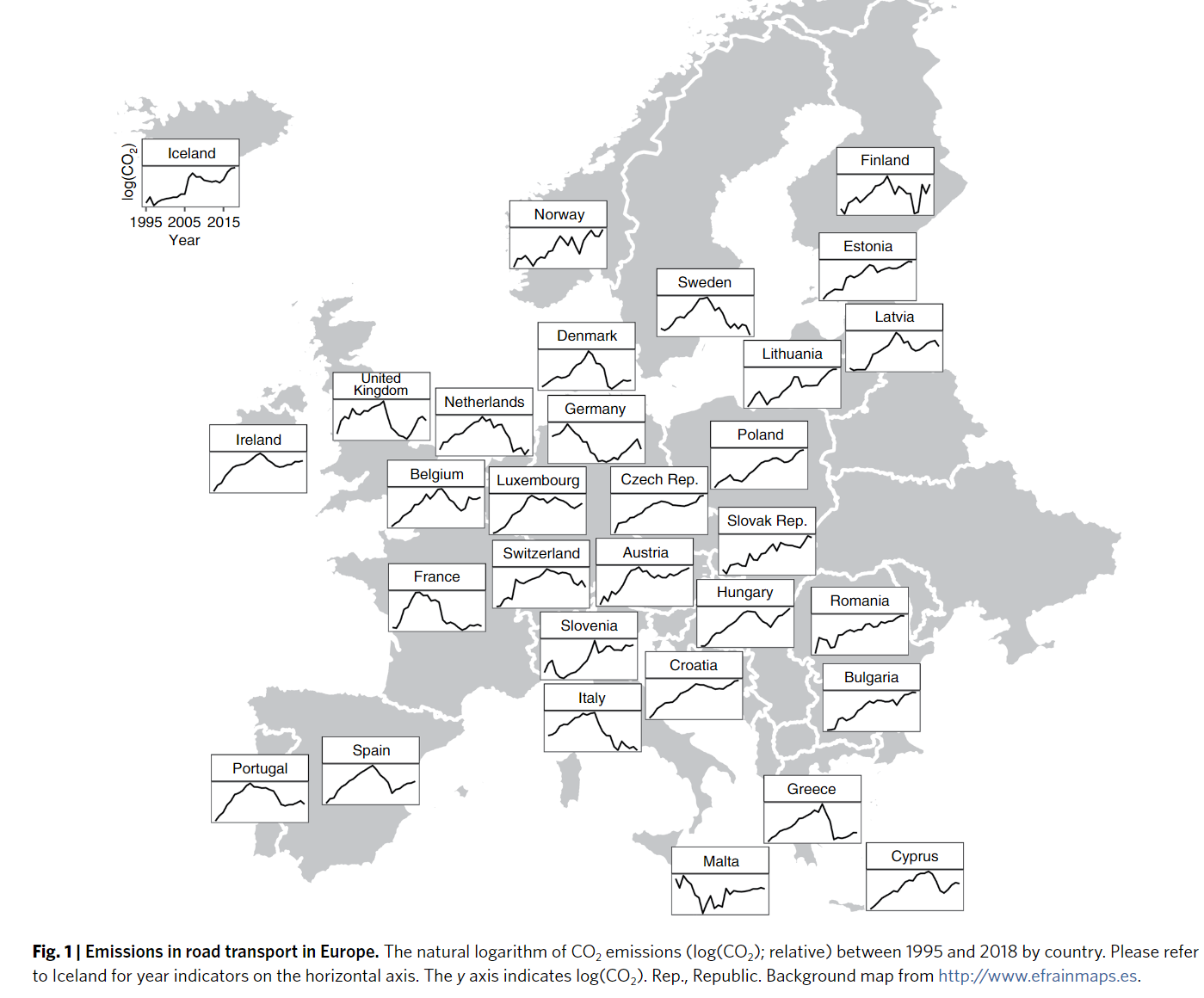
- The successsful of carbon, fuel or road-use taxes with additional vehicle taxes or subsidies are implemented in Finland, Sweden, Ireland, and Luxembourg
Coding Reference:







