Objective:
- Assess the extent of economic damages from climate change to which the world is already committed by historical emissions and sociaeconomic inertia
Case:
- Global regions (sub-national)
Methodology:
- Fixed-effects panel regression:
- Baseline: $\Delta lgrp_{r,y} = \mu_r + \eta_y + k_ry + \alpha C_{r,y} +\epsilon_{r,y}$
- Cumulative effect of all lagged terms $\Delta lgrp_{r,y} = \mu_r + \eta_y + k_ry + \sum_L \alpha_L C_{L,y-L} +\epsilon_{r,y’}$
- Robust: Monte Carlo and restricted distributed lag model
- Projection future scenario
- Grid Temperature: WE5E, CMIP6
- Economic: DOSE database (subnational), SSP
- Mitigation cost
Findings:
- A dependence of the growth rate on a change in climate variables
- Median committed climate damage are larger than the median mitigation costs
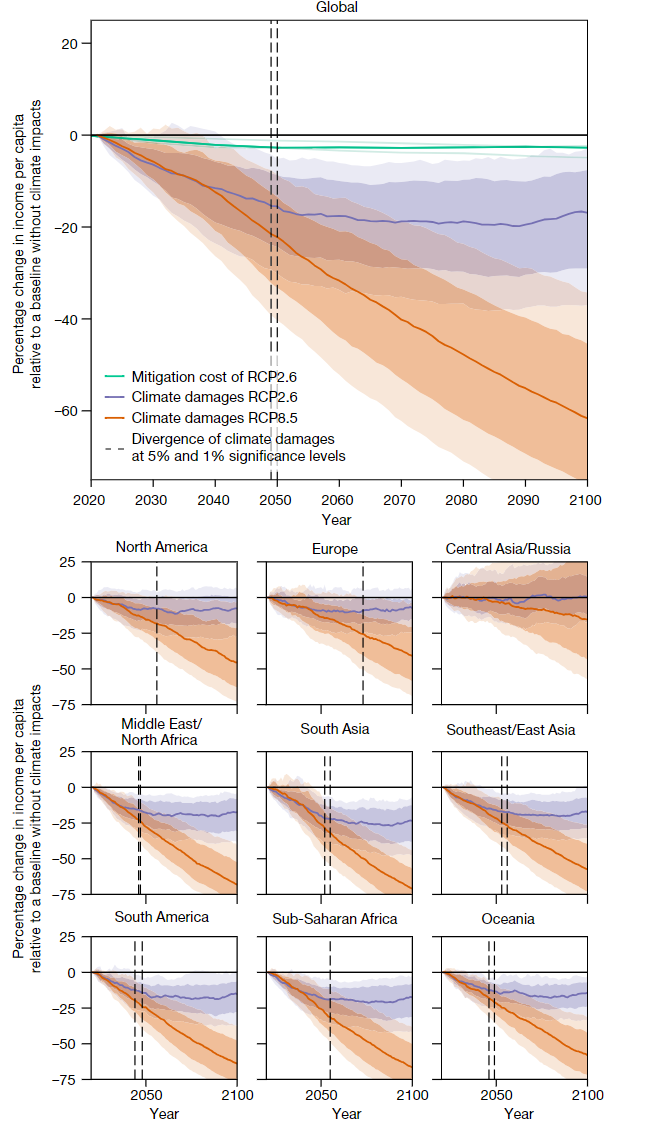
- Physical damages from climate change are simply not large enough to outweigh mitigation costs until the second half of the century
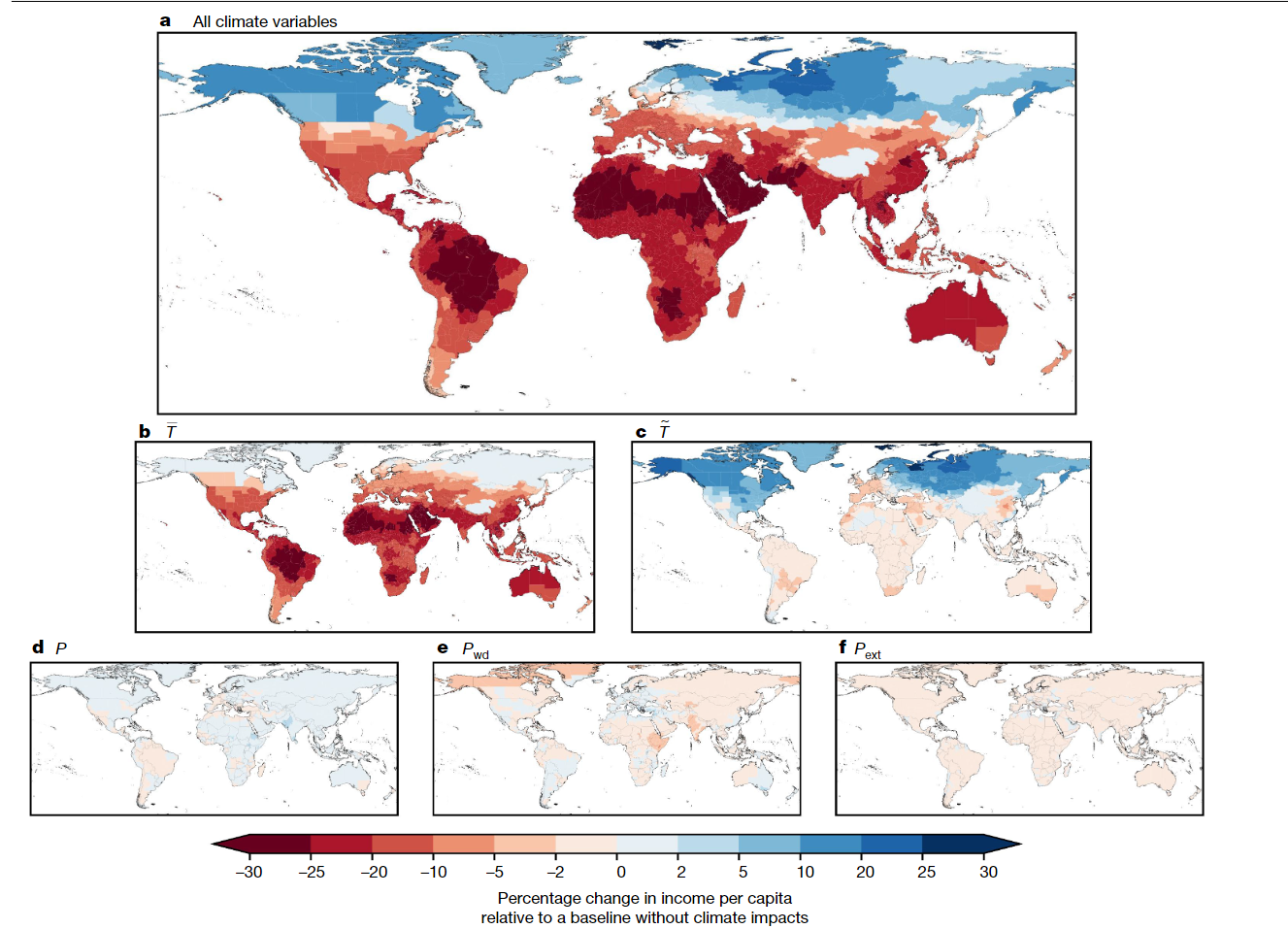
- Committed damage primarily arise through changes in average temperature
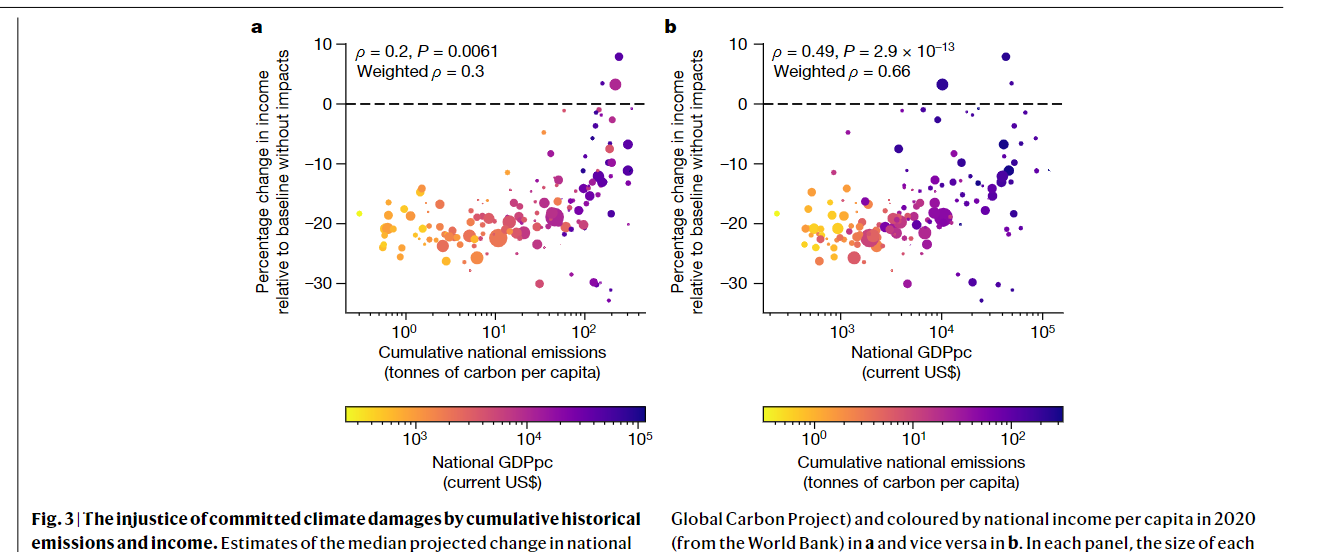
- Committed damages are significantly larger in countries with smaller historical cumulative emissions, as well as in regions with lower current income capita
- The countries with low income are committed to an income loss that is 8.9 percentage points greater than the upper quartile
Coding Reference:



