Objective:
- Test whether the degree of variability in realizations of temperature has an effect on macro-economic outcomes by assessing historical changes to economic data and day to day temperature variability on a global scale
Case:
Methodology:
- Variability index
- Fixed panel regression:
Data Source
- Climate data: ERA5 reanalysis dataset, WFDEI, EWEMBI
- District: GADM
- Population: Global Environment version
- Economic output: FRED, World Bank
Findings:
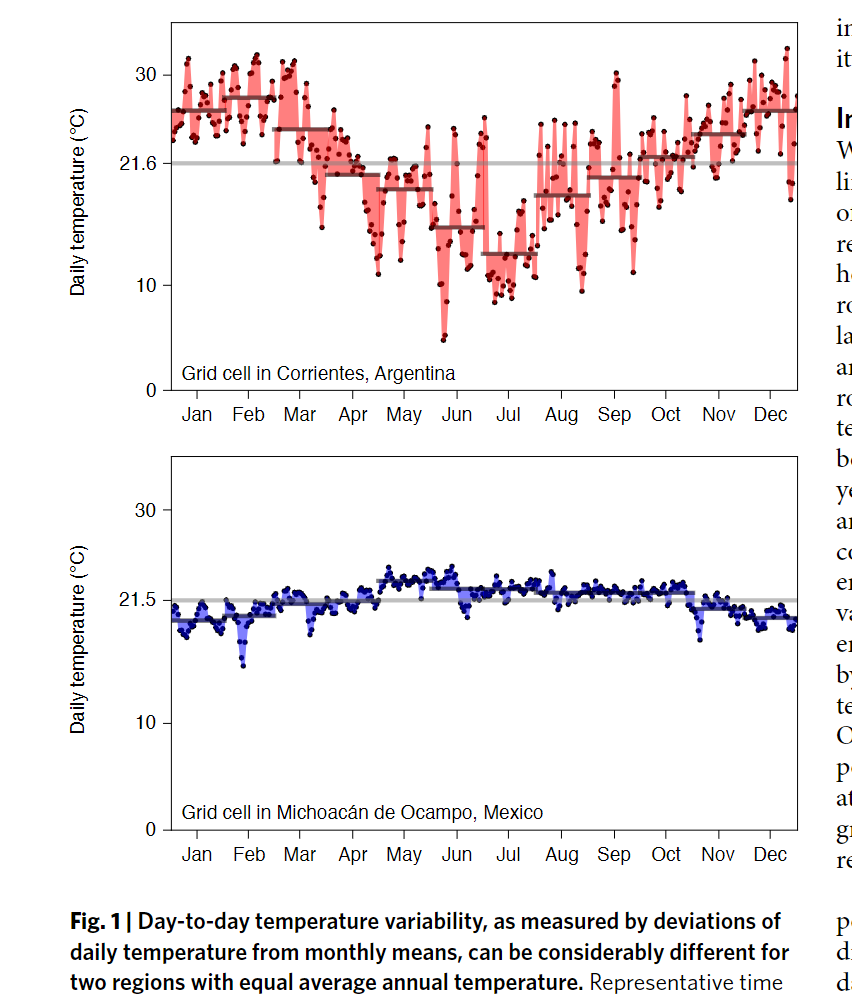
- Day-to-day temperature variability has a negative impact on regional growth rate
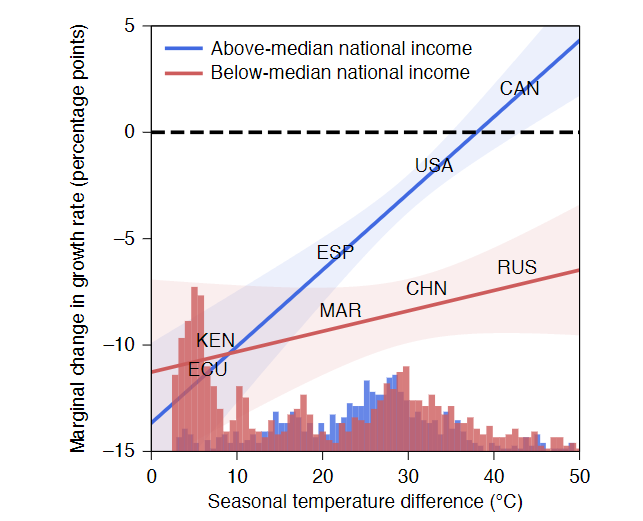
- Countries which experience smaller seasonal temperature differences are affected more by a given changes in day-to-day temperature variability
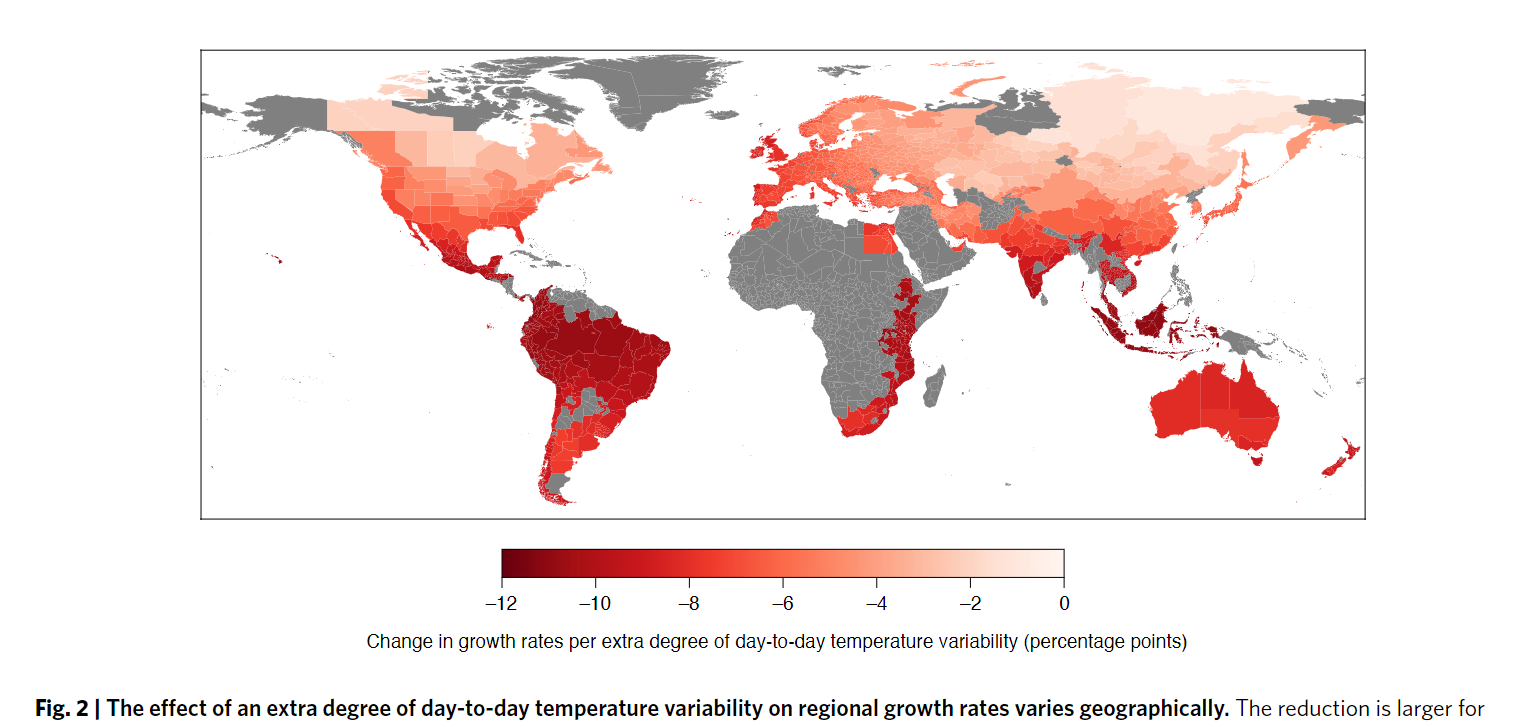
- The marginal losses from an increase in day-to-day temperature variability are largest in low-latitude and costal regions
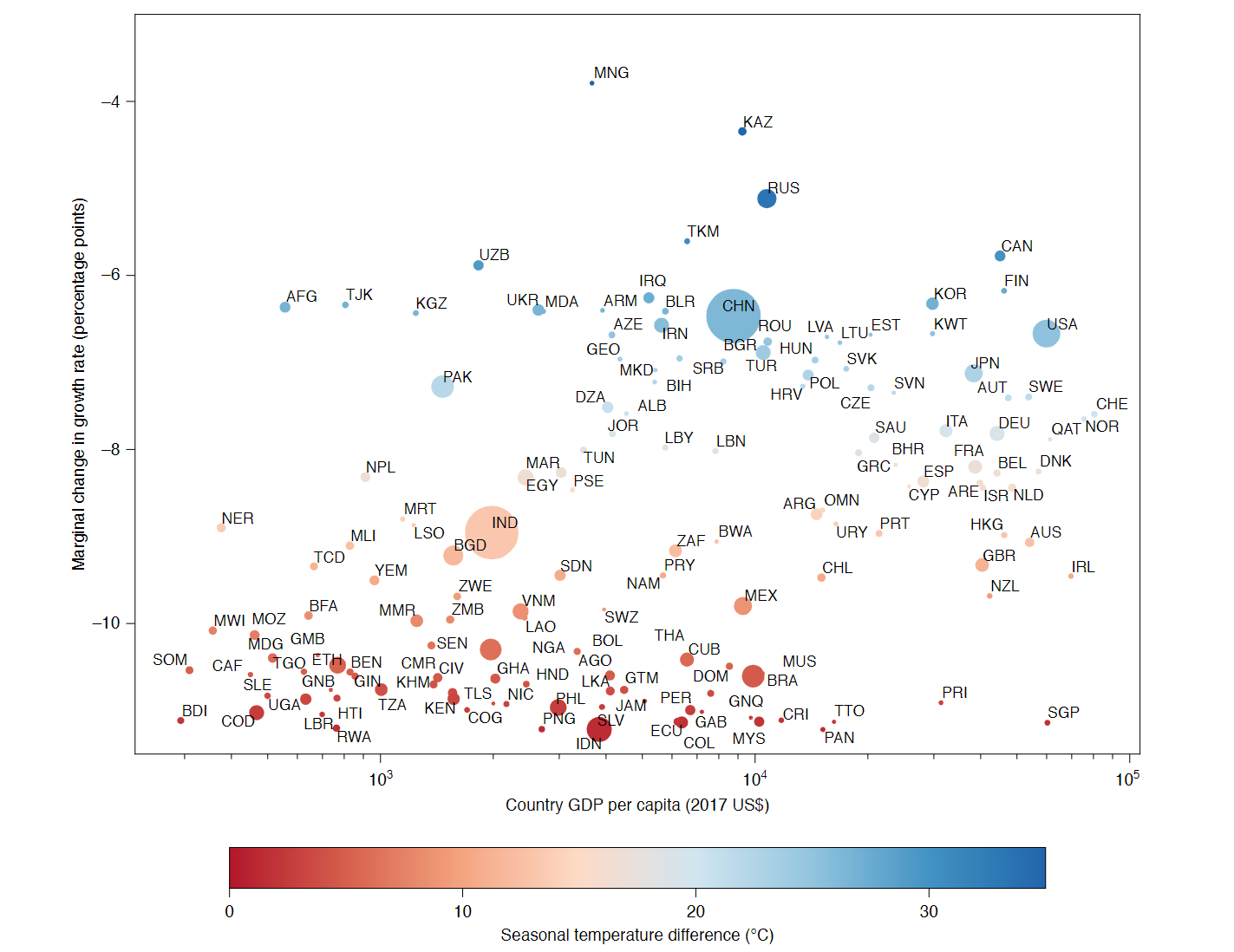
- Marginal losses from an increase in day-to-day temperature variability are generally larger for regions in low-income nations compared with those in higher-income nations
Coding Reference:




