Objective:
- Identify key trends in the changing nature of urban inequality as it relates to the social reproduction of US households through the lens of water access
Case:
Methodology:
Data Source
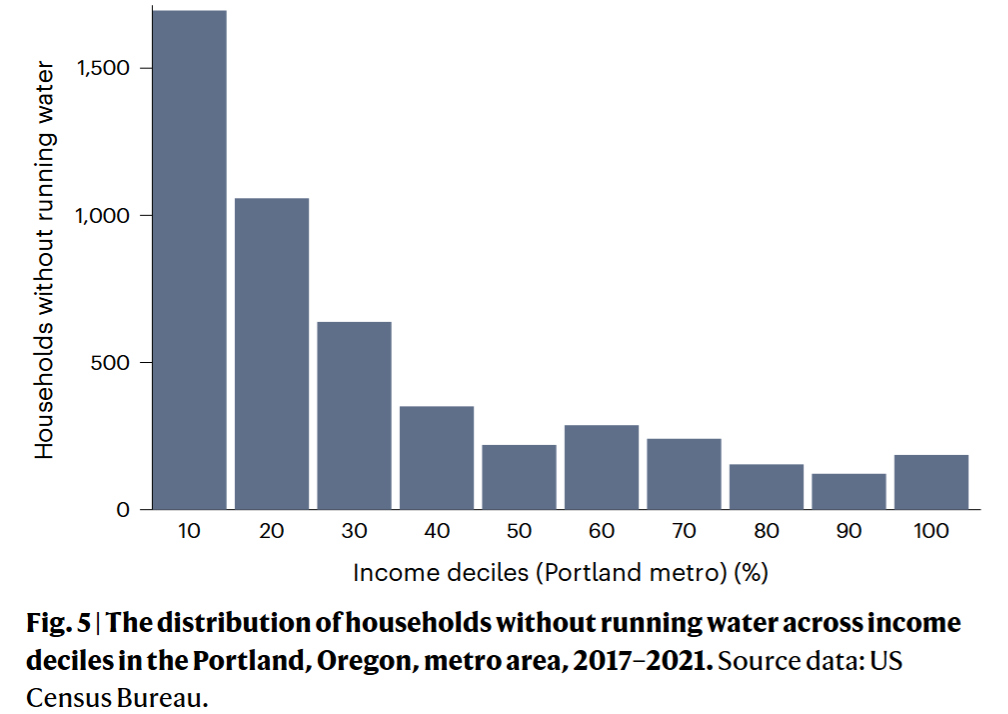
Findings:
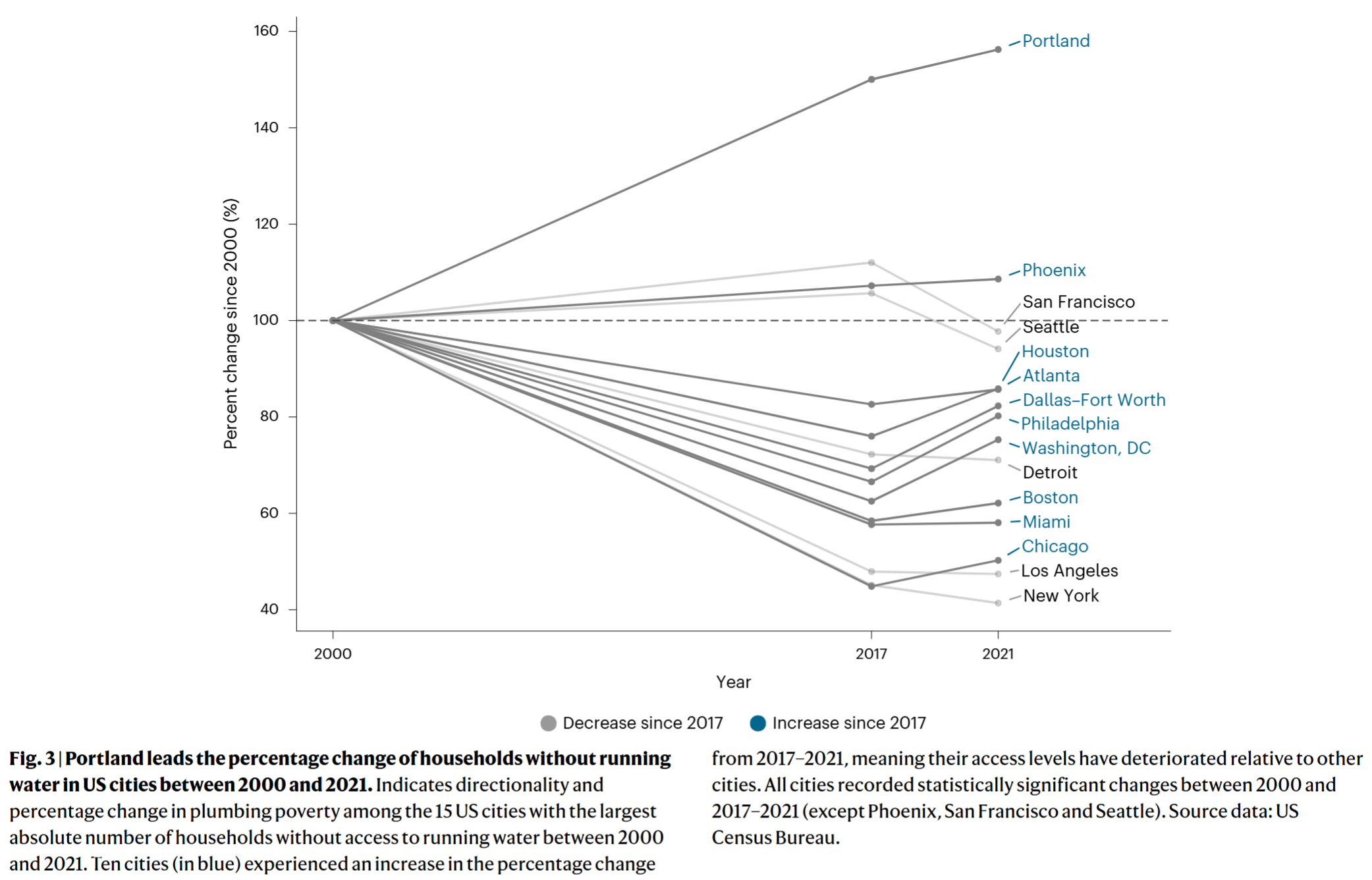
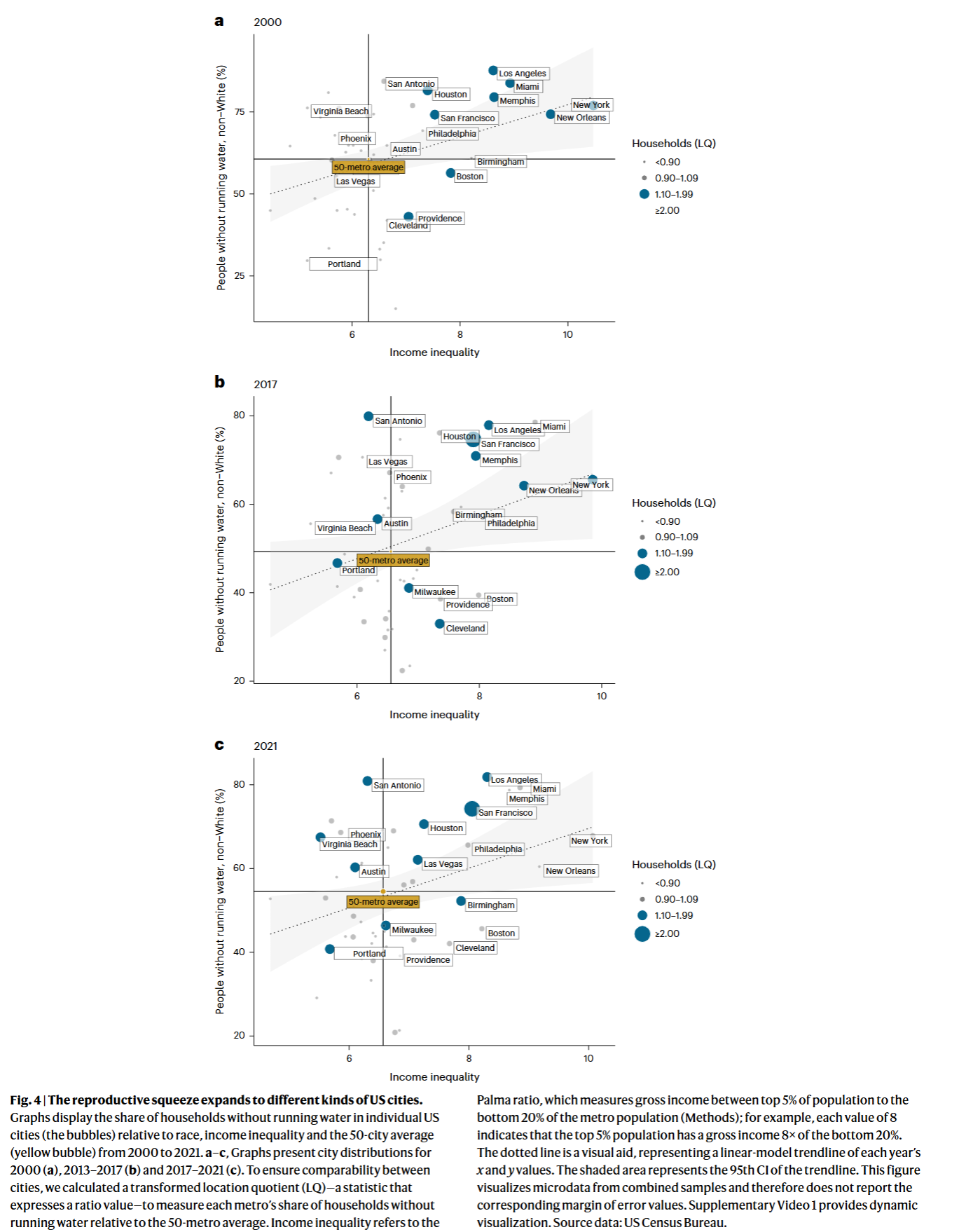
- The story of water access inequality in the US has morphed from a predominantly rural to a majority urban problem
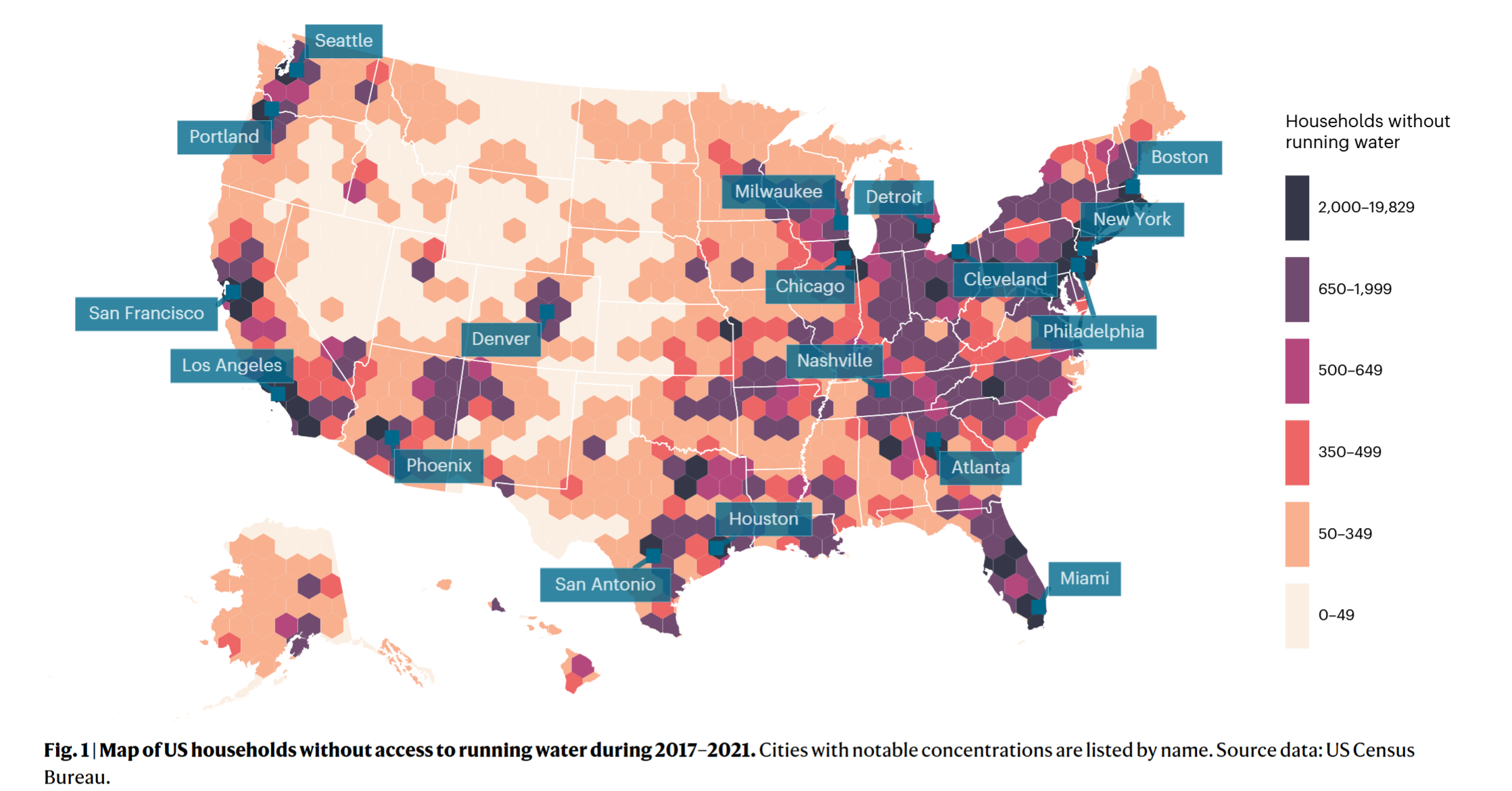
- 71.7% US households without running water in cities
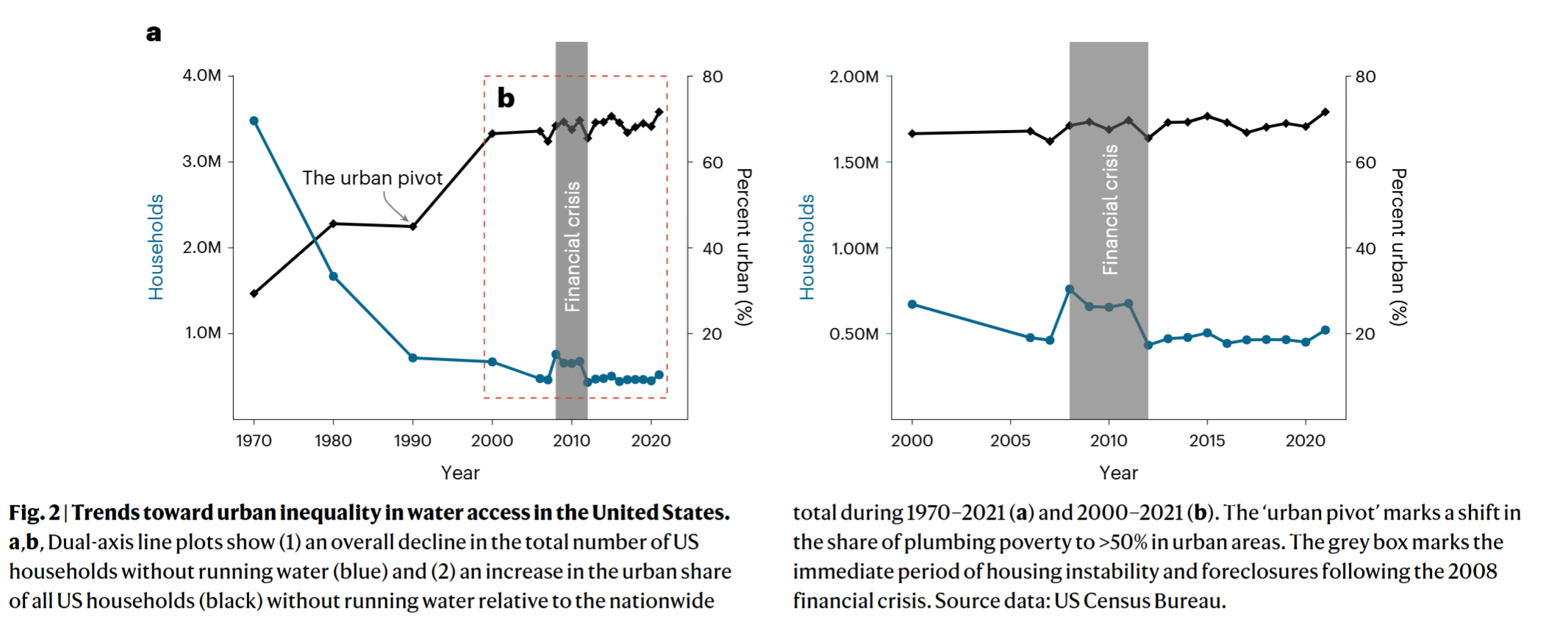
- Housing financial crisis pushed more household into plumbing poverty
- Subdistricts located in the center layer generally featured the lowest average HUEs across China; with an increase in spatial distance to the city center
Coding Reference:





