Objective:
- Quantify the impact of urban form on a diverse range of local and city-level outcomes related to water and sanitation
Case:
- 100 Cities in Asia, Africa, and Latin America
Methodology:
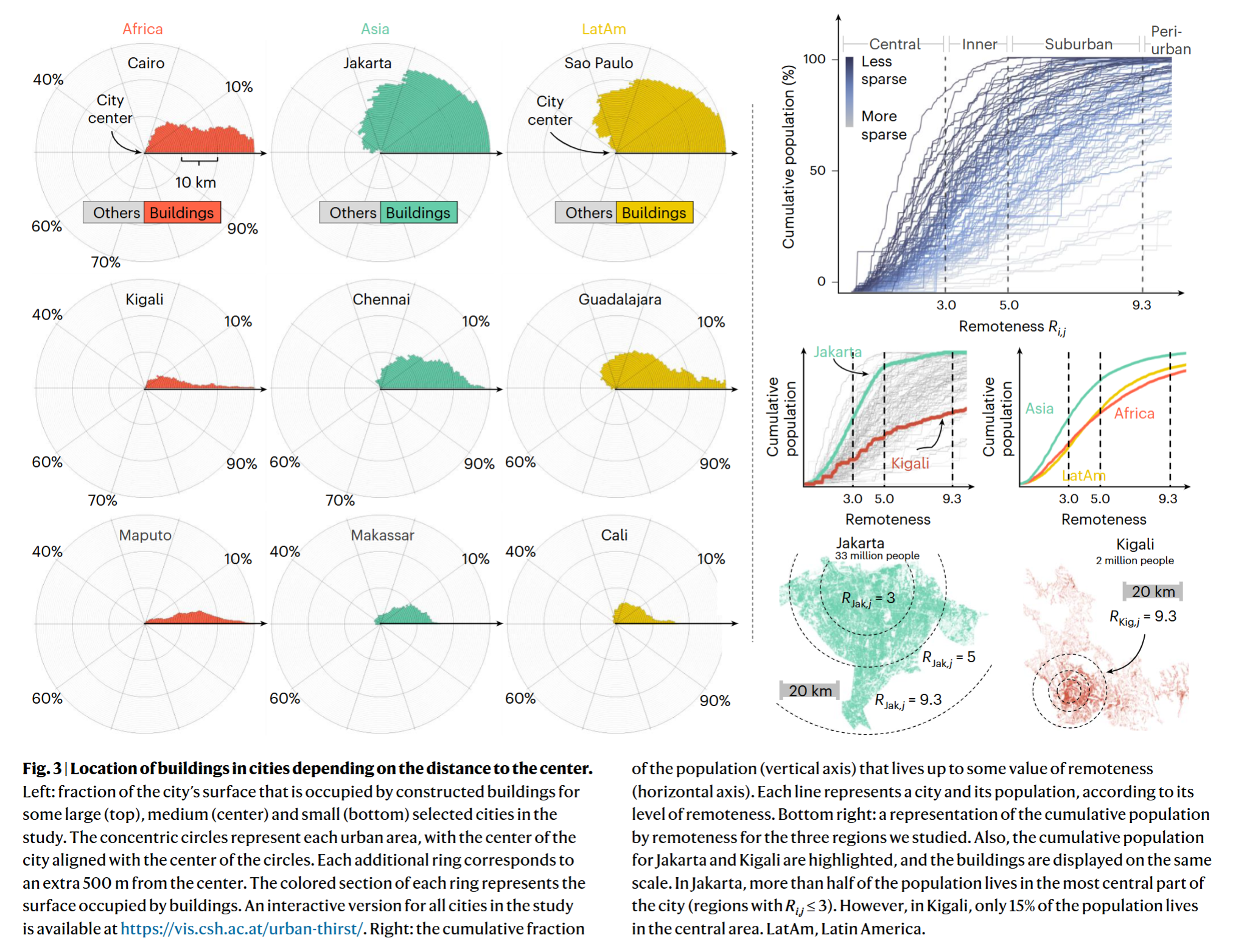
- Sparseness index
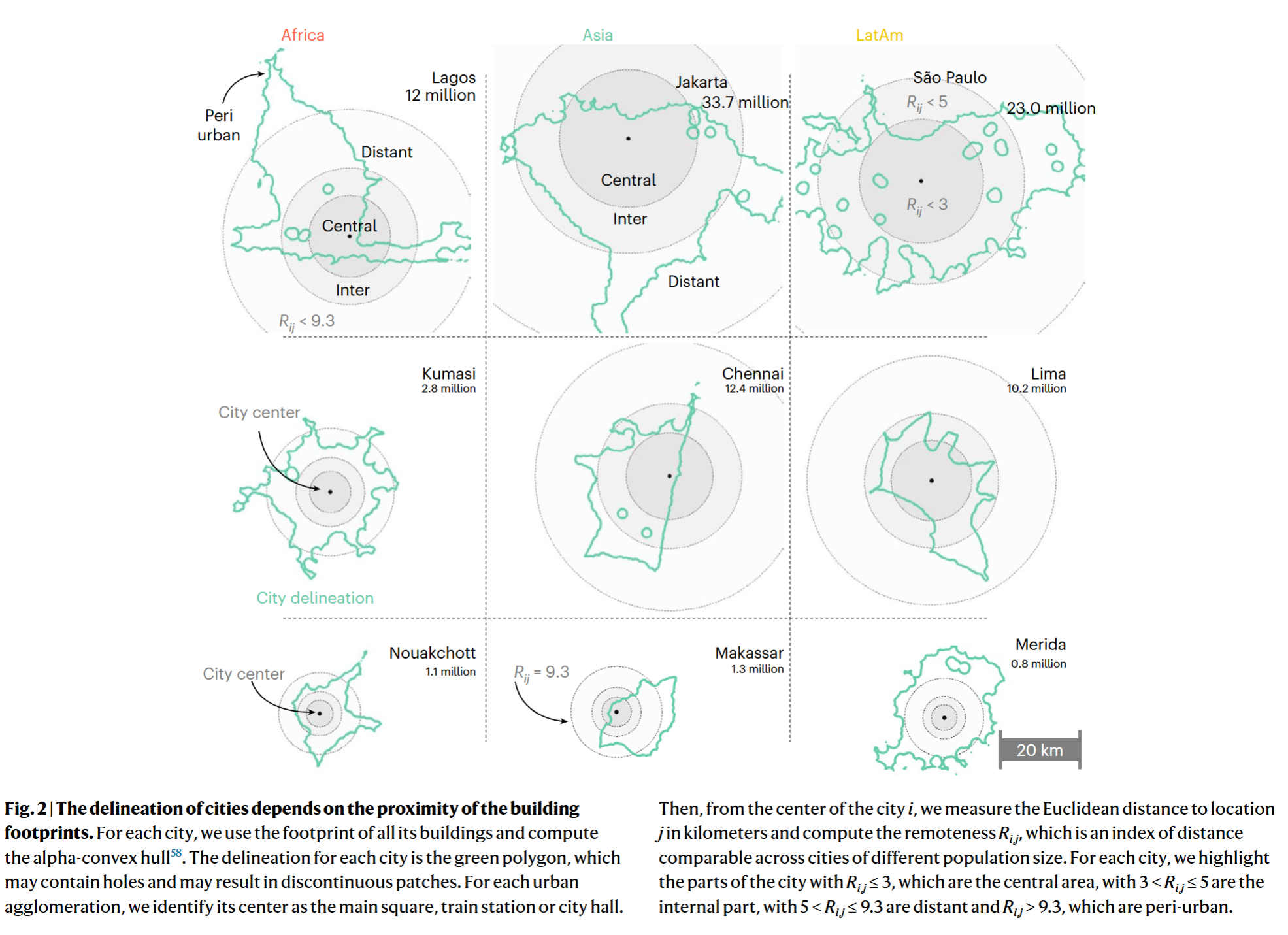
- Remoteness index
Data Source
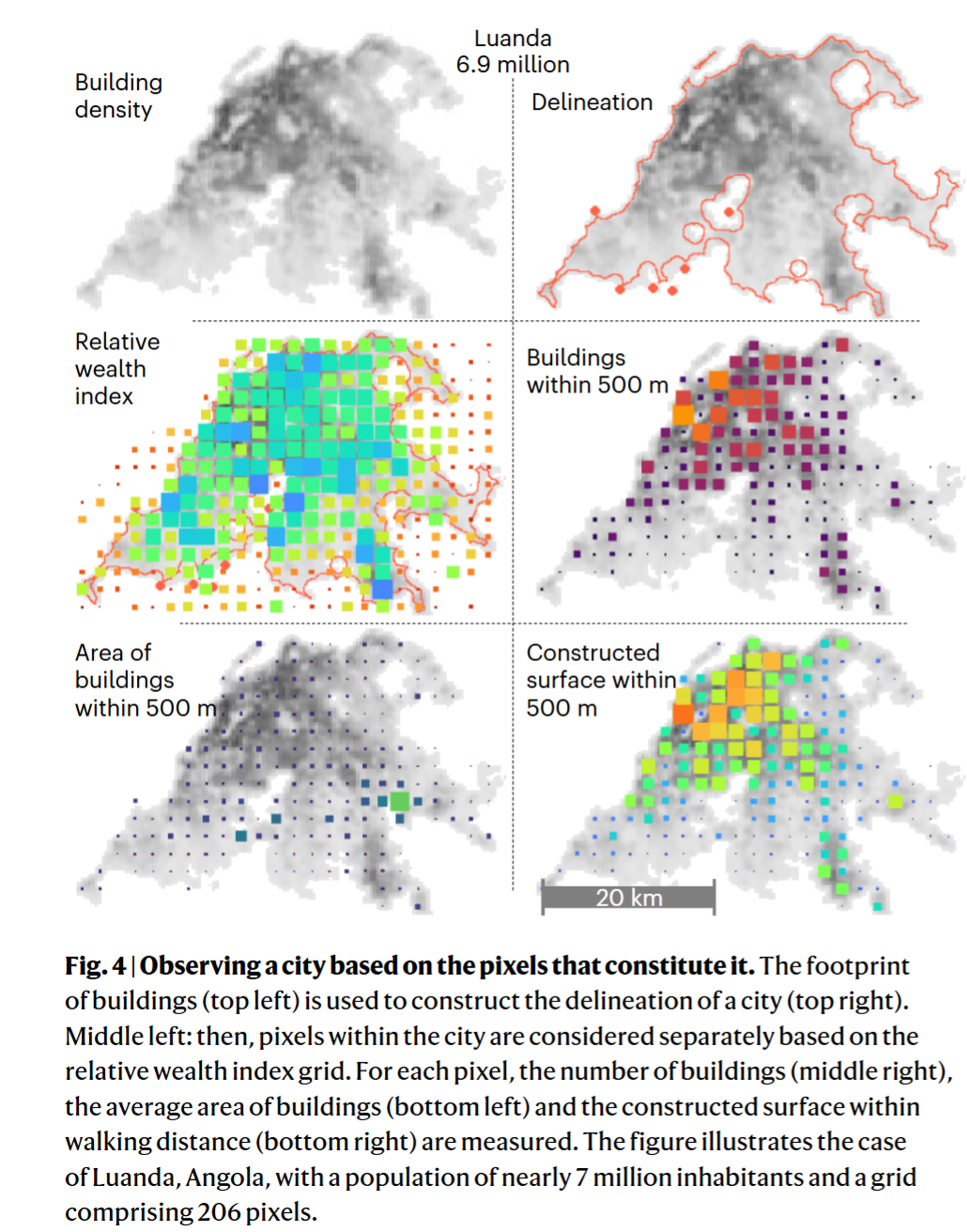
- Building footprint
- Survey
Findings:
- Less remote areas have higher average income, are closer to critical infrastructure and have higher access to sewage and piped water
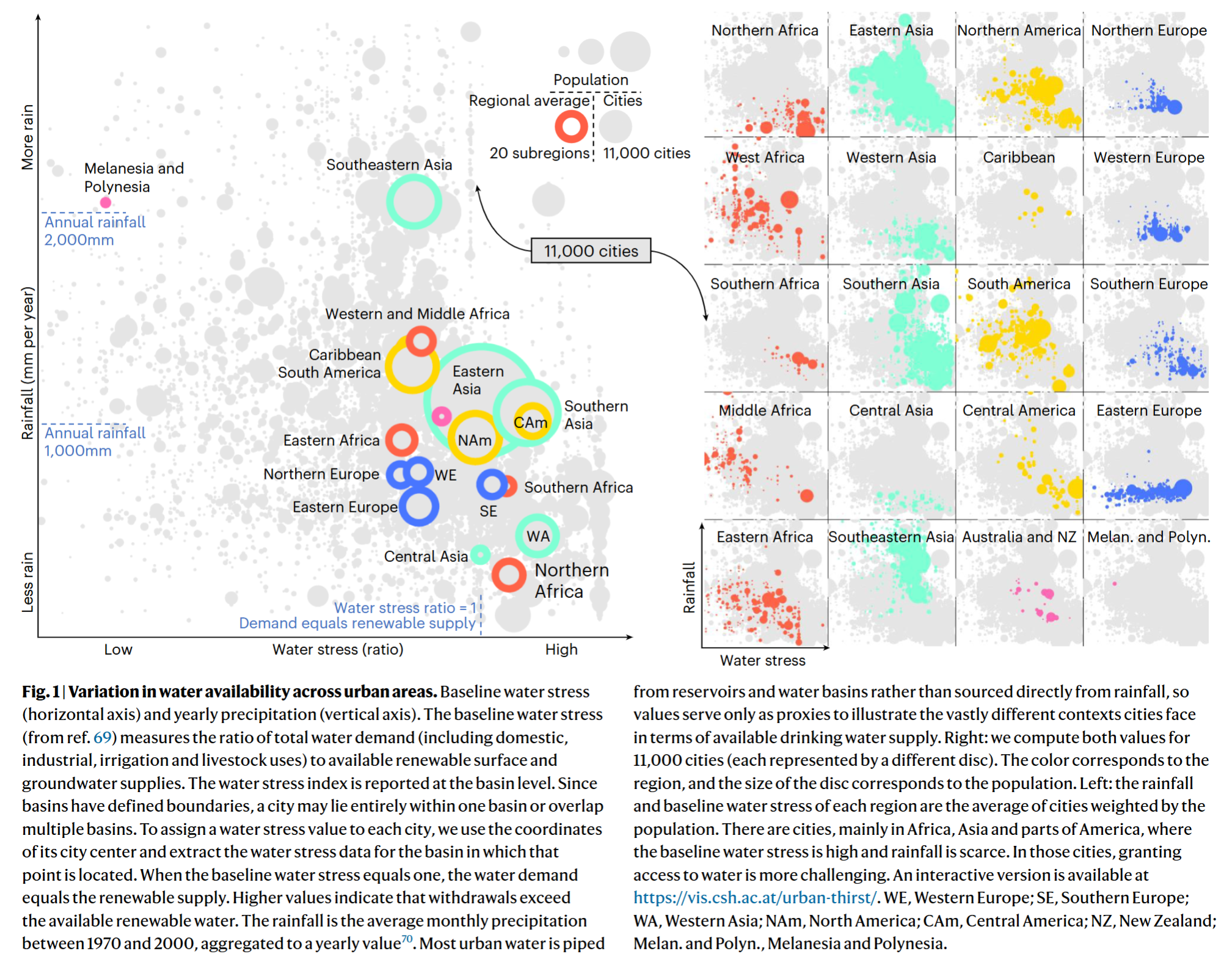
- Compact growth can bring benefits in accessing to piped water and sewage services
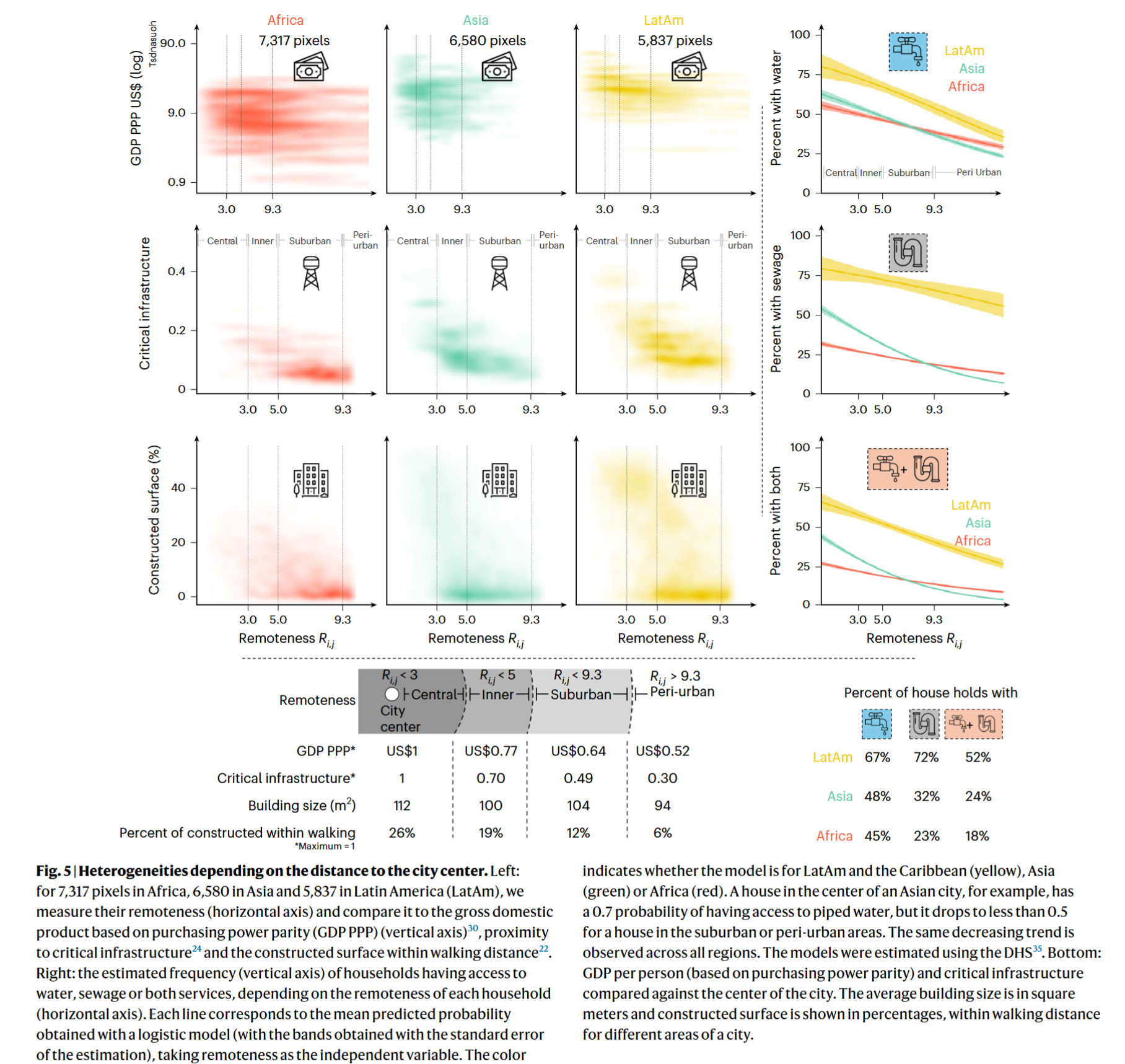
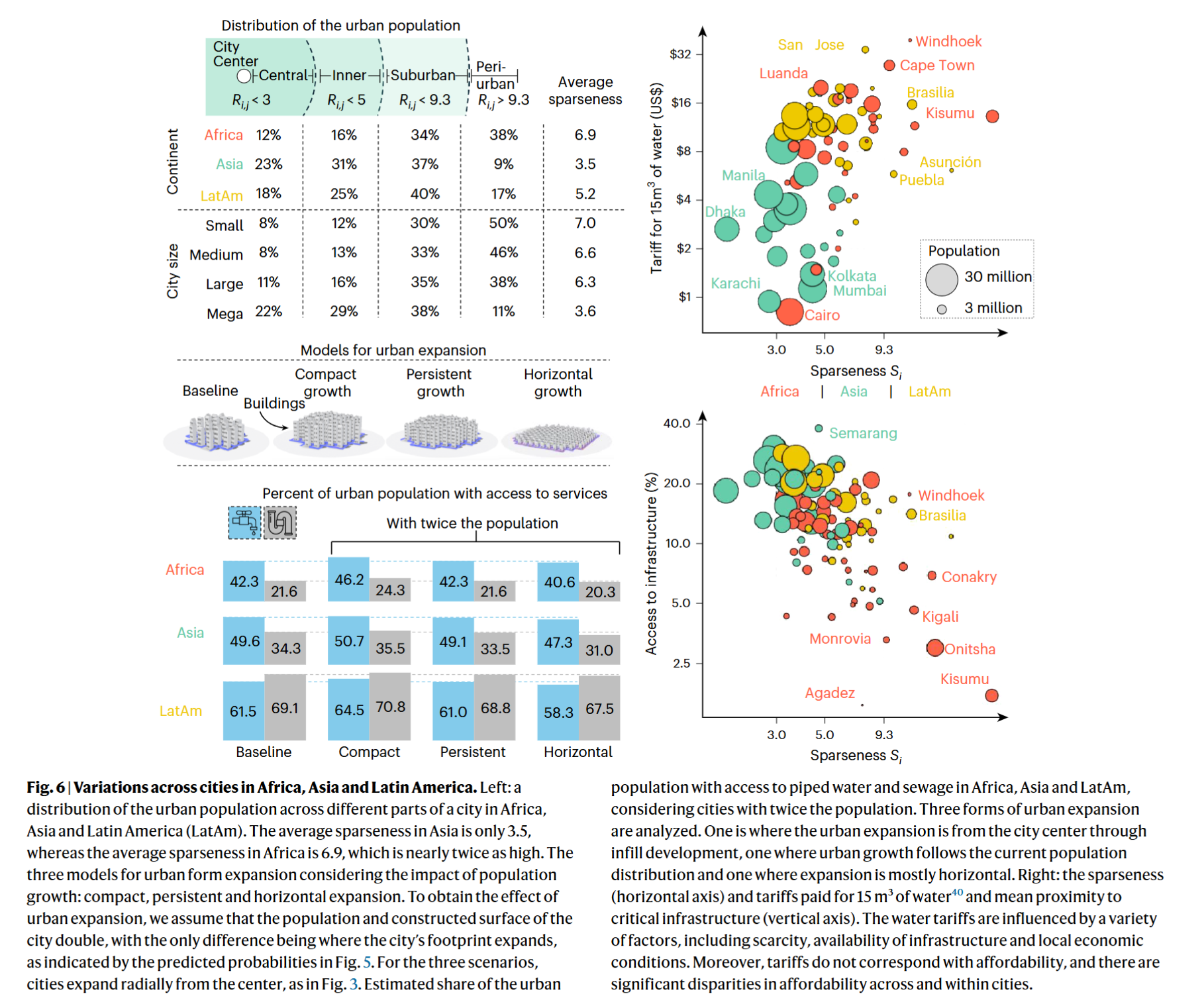
Coding Reference:






