Objective:
- Investiagte age-based household carbon footprints in China and its provinces by compiling a global MRIO table
Case:
Methodology:
- international flow
- migration rate
- MRIO
Data Source
Findings:
- East provinces tend to have higher total carbon footprints
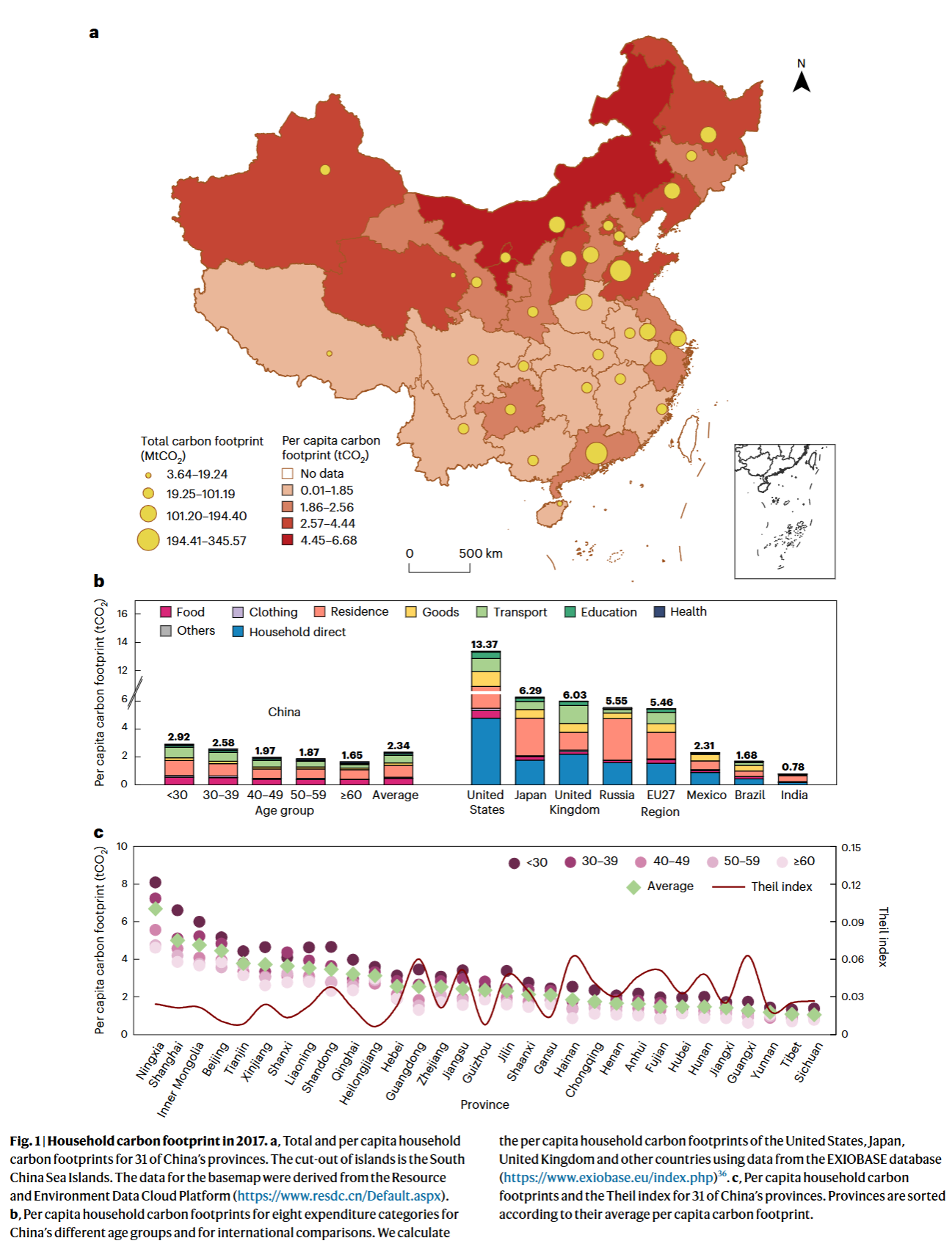
- China’s per capita carbon footprint is much lower than that of developed countries
- Carbon footprint is inversely correlate with age: young people have relatively higher household carbon footprint than those of midlle and older people
- Two top consumptions: related to residence and transport
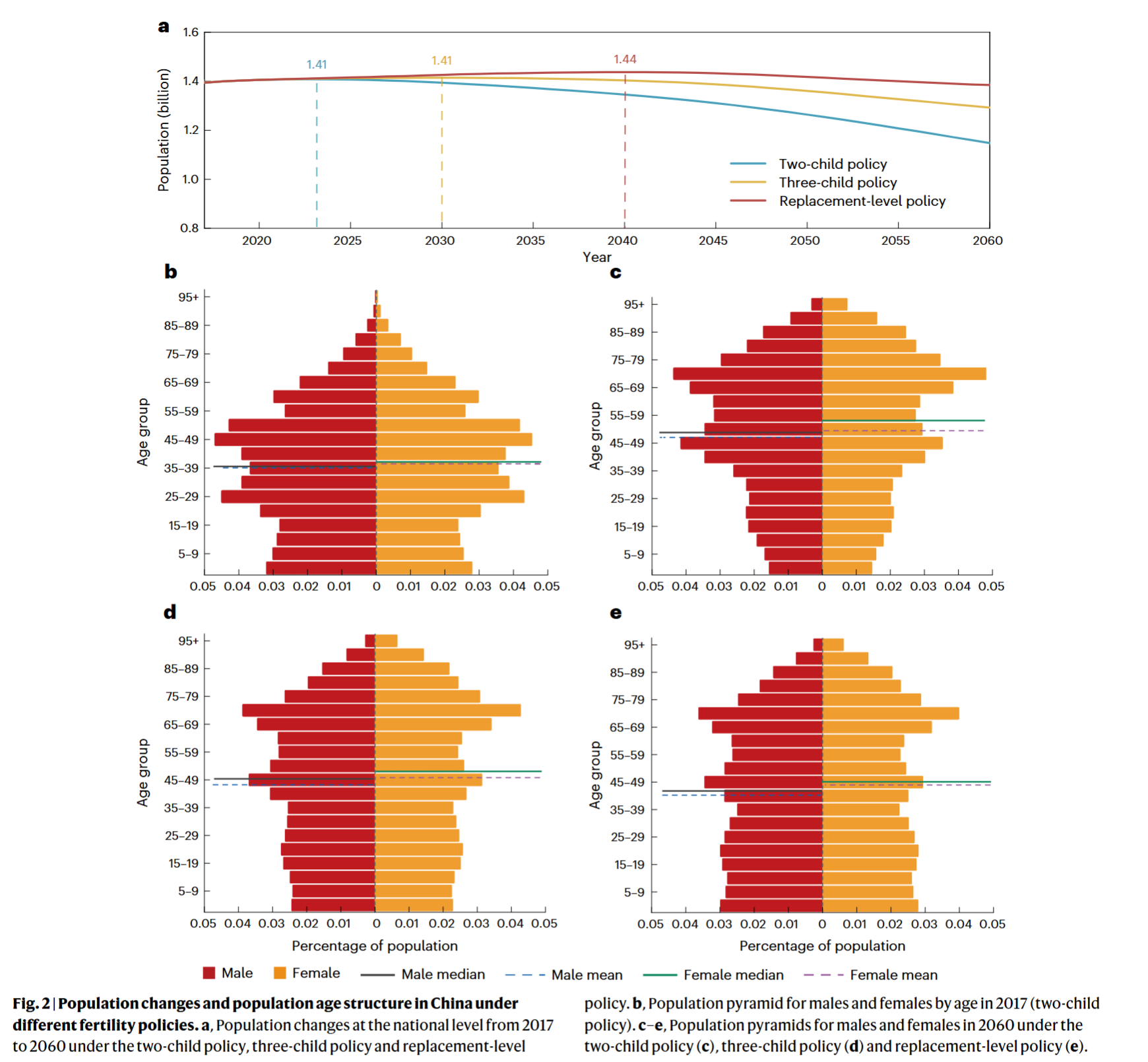
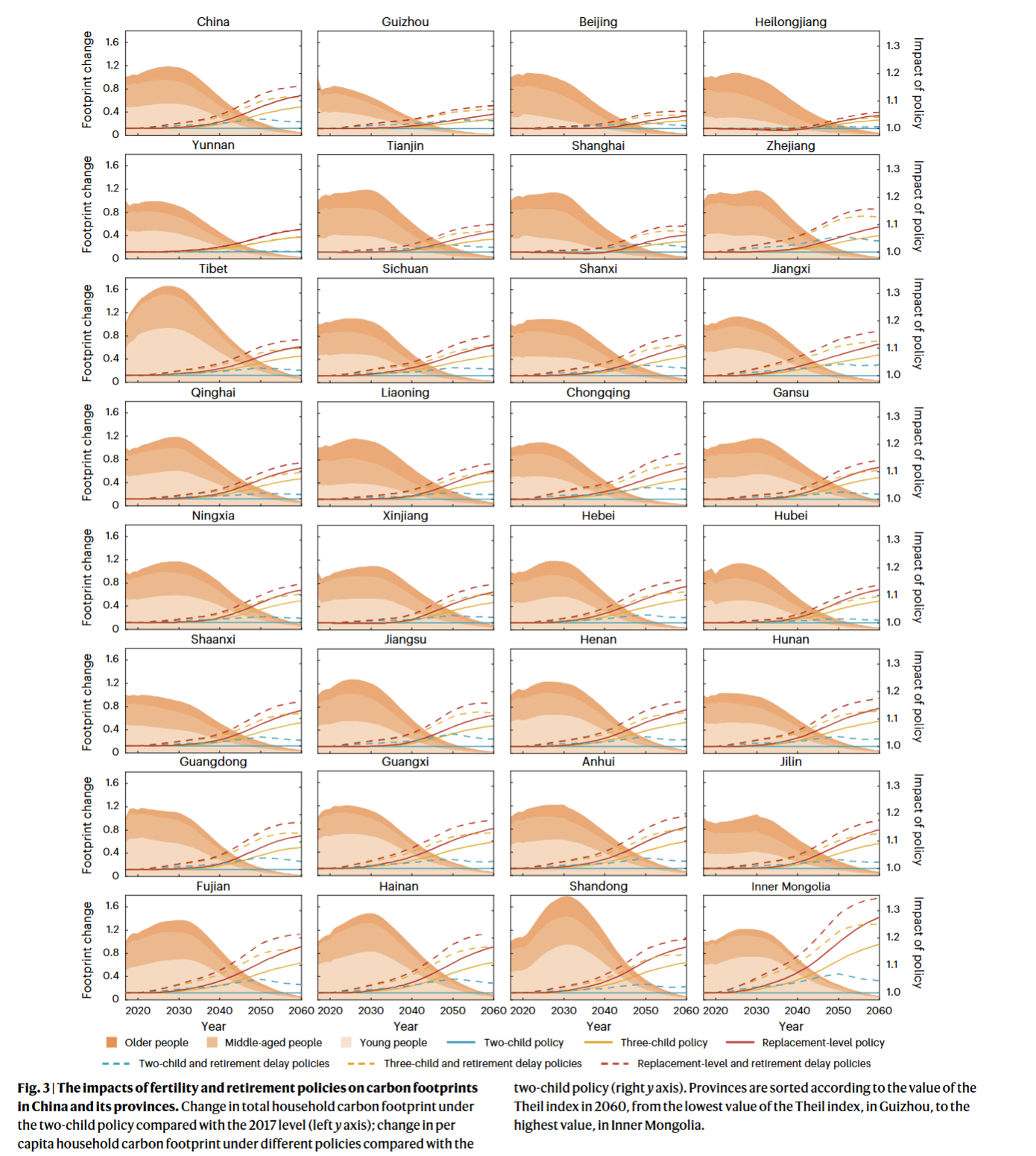
- Fertility in combination with retirement delay tend to further increase the carbon footprint in China
Coding Reference:



