Objective:
- Quantify the city-scale building energy use for 277 urban areas across contiguous US in the mid-21st century, with a focus on assessing the impacts of climate change, population growth and power sector decarbonization
Case:
Methodology:
- Bottom-up model: EnergyPlus
- Linear regression
Data Source
- High-granularity End-Use Load Profiles (EULP)
- Population
- Hourly weather data
Findings:
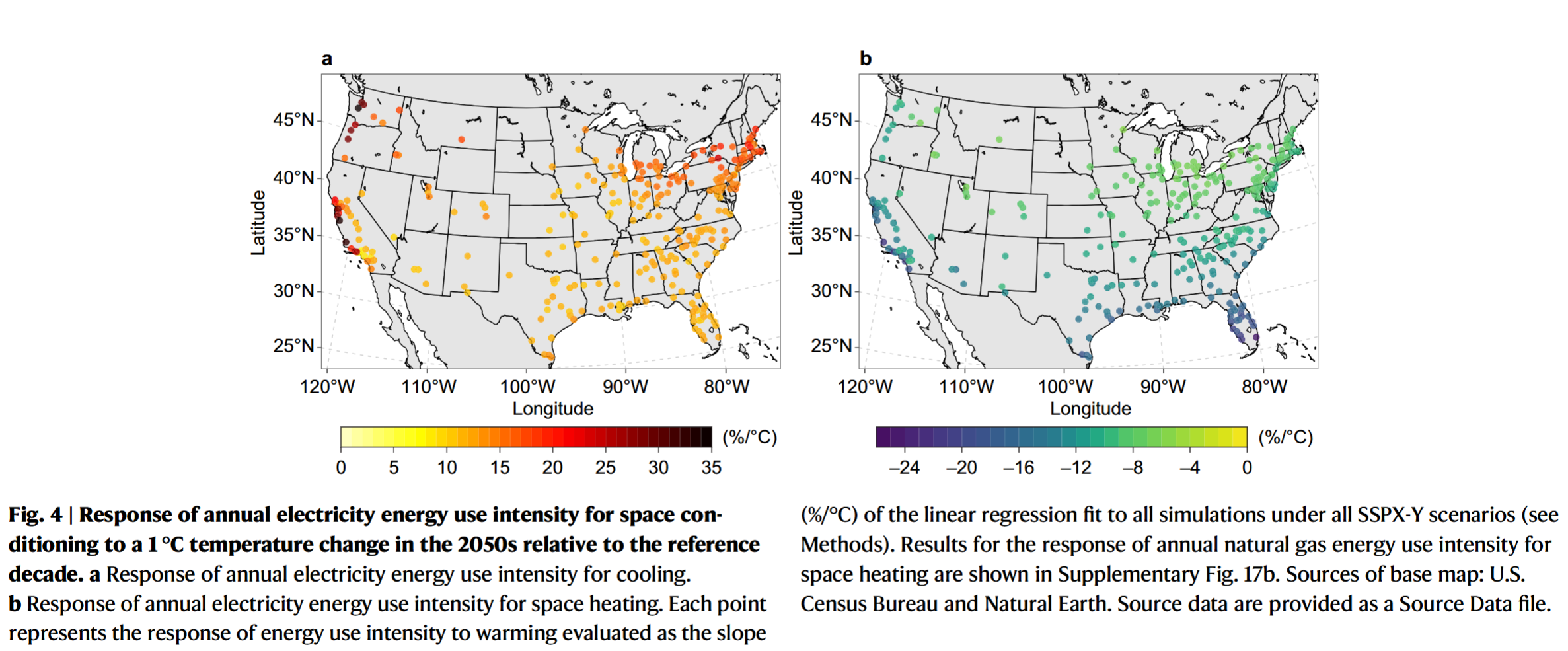
- The mean mid-century annual building E-EUI for space heating is projected to decrease by 13.5-21.2% when compared with the reference-decade level
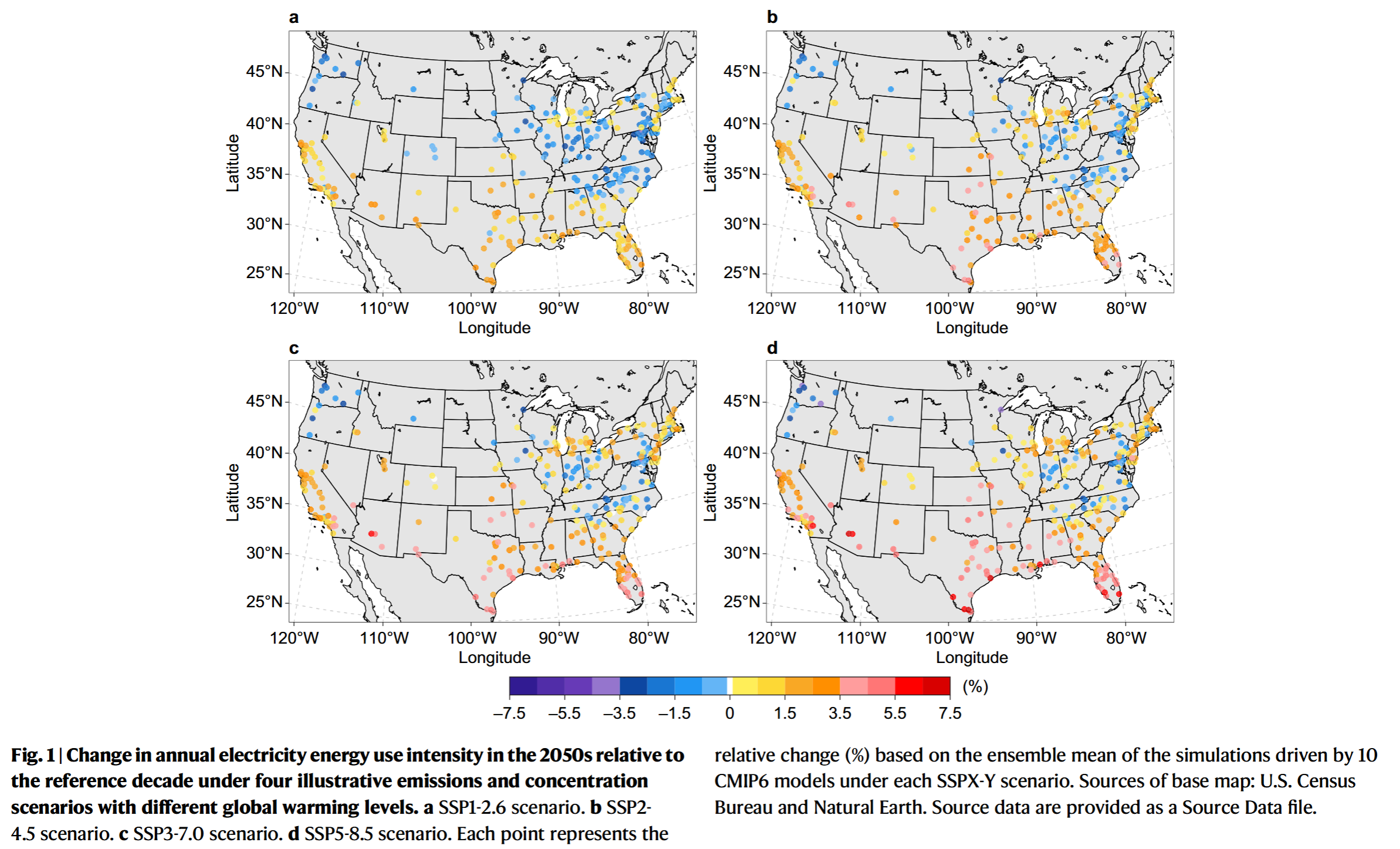
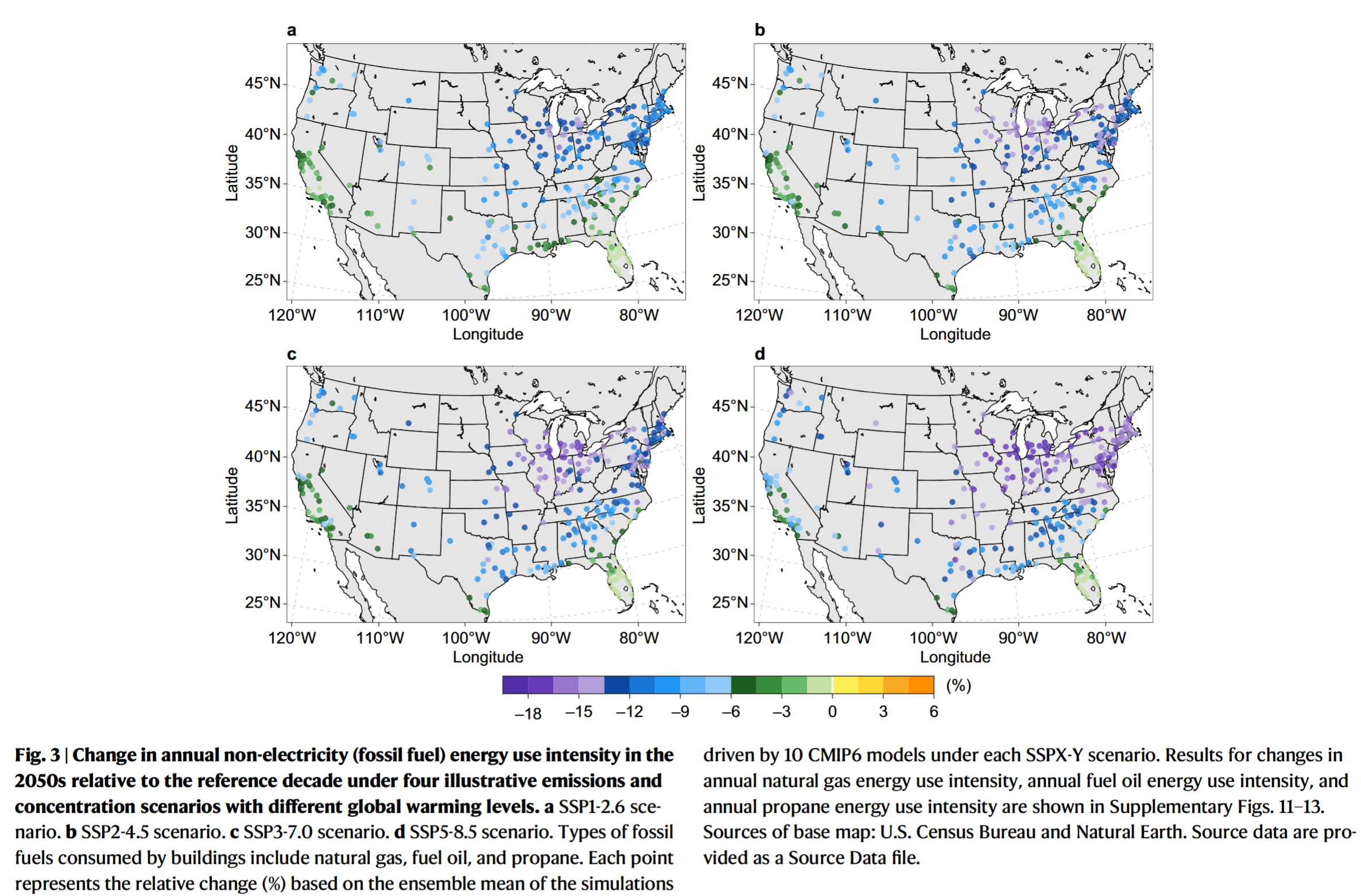
- Fossil fuels, including natural gas, fuel oil, and propane, account for ~40% of the building energy use in contiguous US (CONUS) urban areas
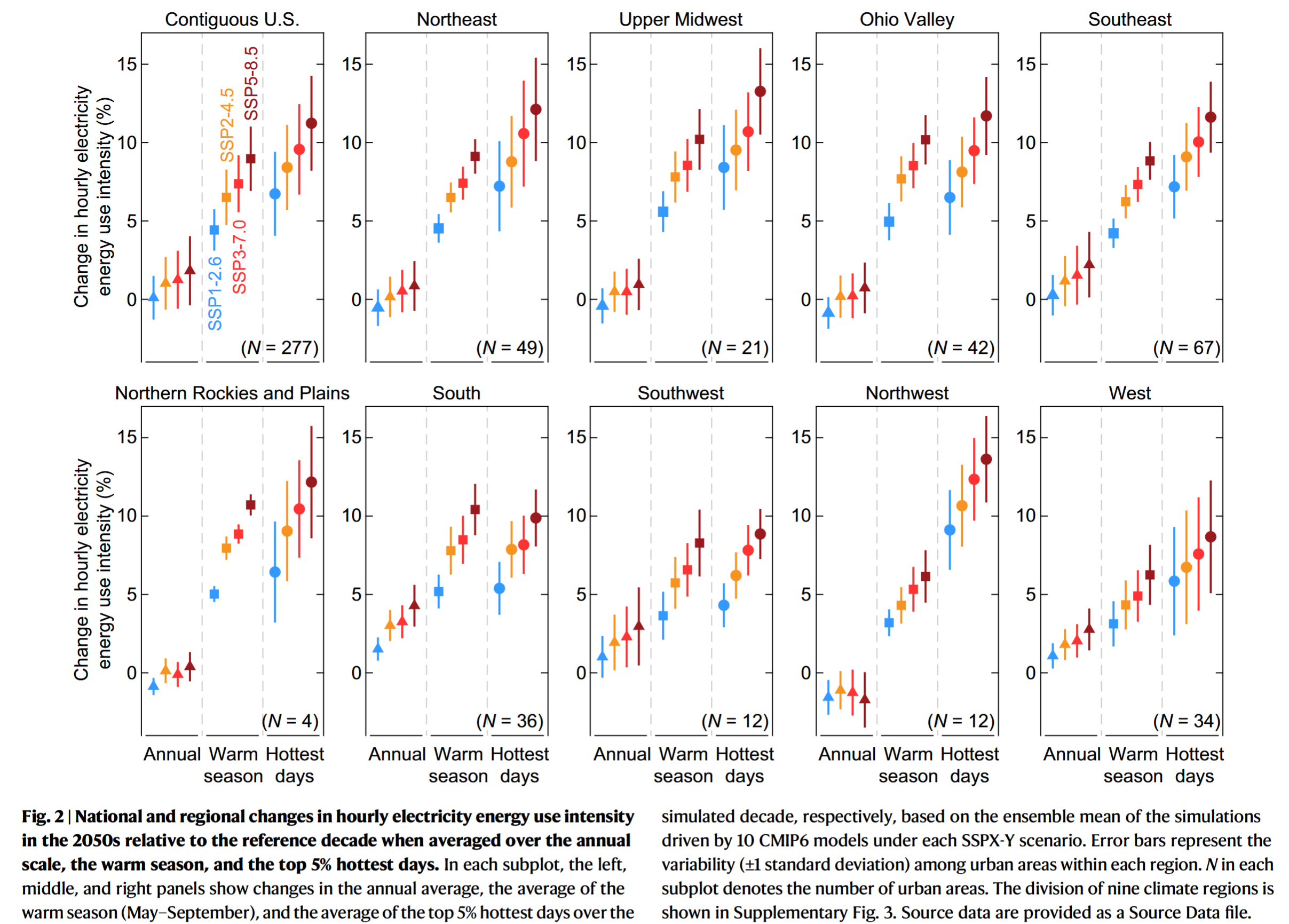
- City-scale building E-EUI for cooling rises by 13.8%
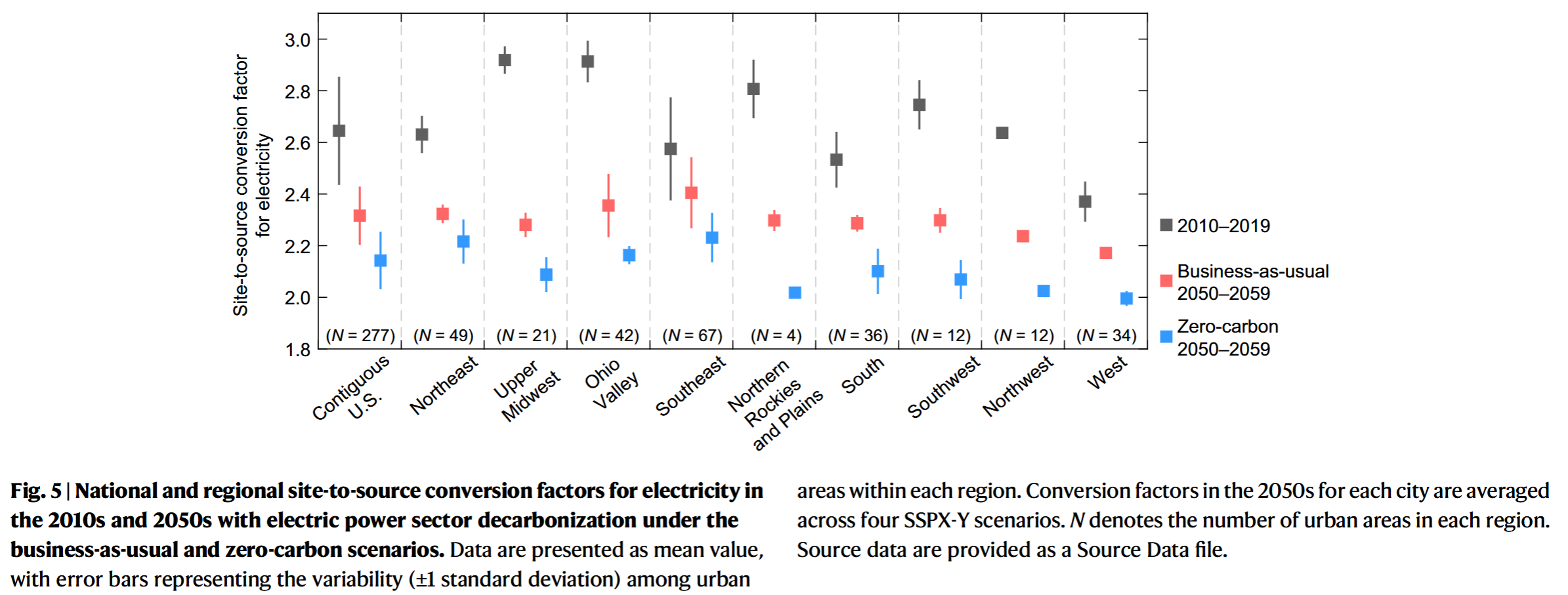
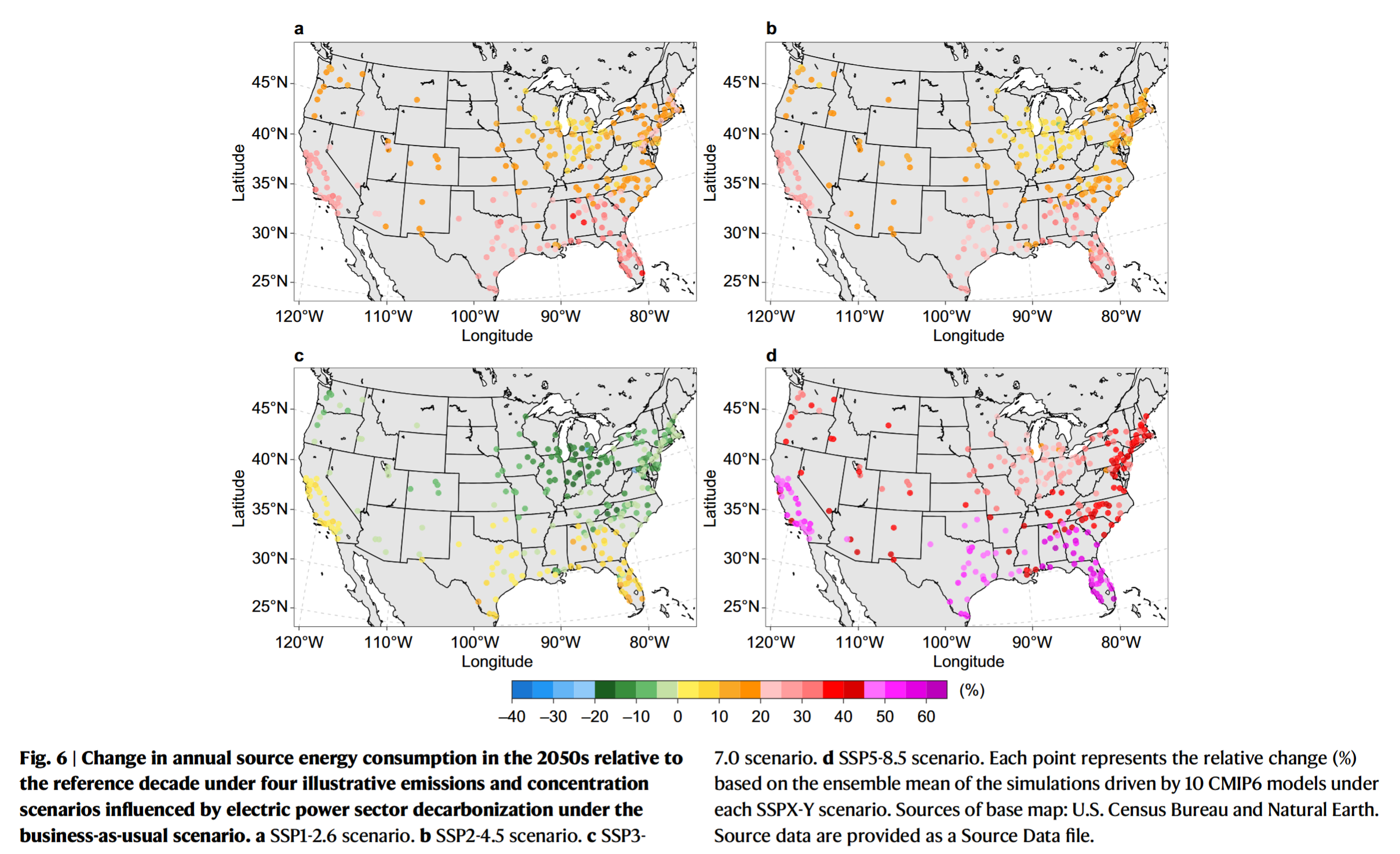
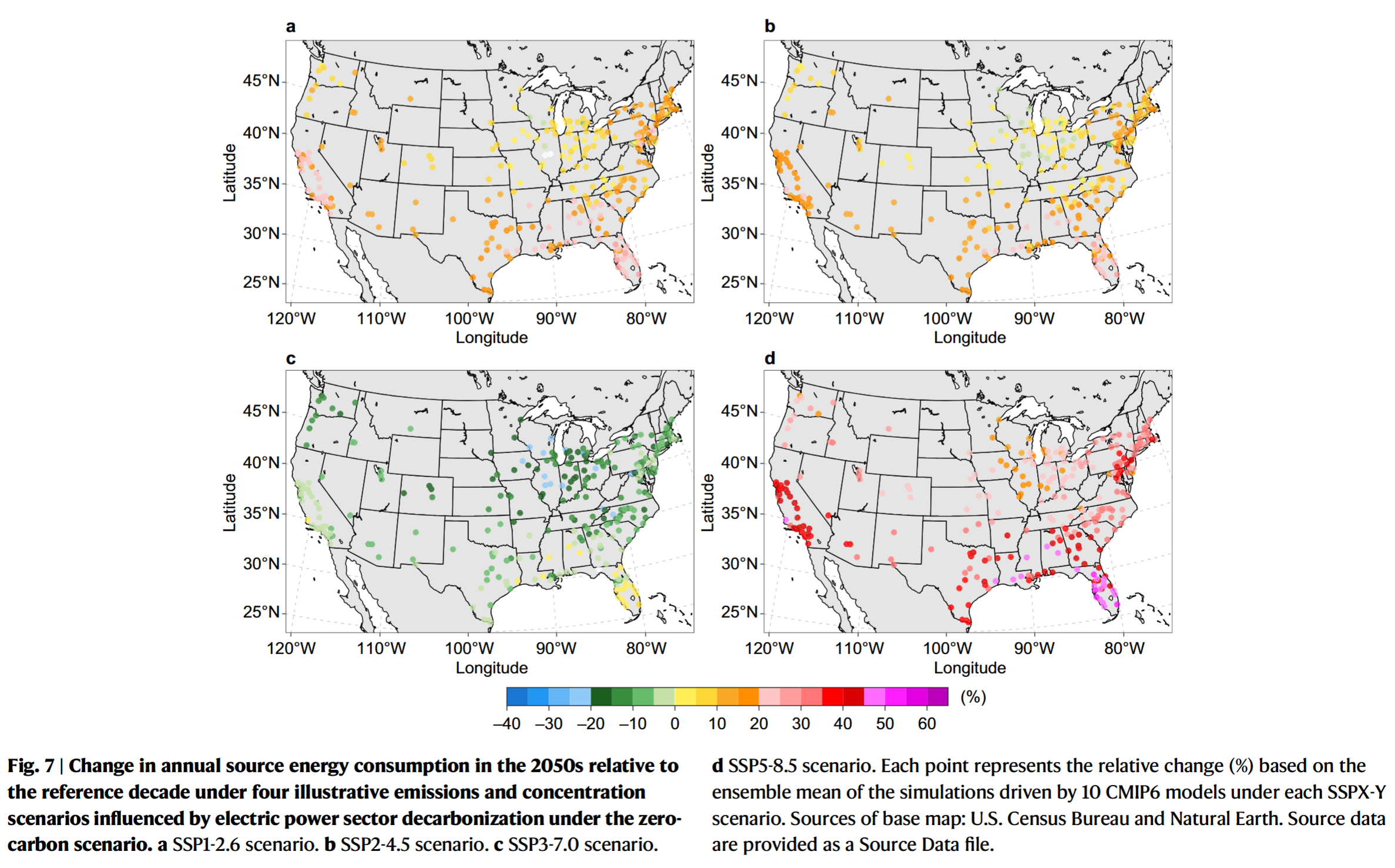
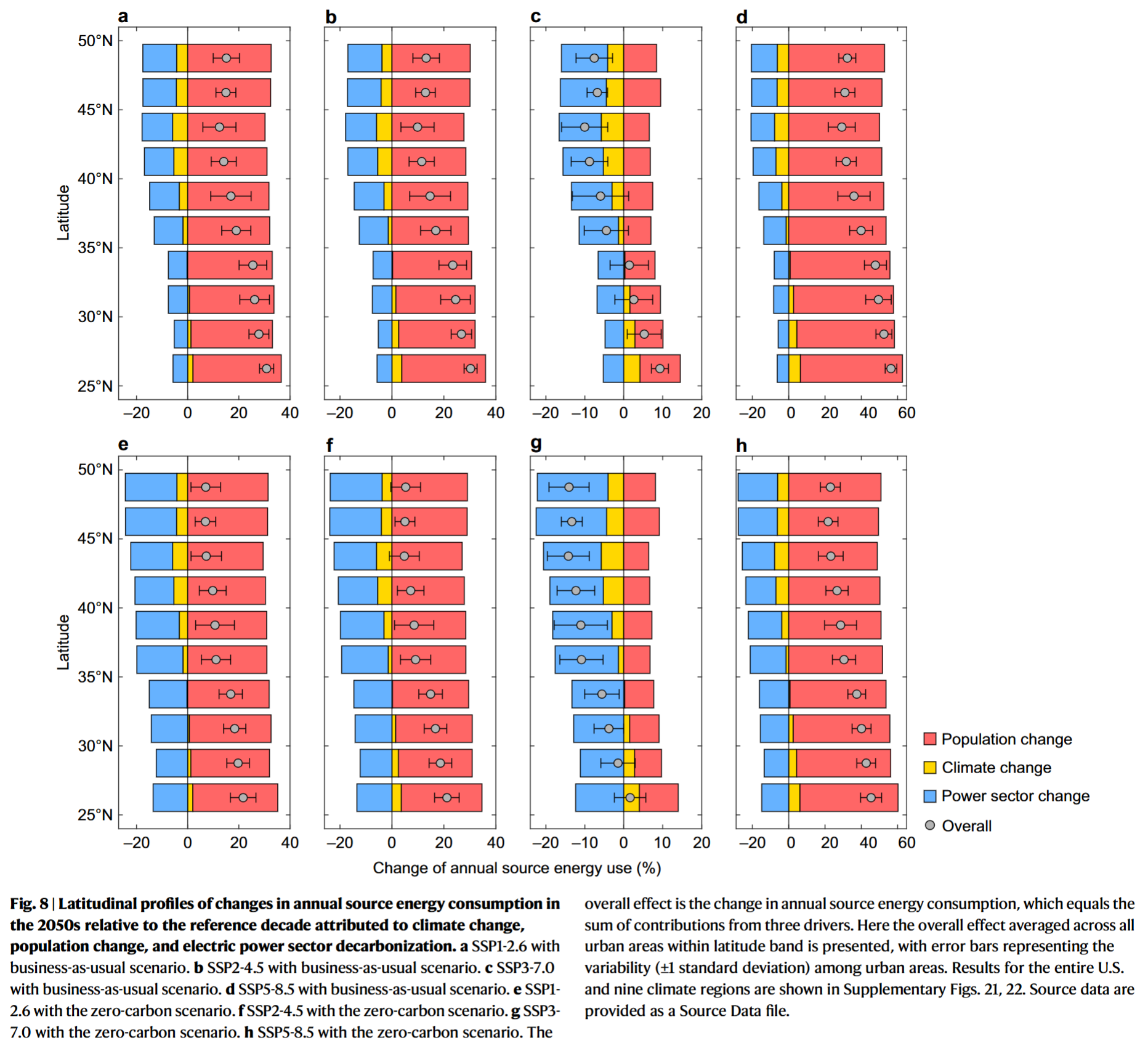
Coding Reference:








