Objective:
- Gain new insight into the response of air quality to Nr emission changes driven by short-term compared to long-term policies and to understand how PM2.5 and N composition are changing under the influence of anthropogenic activities and climate change
Case:
Methodology:
Data Source
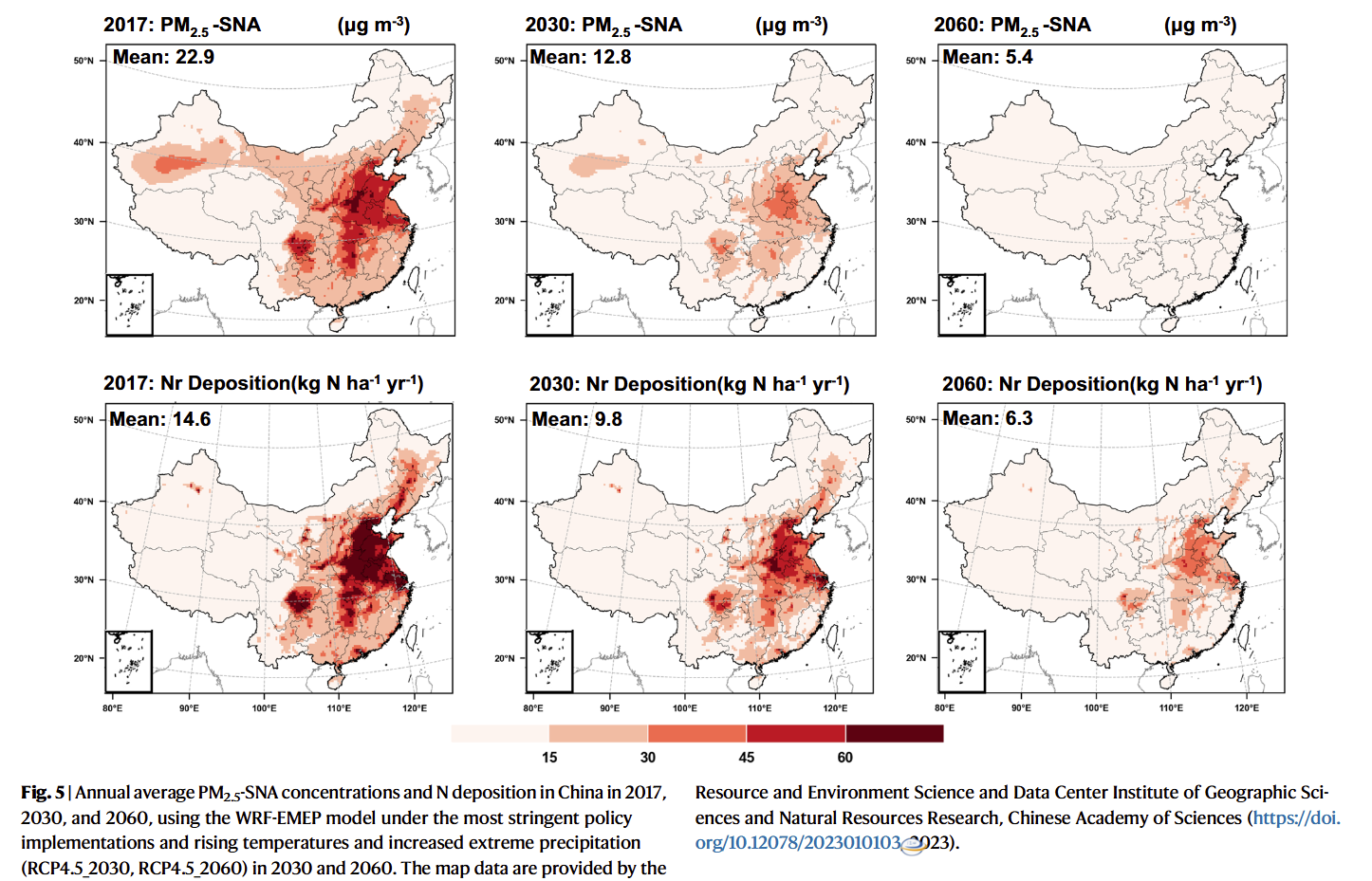
Findings:
- Short-term abatement measures during important international events substantially reduced PM2.5 concentrations, but air quality rebounded to pre-event levels after the measures ceased
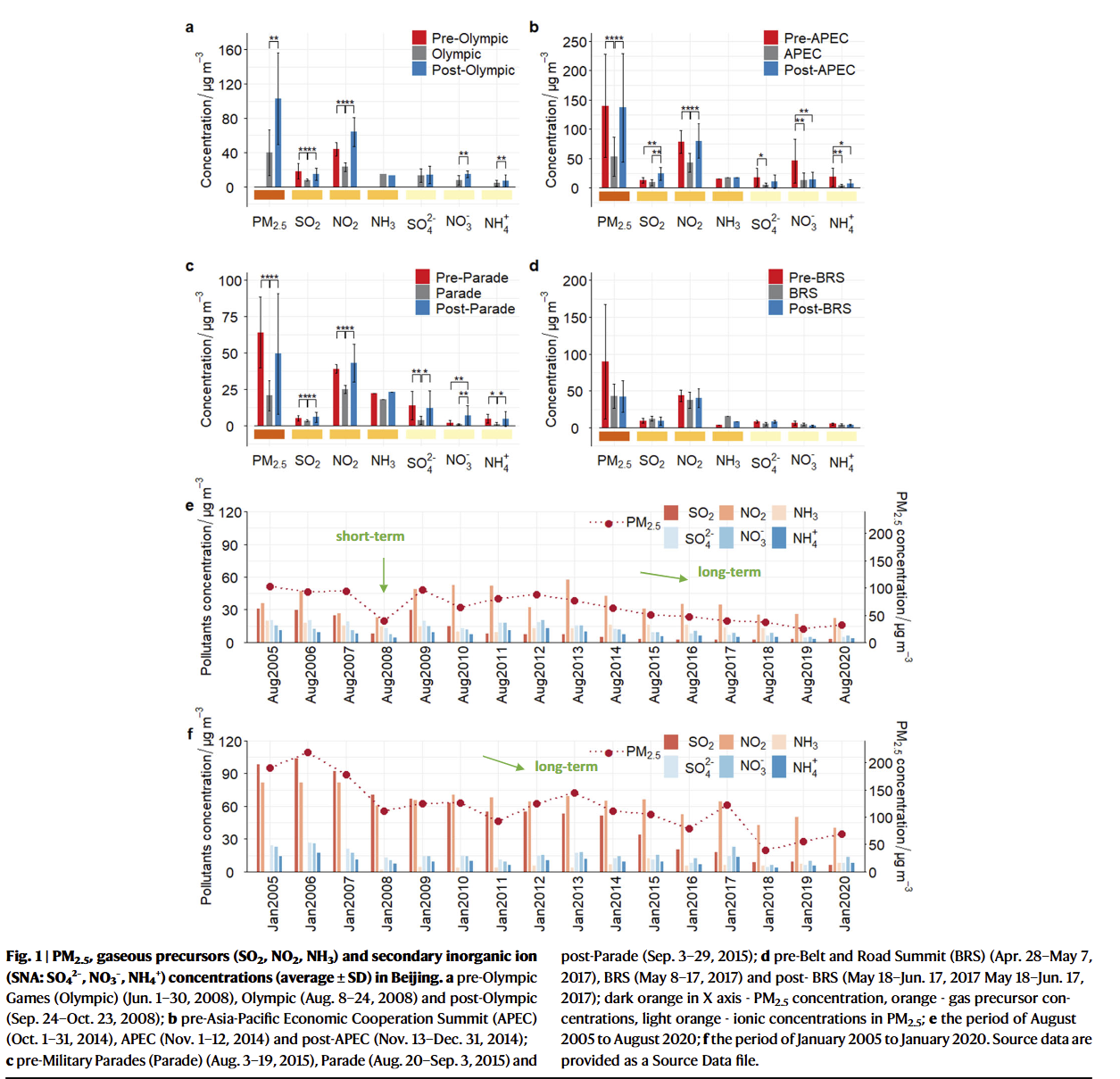
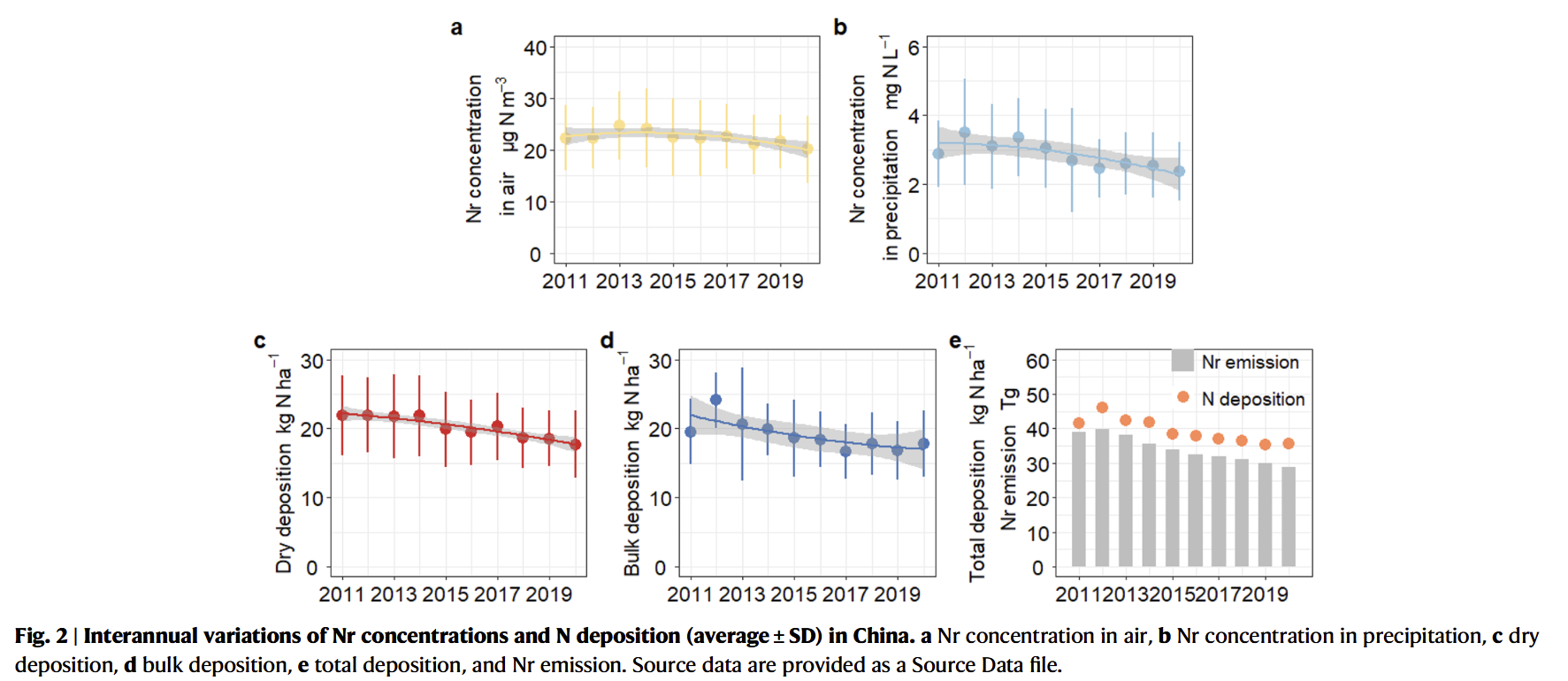
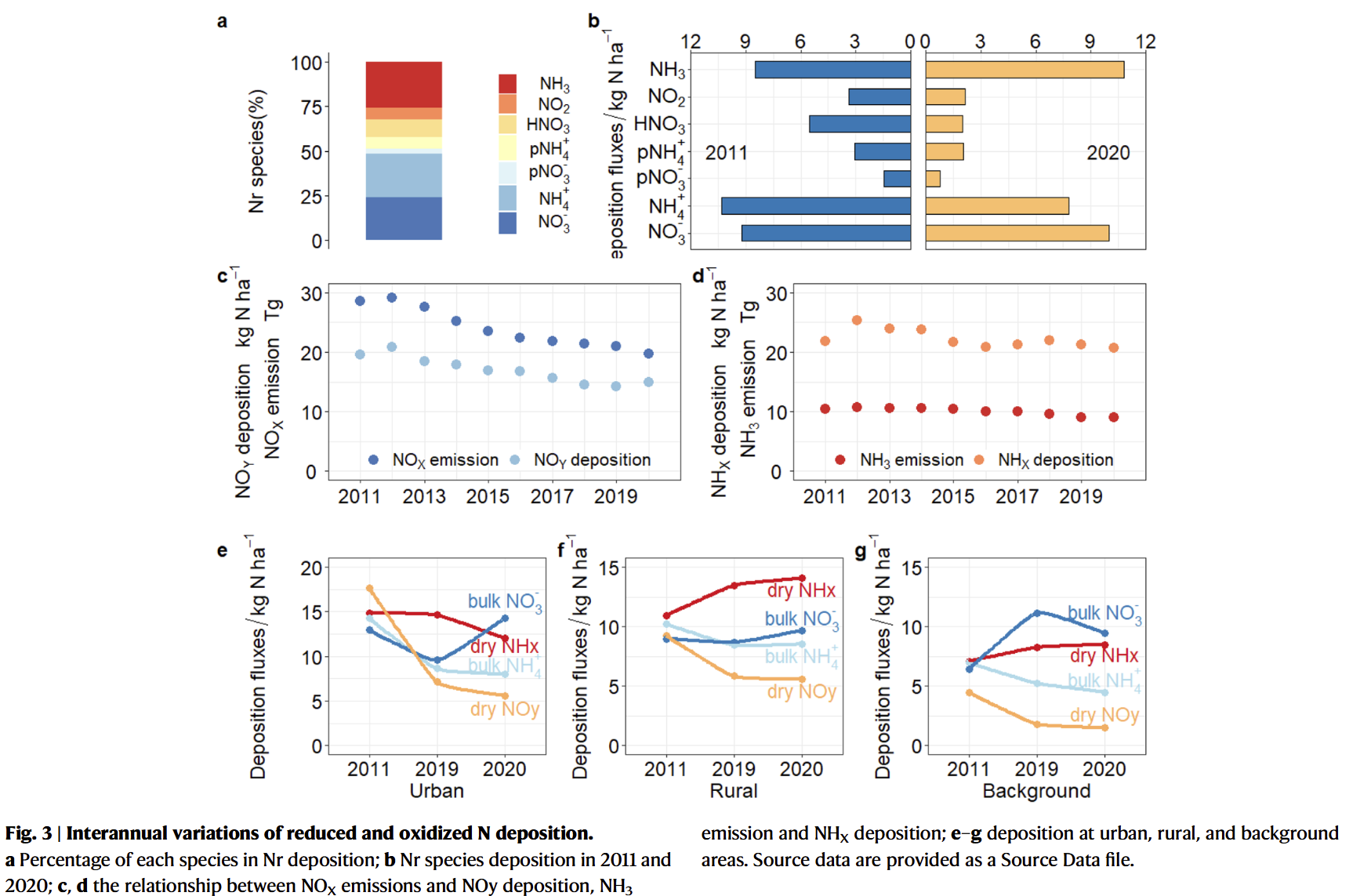
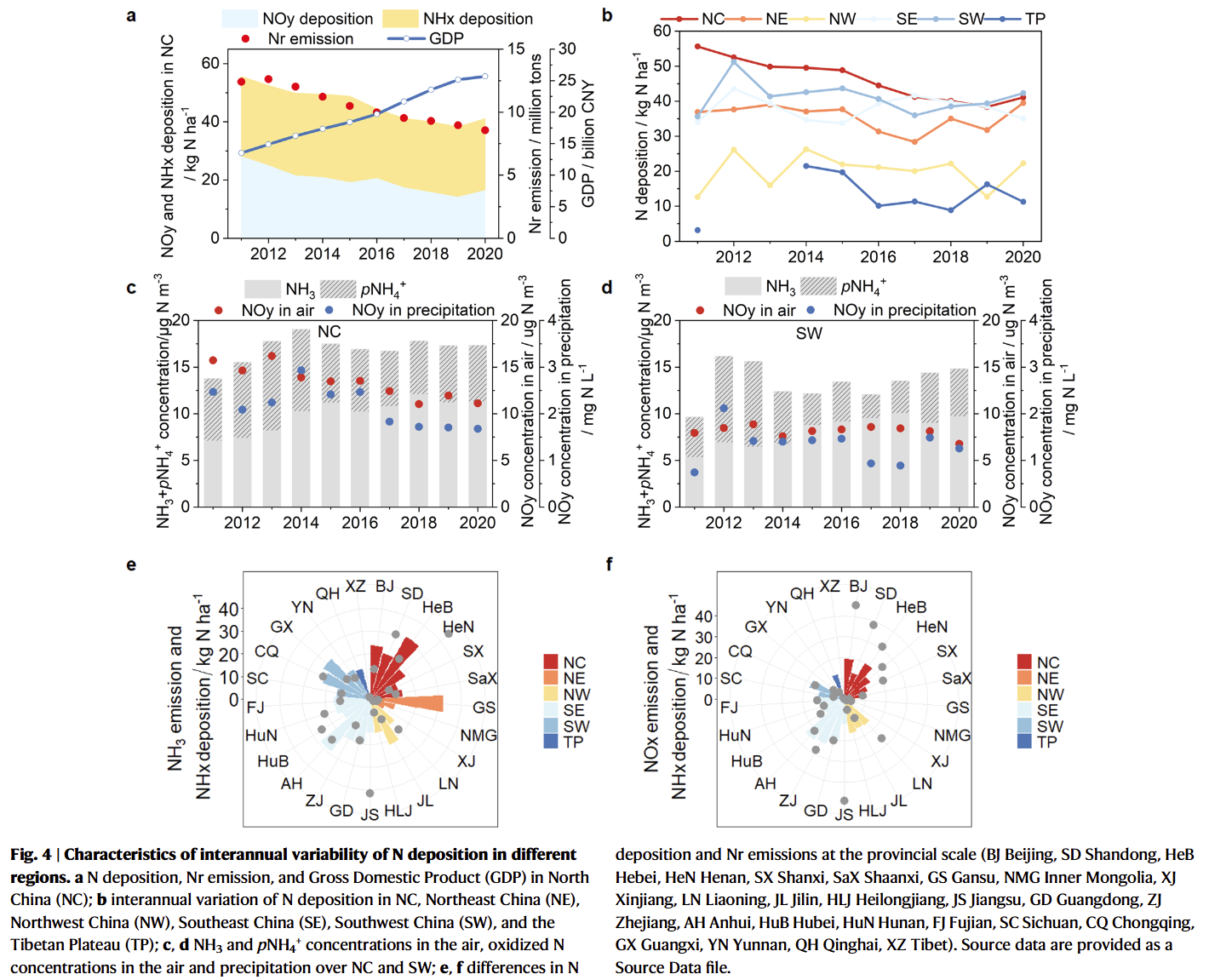
- Long-term adherence to strict emission reduction policies led to successful decreases of 54% in PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing
Coding Reference:





