Objective:
- Understanding the relationships between urban public transport structure and residential density, governed by a scaling relationship with transport accessibility to jobs
- Modifiable areal unit problem (MAUP)
- The more transit services available, the higher the density of the population
Case:
- US census blocks
- 48 major metropolitan statistical areas (MSA)
Methodology:
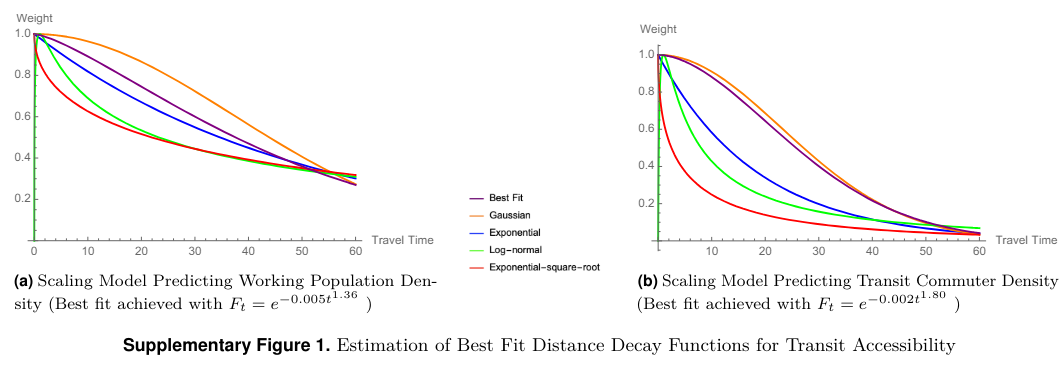
- First: $\rho_w = \beta_0 A_T^{\beta_1}$
- Second: $\rho_r = \rho_w * S_r = \gamma_0 A_T^{\gamma_1}$
- where $S_r$ is the commute mode share, $\rho_r$ is the ridership
- $\gamma_0, \gamma_1$ reflects the returns to scale
- Model fit: $R^2$ (best fits is at 45 minute threshold)
Data Source: Open
- Job accessibility is defined as the number of jobs reachable by PT in a given travel time (Accessibility Observatory)
- US Census Bureau
- American Community Survey
- Employer-Household Dynamics (OD)
Findings:
- Both the total working population and the total transit commuters scales with transit accessibility to jobs
- Transit commuters with lengthy commutes tend to have shorter commute times after residential location change
- Both transit commuters and the working population can be predicted using transit accessibility to jobs
- More accessible job oppotunites is associated with higher residential density
- Transit rider density rises faster than population density with increasing transit accessibility
- Efficiency through scale is more evident for transit rider densities than it is for the working population density
- Auto-user density declines at high transit accessibility.
- Larger cities have a greater transit ridership return on accessibility than smaller cities
- Historical city size affects the scaling coefficients
- Transit accessibility expansion induces further transit use and land-use intensification
- Similar observation for inetrcity scaling
Coding:

