Objective:
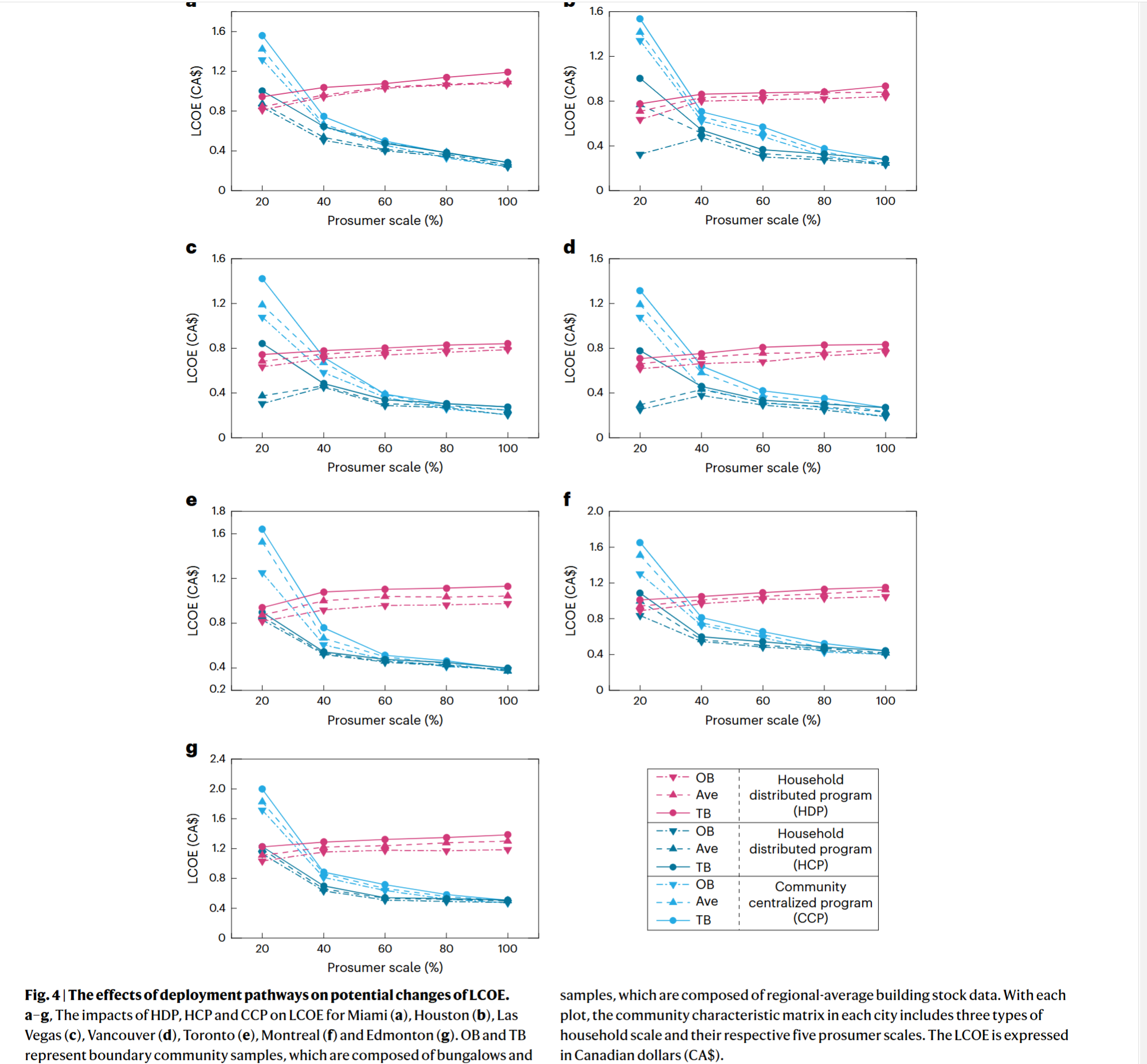
- Introduce a bottom-up energy model linking climate, human behaviour, community archetypes and energy system models, aiming to ensure cost-effective deployment pathways of community green hydrogen systems for highly diverse urban residential communities
Case:
Methodology:
- Bottom-up energy model (Climate-human model)
Data Source
Findings:
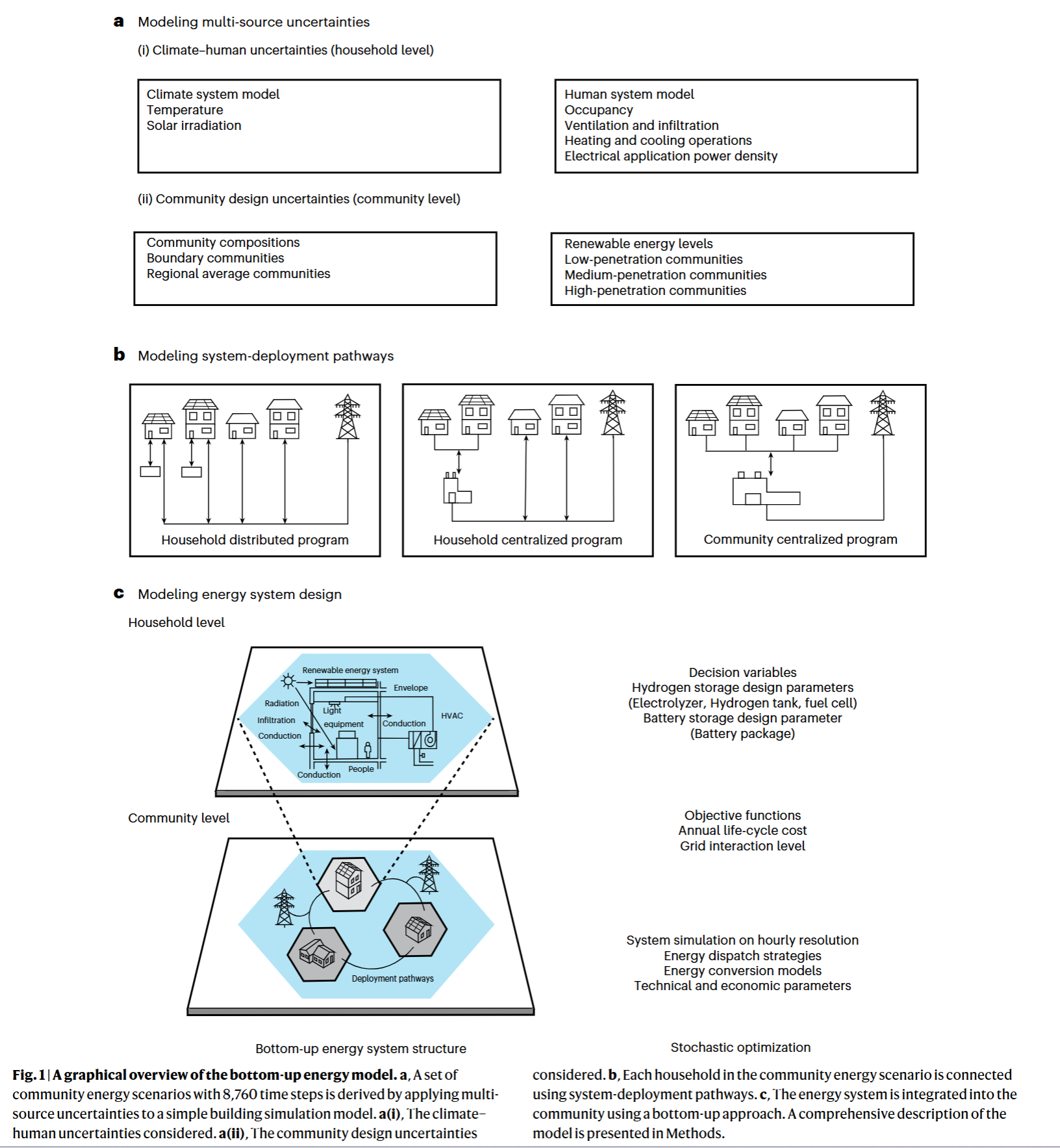
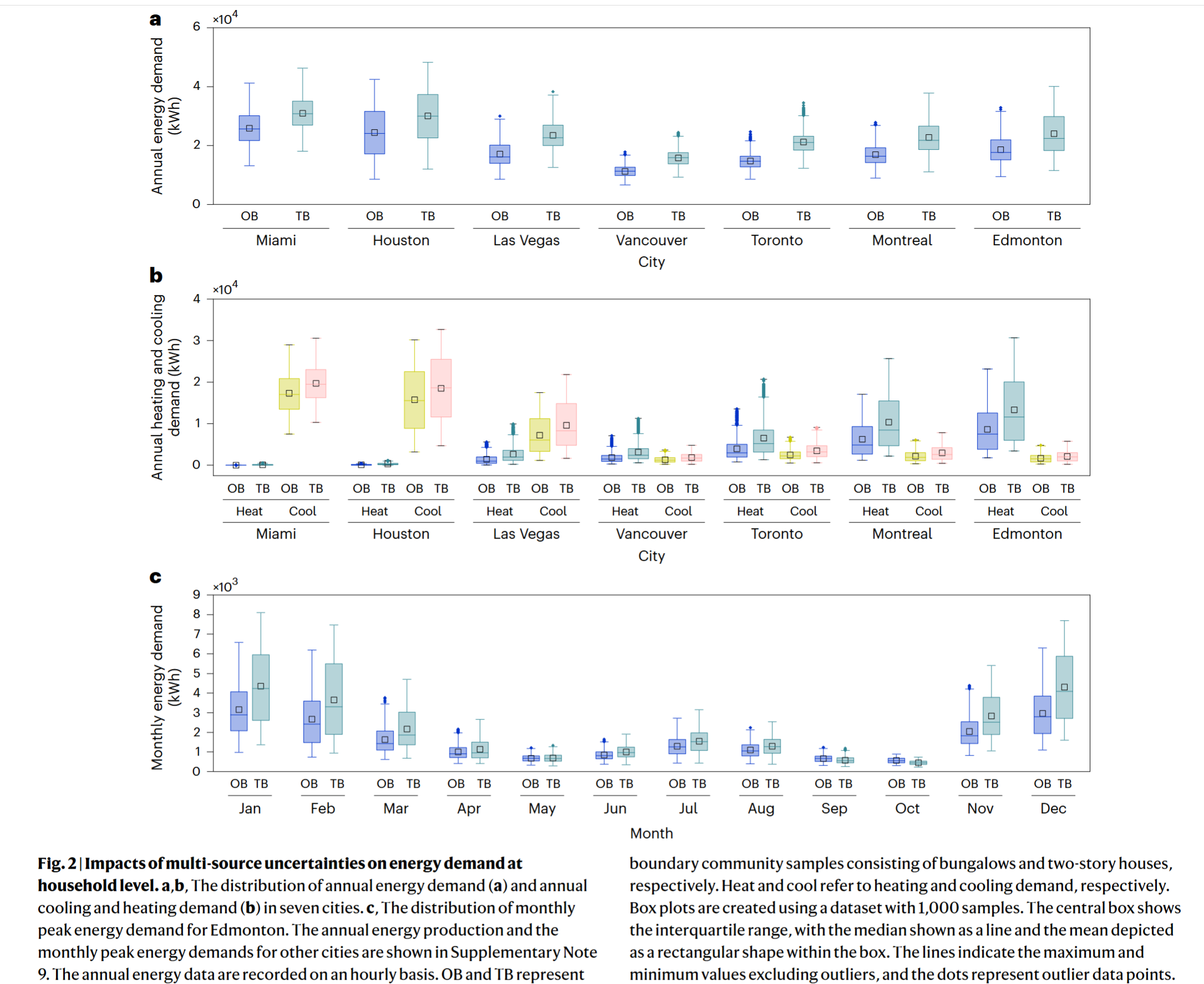
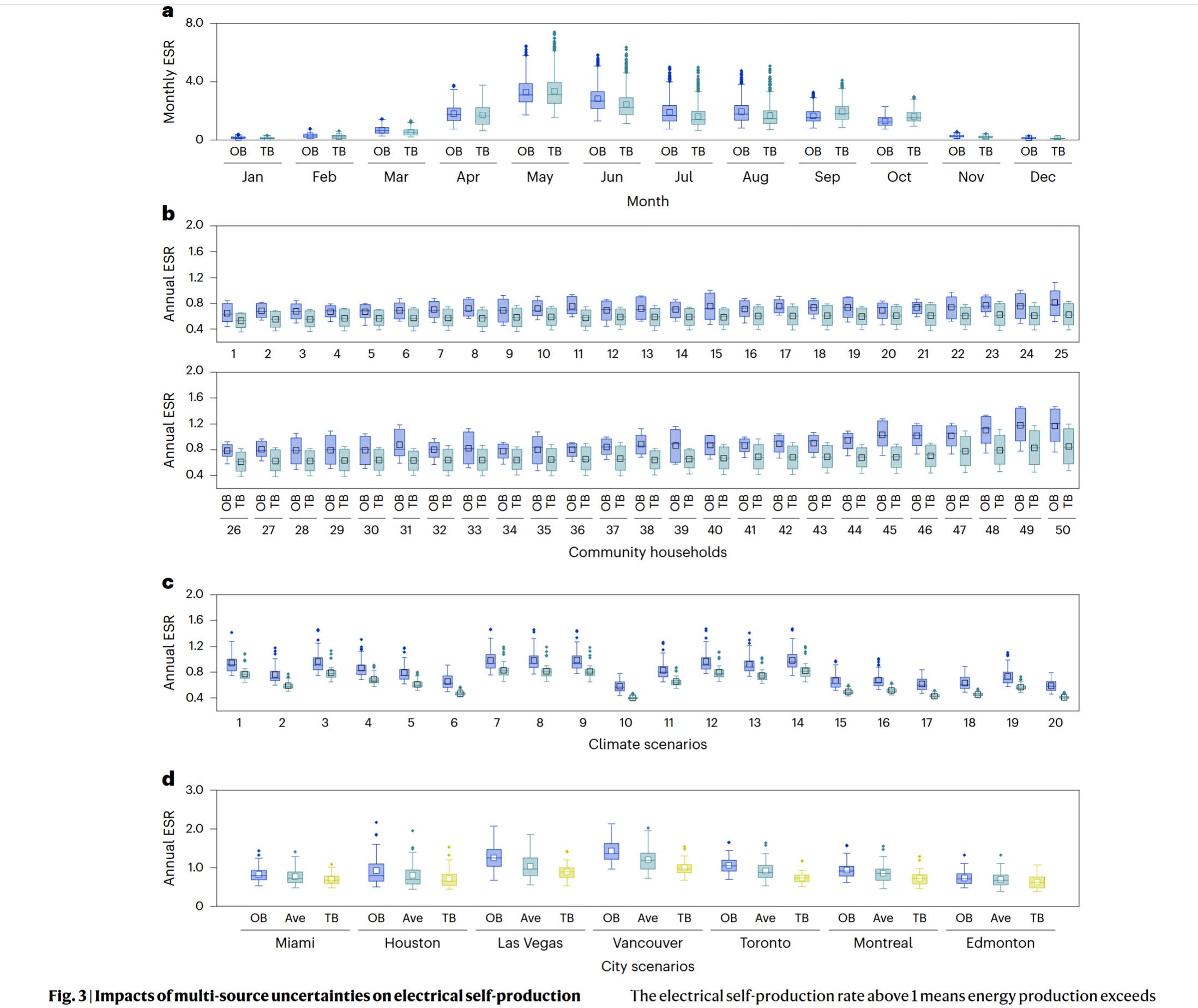
- Climate and human uncertainties show a more uneven and significant effect on the energy demand side rather than on the energy production side
- Cities in higher tiers exhibited higher HUEs, which a decrease as the tier lowered
- Cities in the southeastern coastal area of China featured the highest HUEs
- Subdistricts located in the center layer generally featured the lowest average HUEs across China; with an increase in spatial distance to the city center
Coding Reference:





