Objective:
- Estimate the spatial and temporal patterns of deaths attributable PM2.5 air pollution (DAPP) based on the CMIP6 dataset, provincial-level disease mortality data and decomposition analysis
Case:
Methodology:
- Comparable risk assessment framework: population attributable fraction
- GBD model
- Decomposition analysis
Data Source
- Global PM2.5 assessment dataset
- CMIP6
- SSP
Findings:
- Population-weighted PM2.5 concentration in China increased by 43.8% from 2000 to 2019
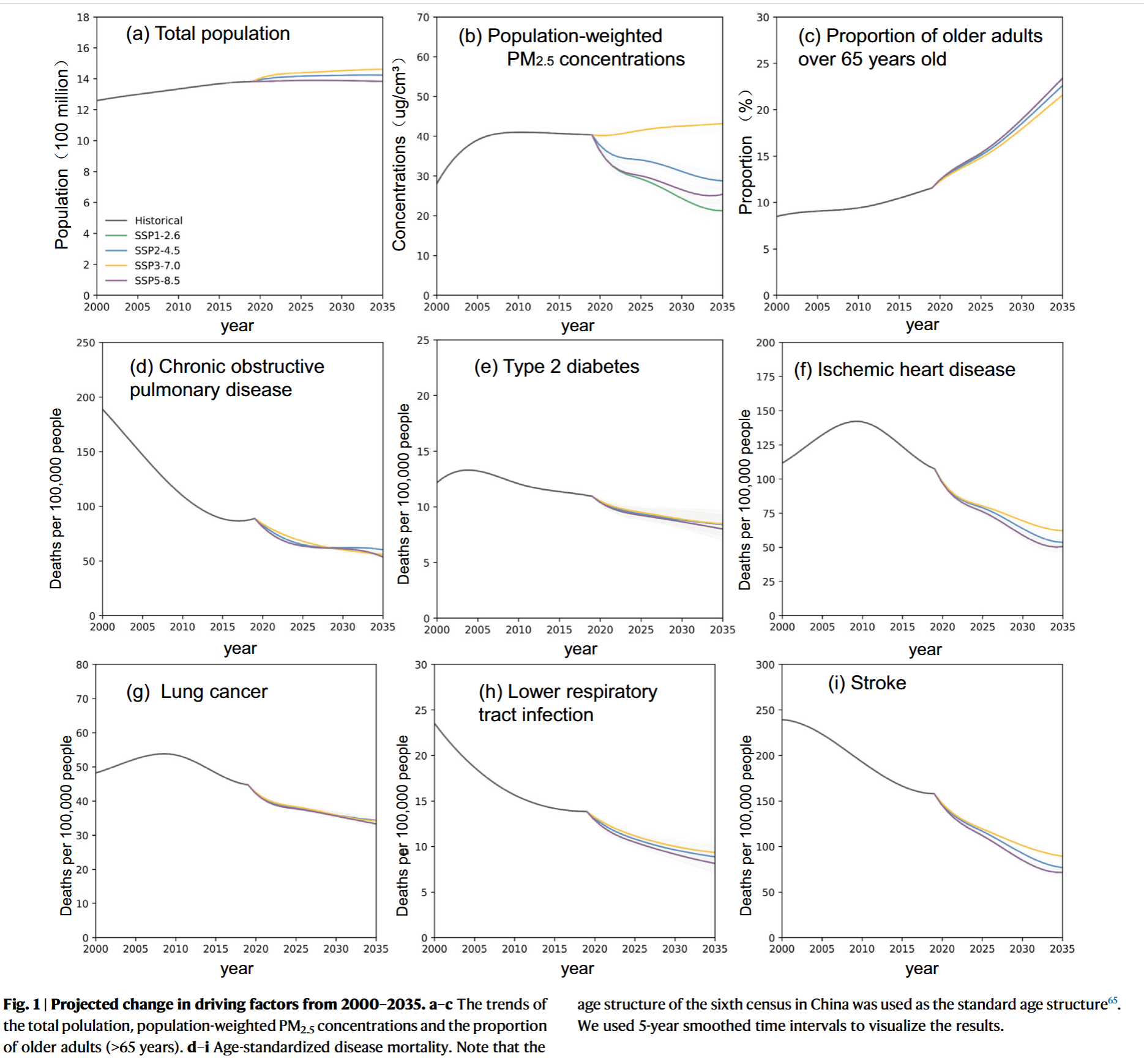
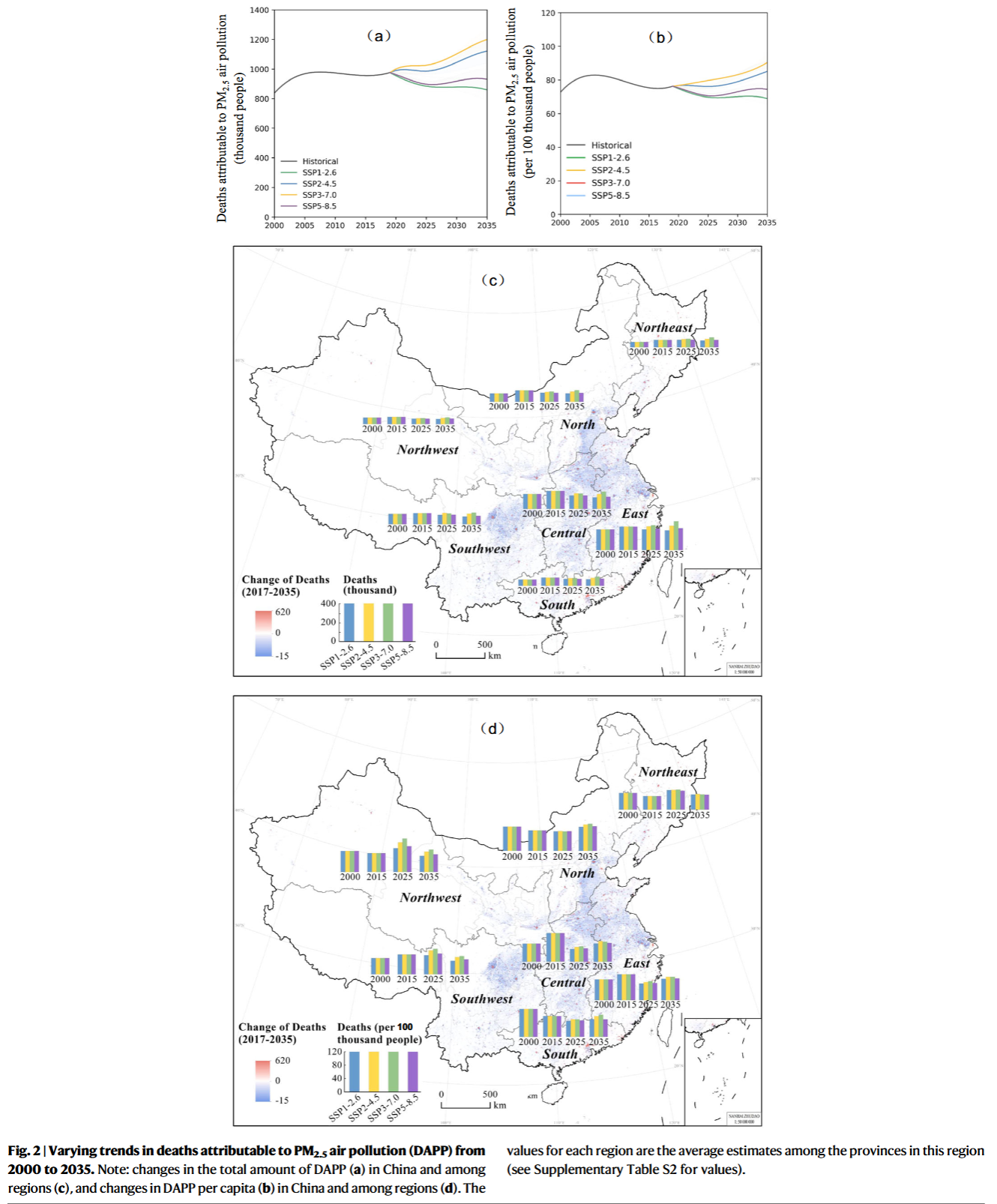
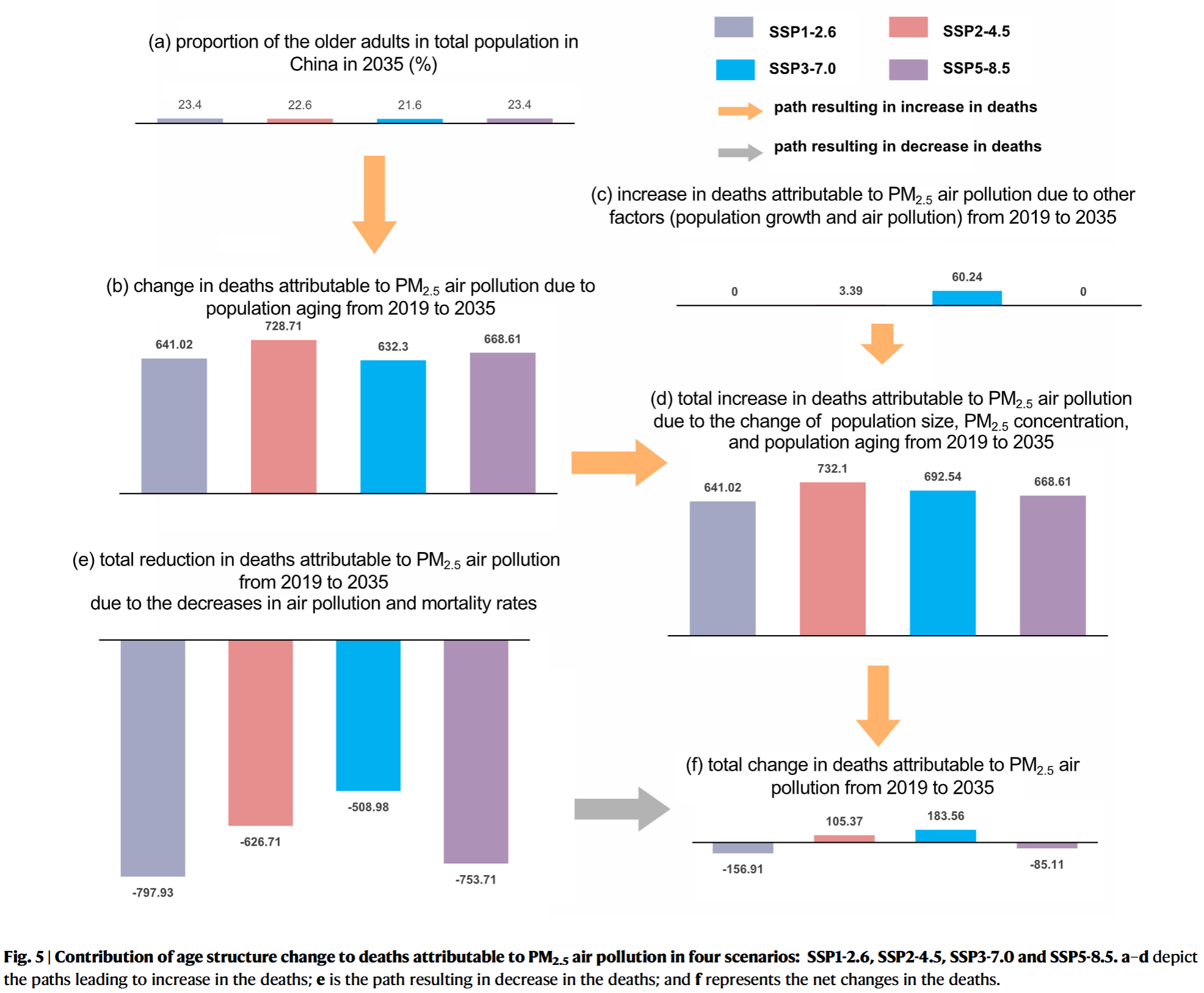
- From 2019-2025, annual DAPP under most scenarios was projected to decline
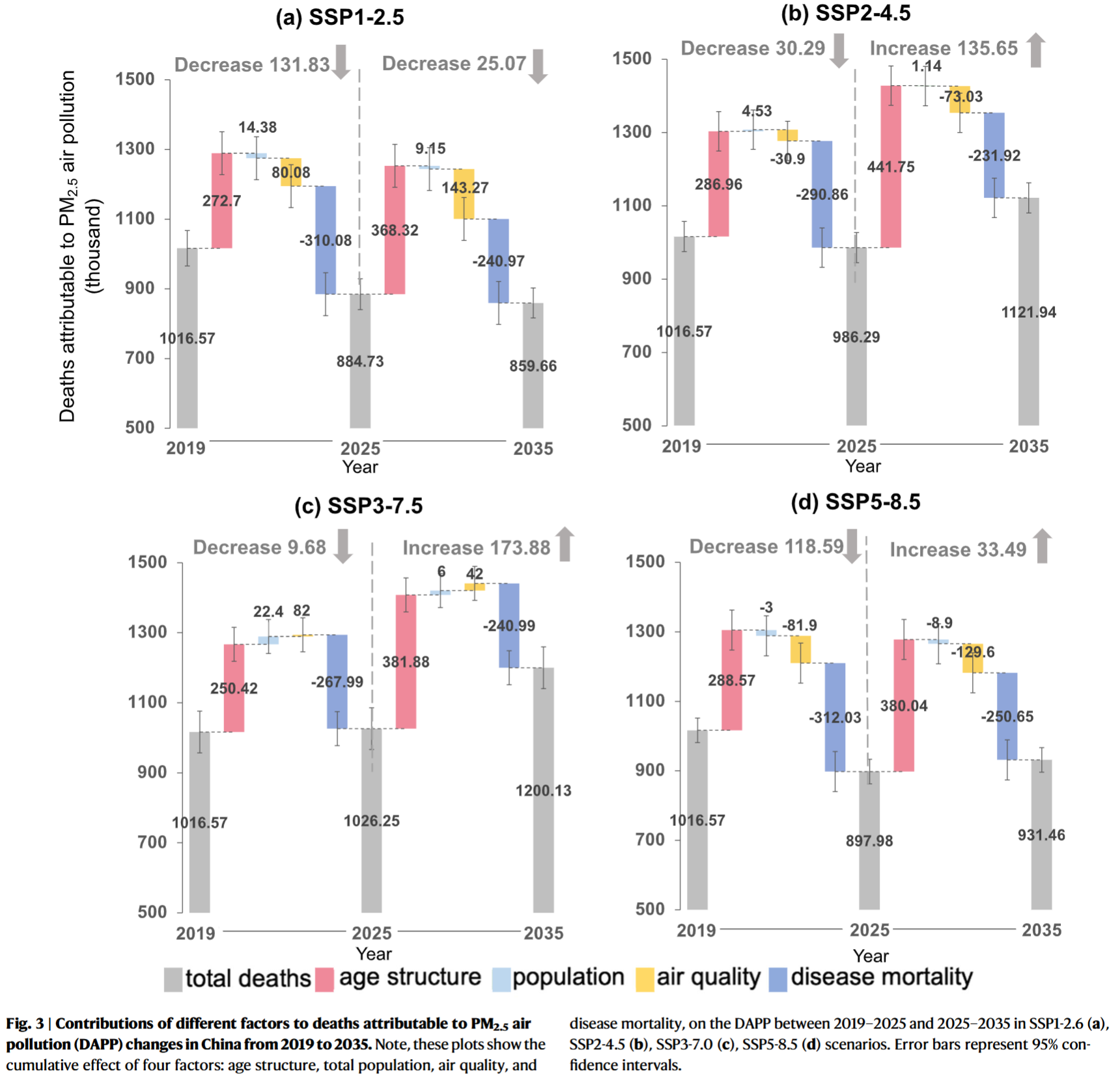
- Population aging was the only factor contributing to the growth of DAPP
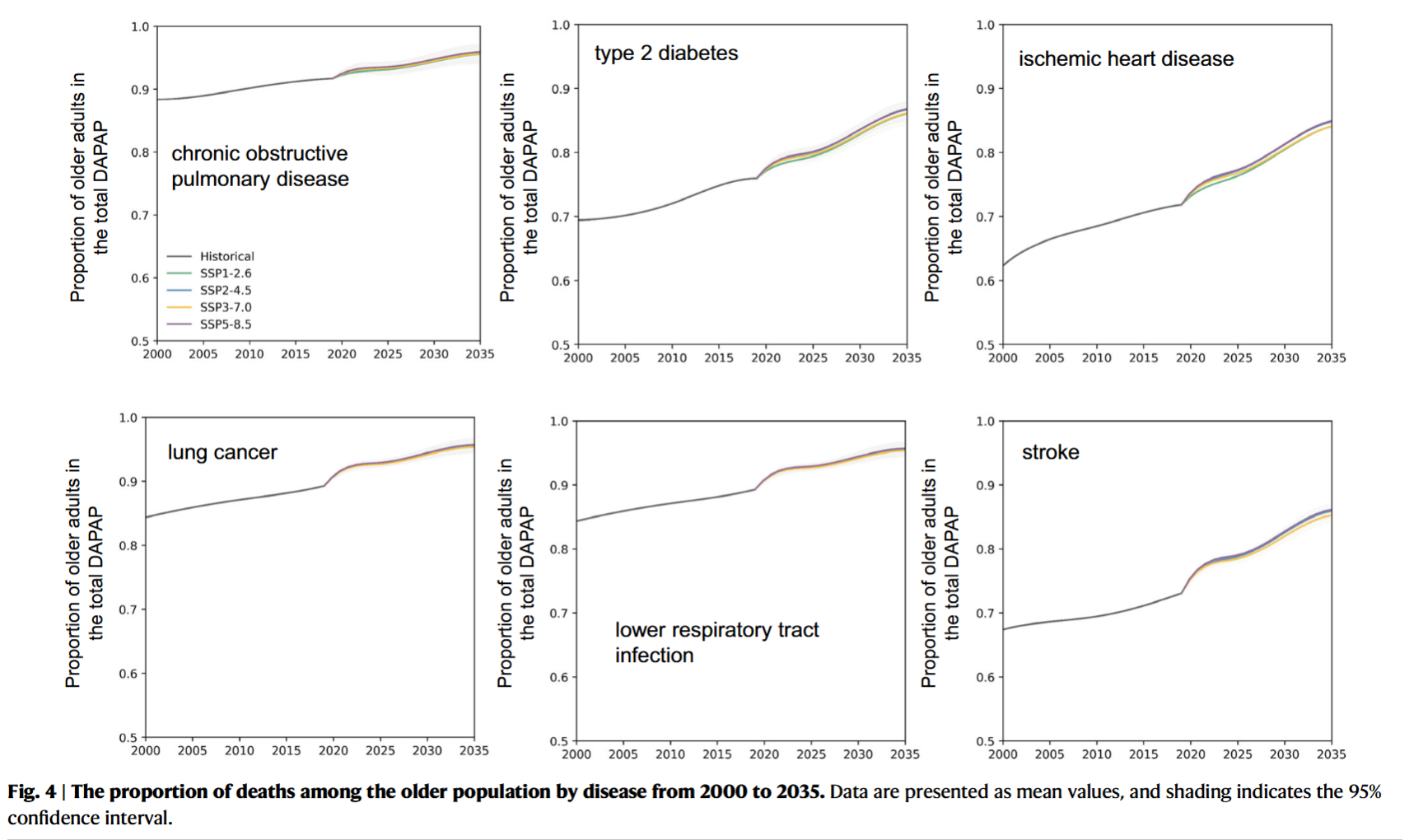
- The older individuals are still the most susceptible group
Coding Reference:





