Objective:
- Analyze the patterns and trends of how the growths in economic wellbeing and trade activities of APAC affected the environmental-social-economic footprints
Case:
Methodology:
Data Source
- MRIO: EXIOBASE
- Emissions and employment
Findings:
- While the footprints of lower-income countries increased with poverty alleviation, most of them are still below the global averages by 2015
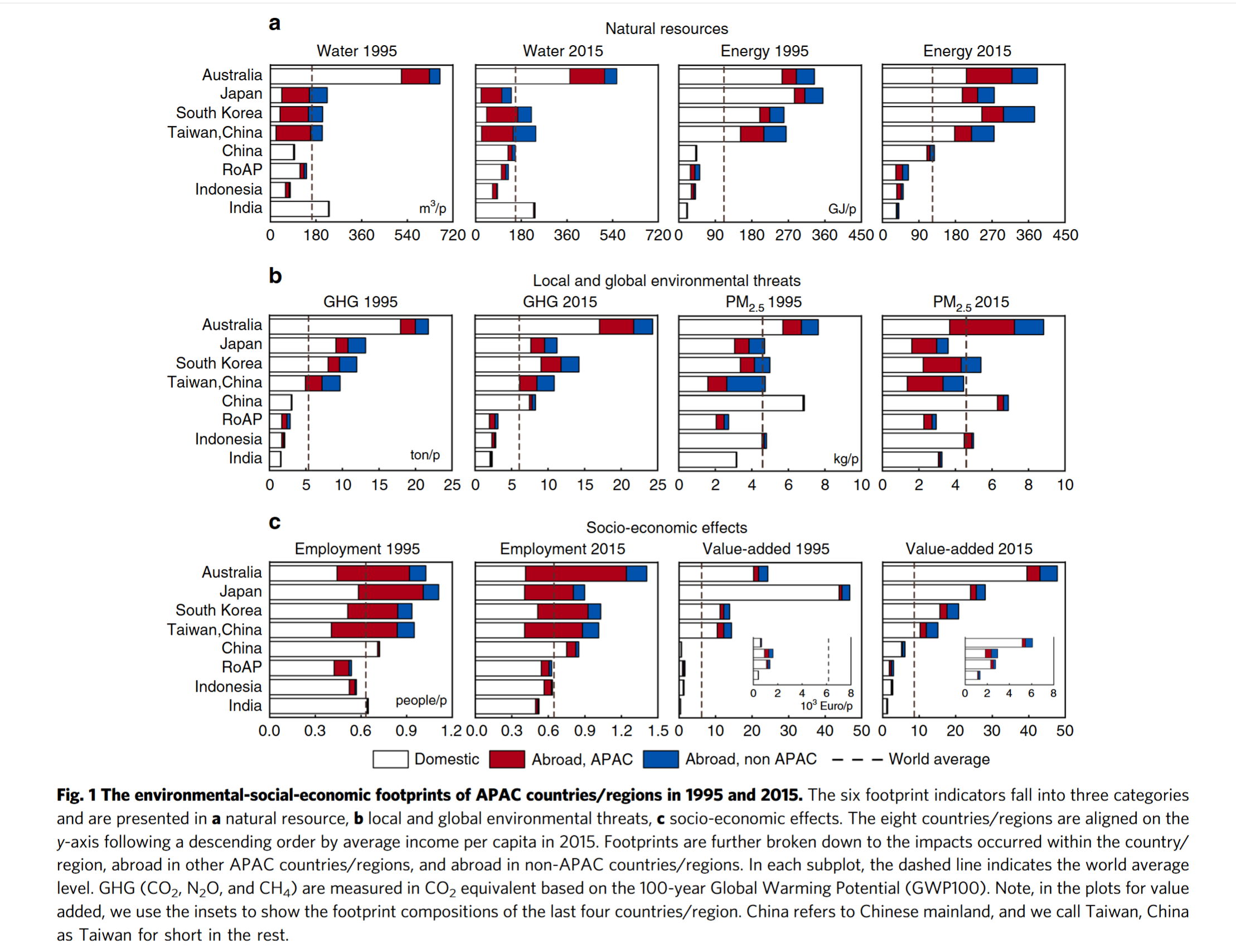
- Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis: environmental pollution first rises and then falls as economic development
- A country/region’s employment and value-added footprints are both positively correlated with its affluence level
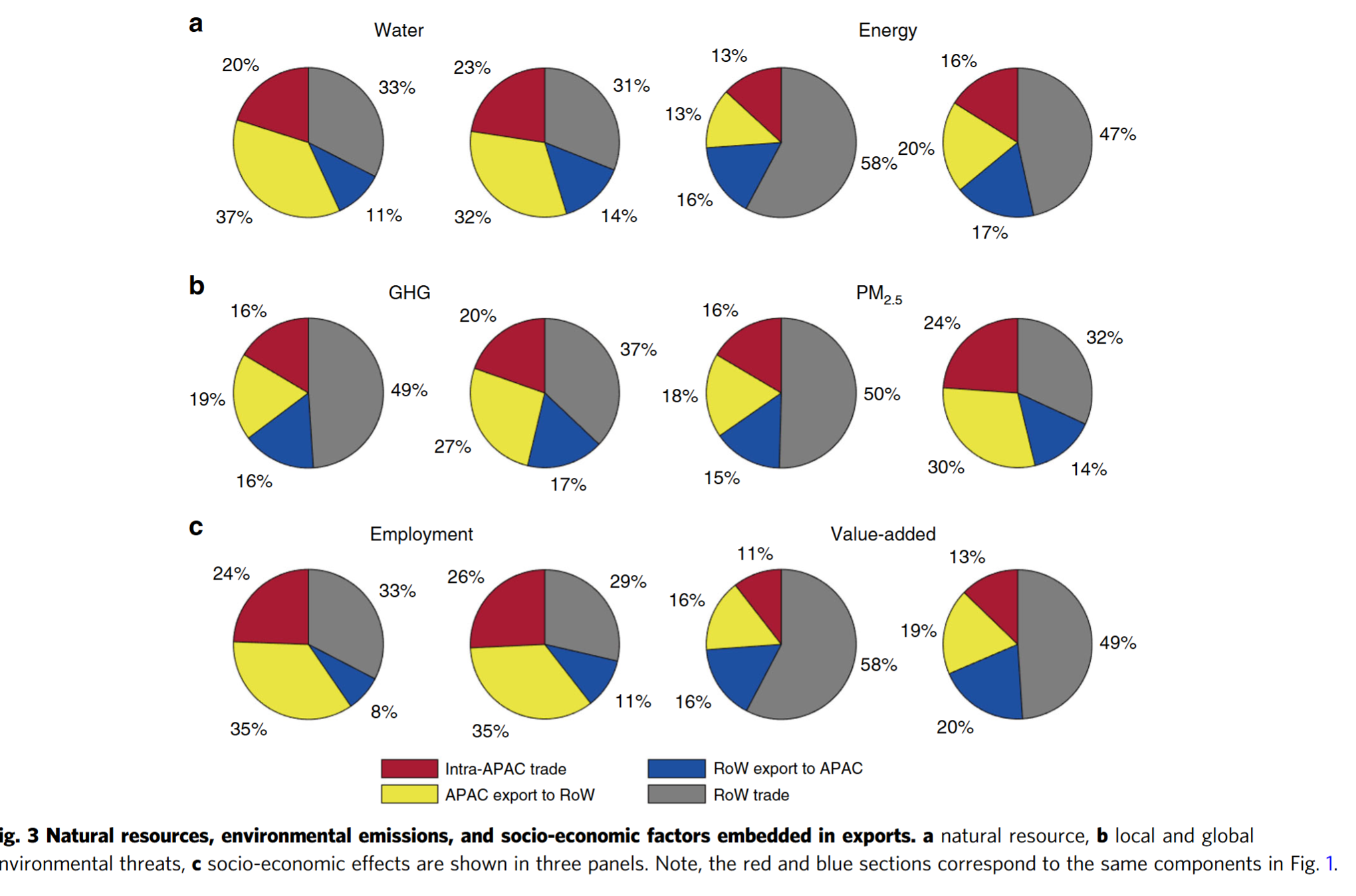
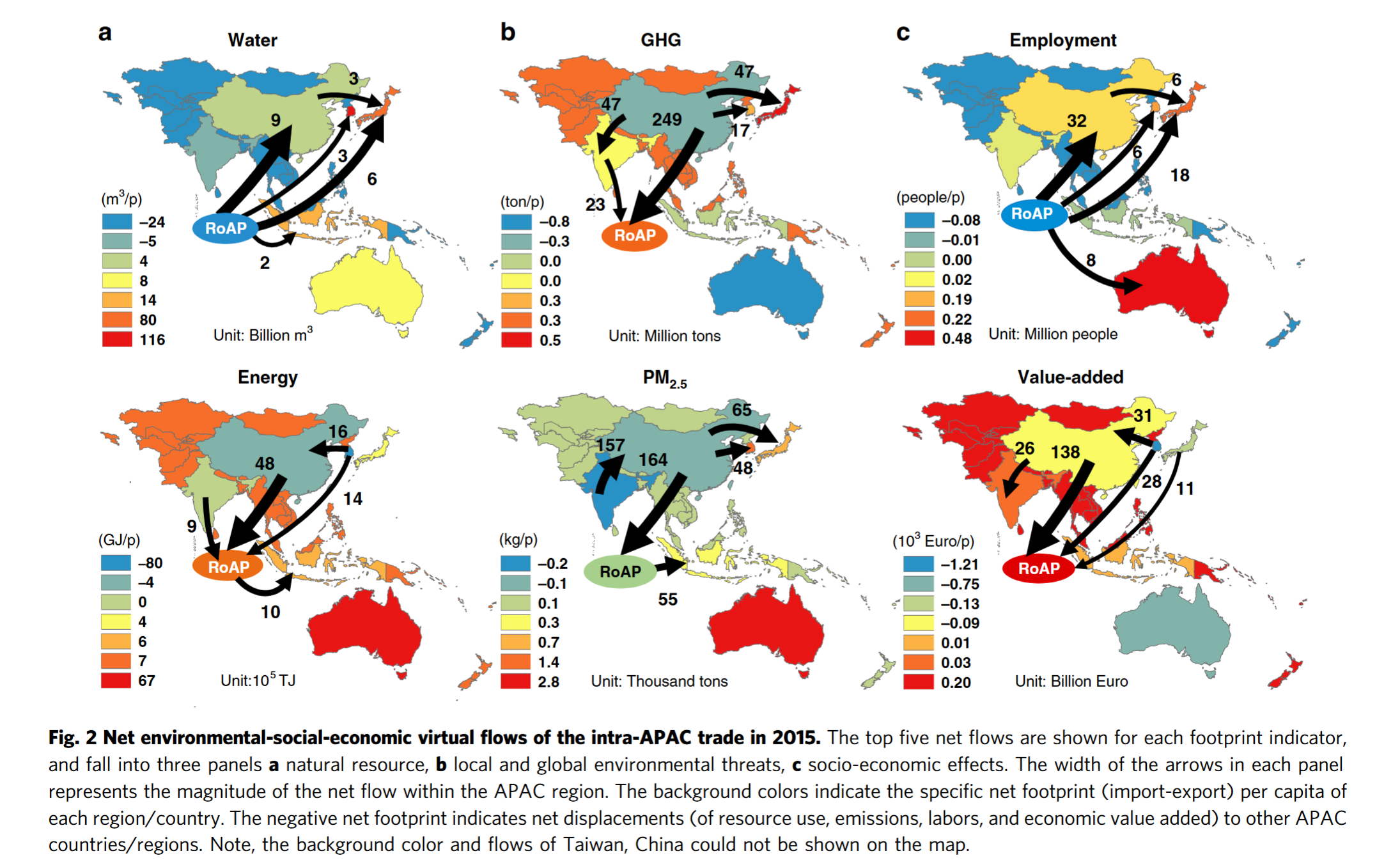
- Richer economies showed high and increasing reliance on outsourcing blue water consumption, PM2.5, and labor abroad
- Final demand of middle- to low-income economies has been largely satisfied by domestic natural and labor sources
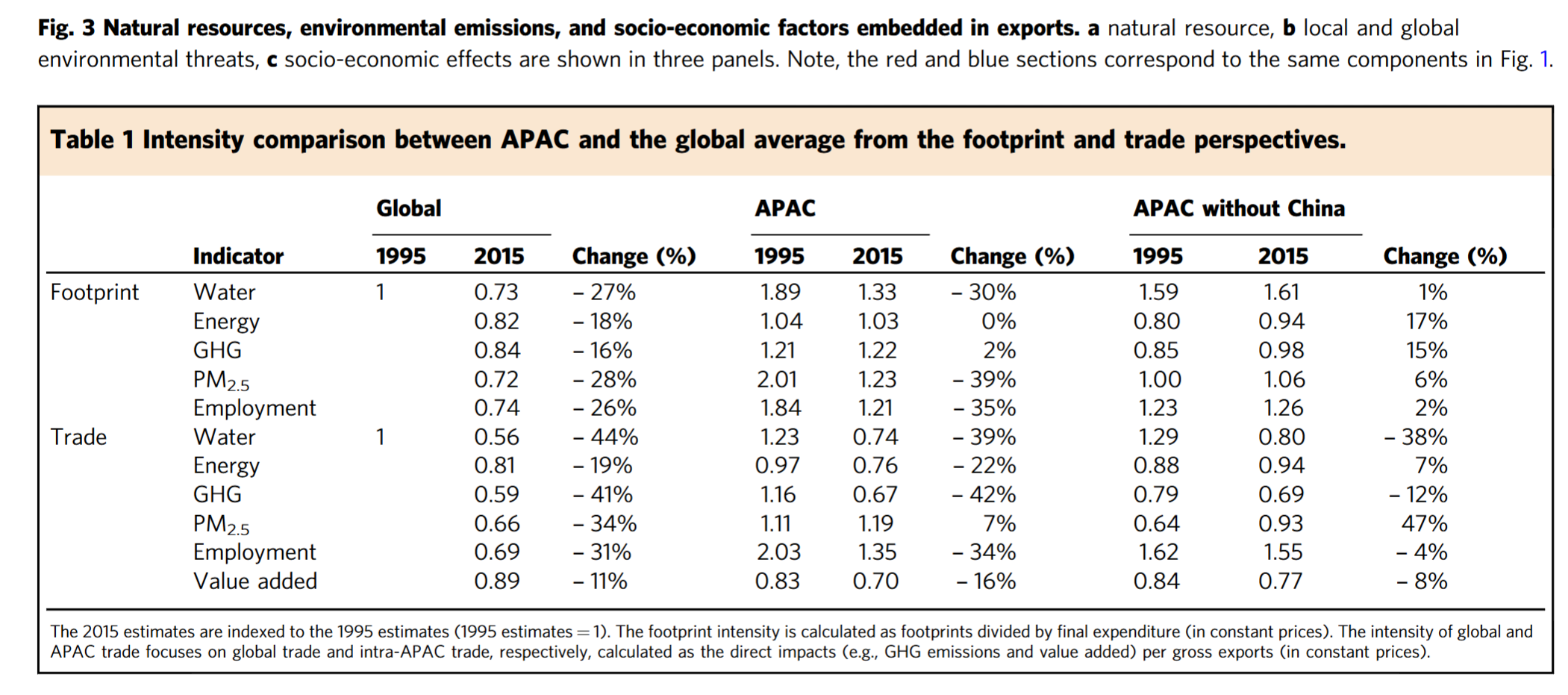
Coding Reference:




