Objective:
- No comprehensive global analysis of emissions from both agriculture and land-use change
Case:
Methodology:
Data Source
Findings:
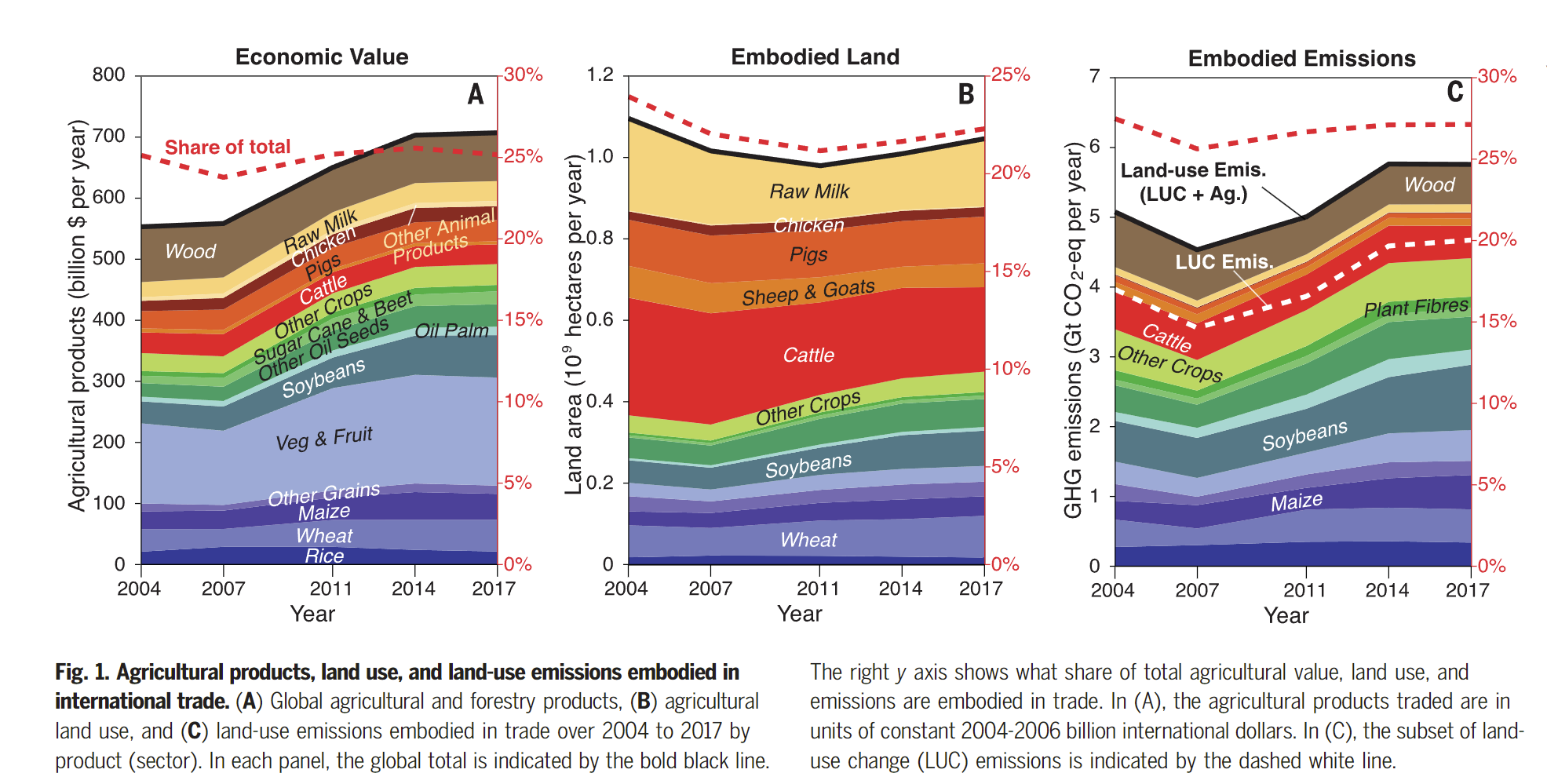
- ~22% of agricultural land were used for traded agricultural products
- A ~27% land-use emissions are embodied in international trade
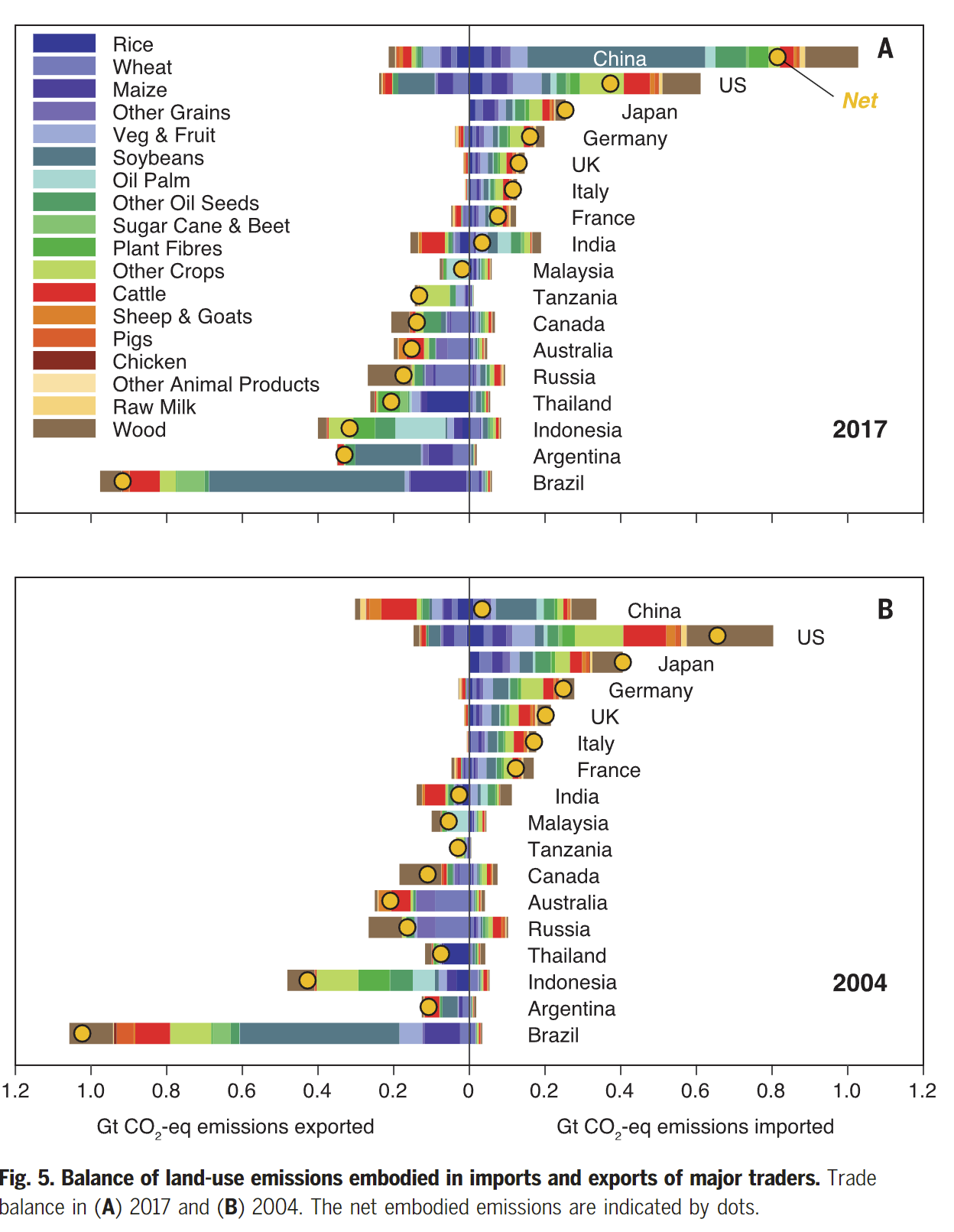
- The dominant global feature of embodied land-use emissions are large exports of emissiosn from countries such as Brazil, Indonesia, Argentina, Austrilia and Canada to consumers in developed regions such as the US, Europe and Japan
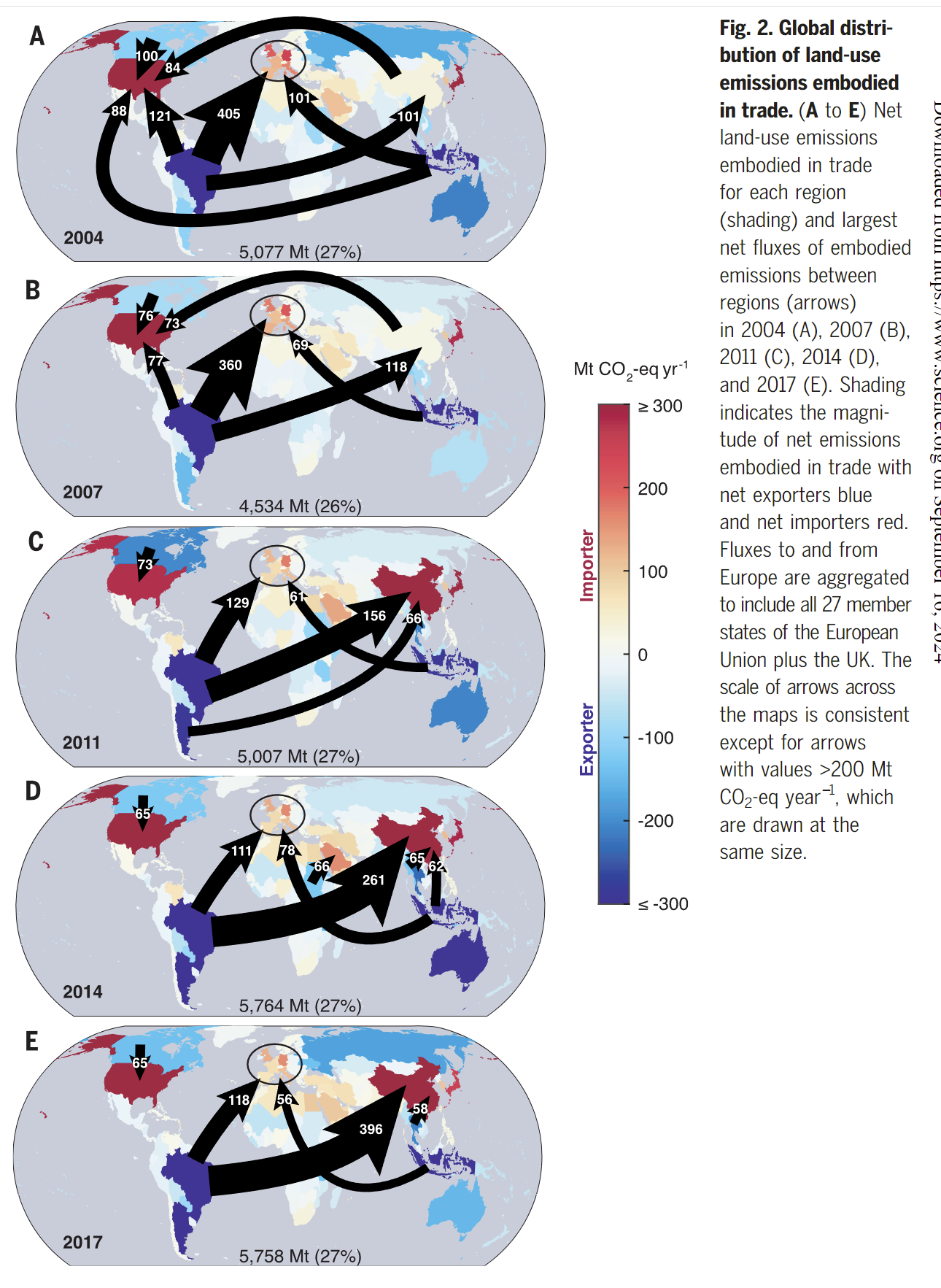
- Of the total global embodied land-use emissiosn, 75 to 81% are related to land-use change
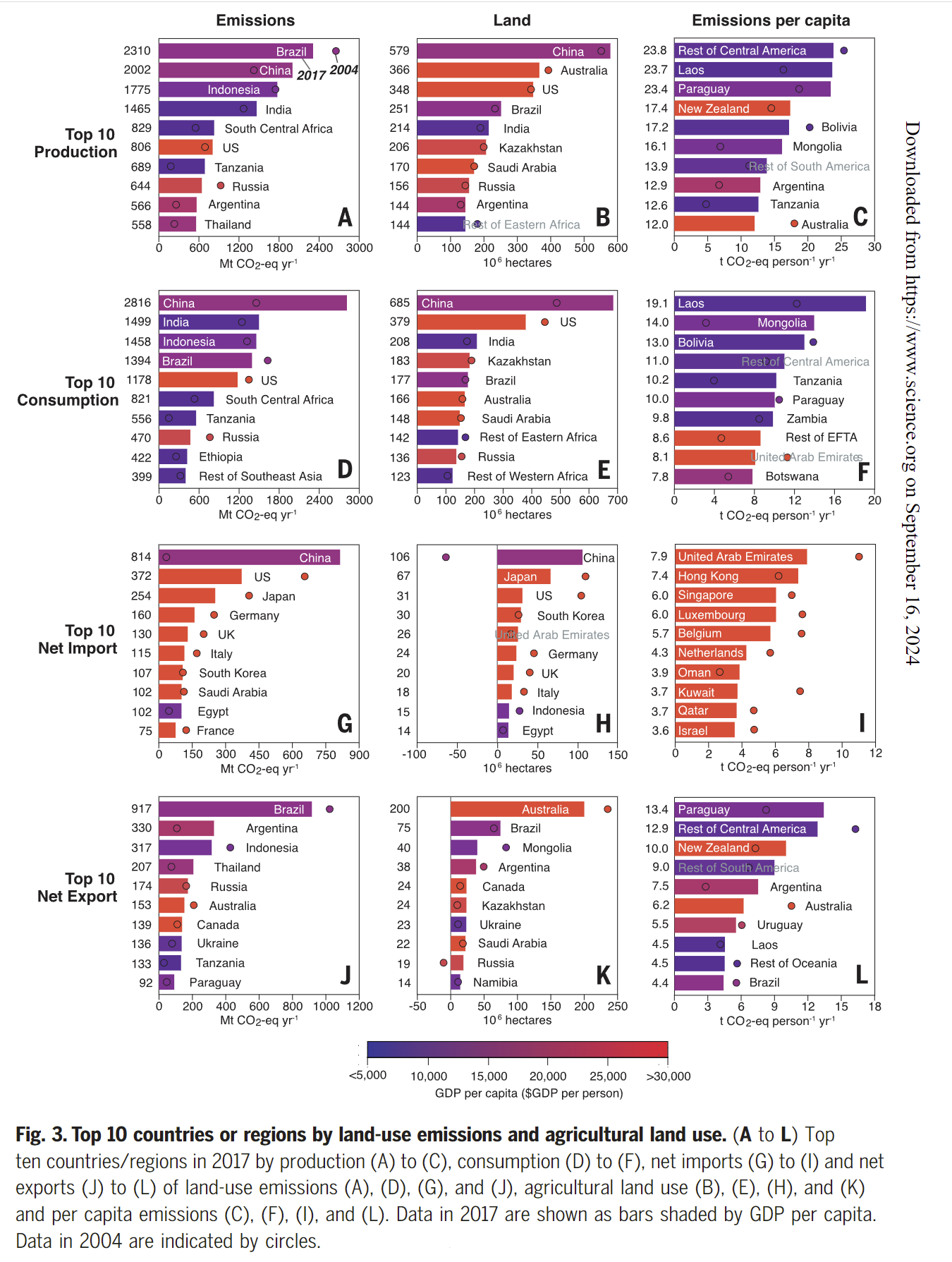
- Brazil was the largest net exporter of land-use emissions in 2017, followed by Argentina, Indonesia, Thailand, Russia and Austrilia.
- The largest net importer of land-use emissions in 2017 was China, followed by the US, Japan, Germany, the UK, Italy, South Korea and Saudi Arabia
- Exports from Brazil, Indonesia, Argentina, Australia, Thailand and Tanzania are particularly emission-intensive
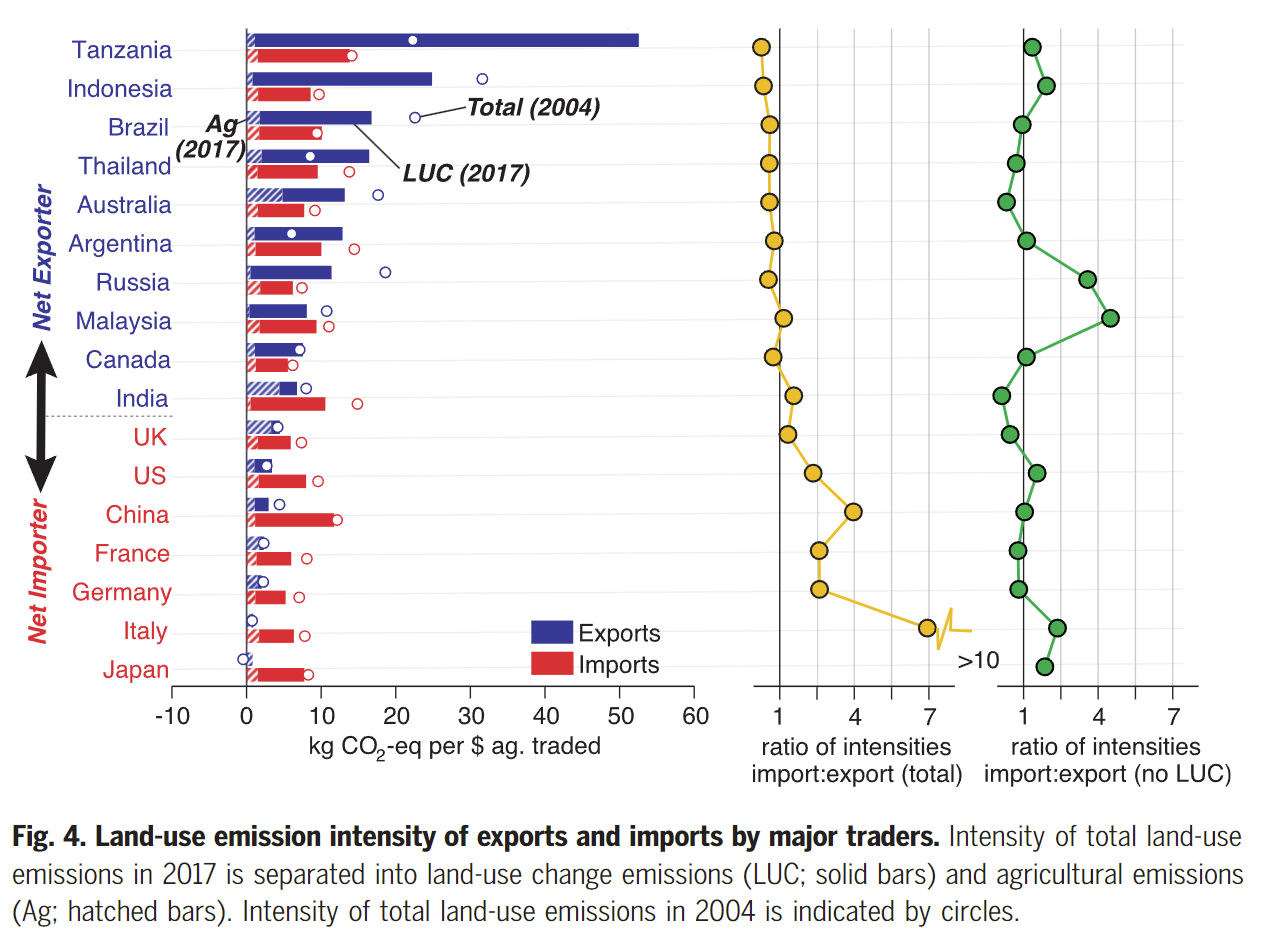
- The emissions intensity of exports from China, the US, Europe and Japan is much lower
- The exported land-use emissions from major exporters are usually dominated by a small subset of exported products
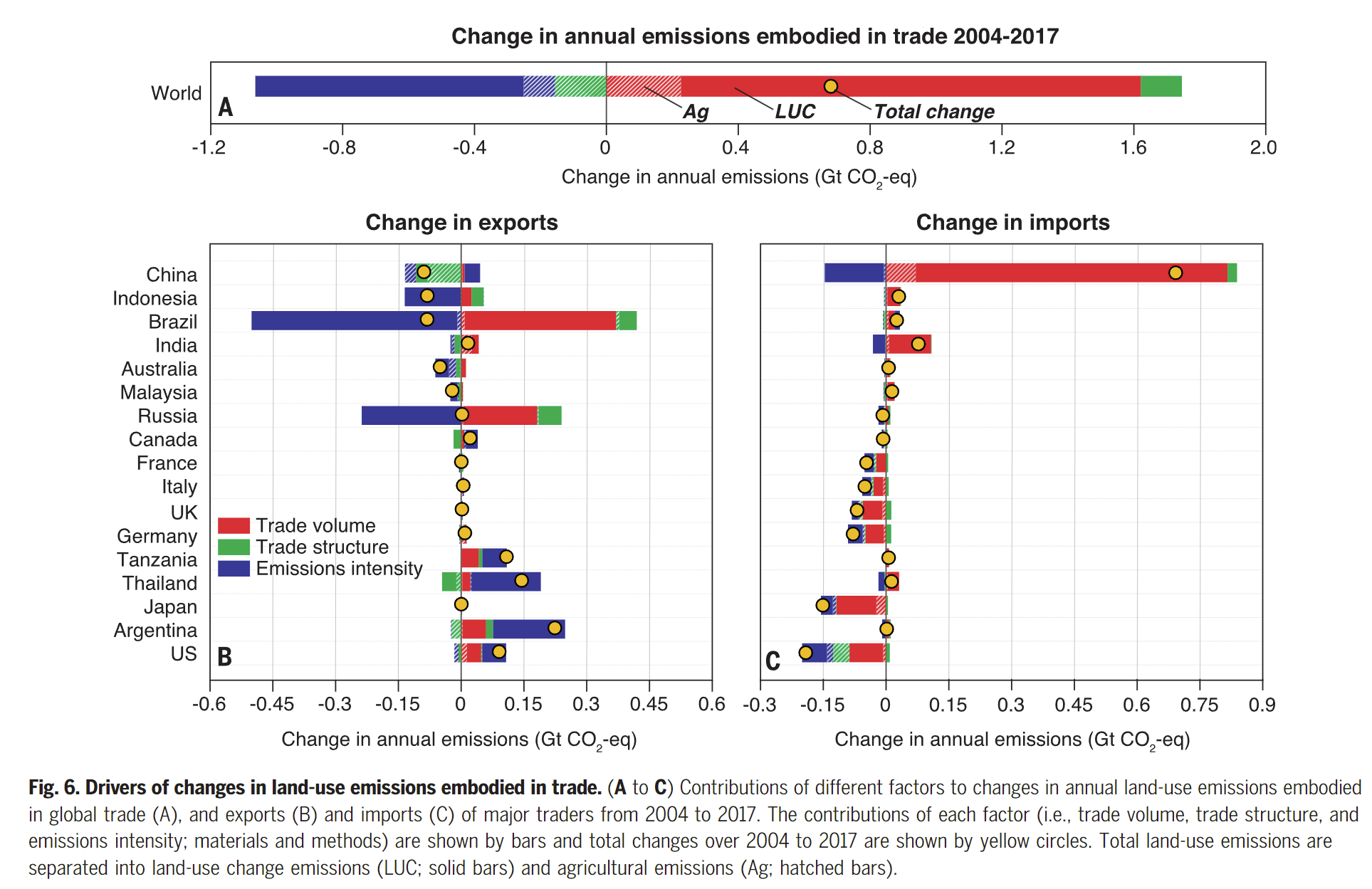
- Land use emissions embodied in global trade increased by 14% between 2014 and 2017; while the land area decreased by 5%
Coding Reference:






