Objective:
- Develop a global high-resolution enhanced vegetation index (EVI) to examine the spatiotemporal processes, influencing factors and implications of global urban vegetation change
Case:
Methodology:
Data Source
- UCDB, GUB, NTL
- Temperature
- CO2
- Urbanization intensity
Findings:
- Areas that had already been urbanized in 1990, which mainly included urbancenters, were the core areas of vegetation change
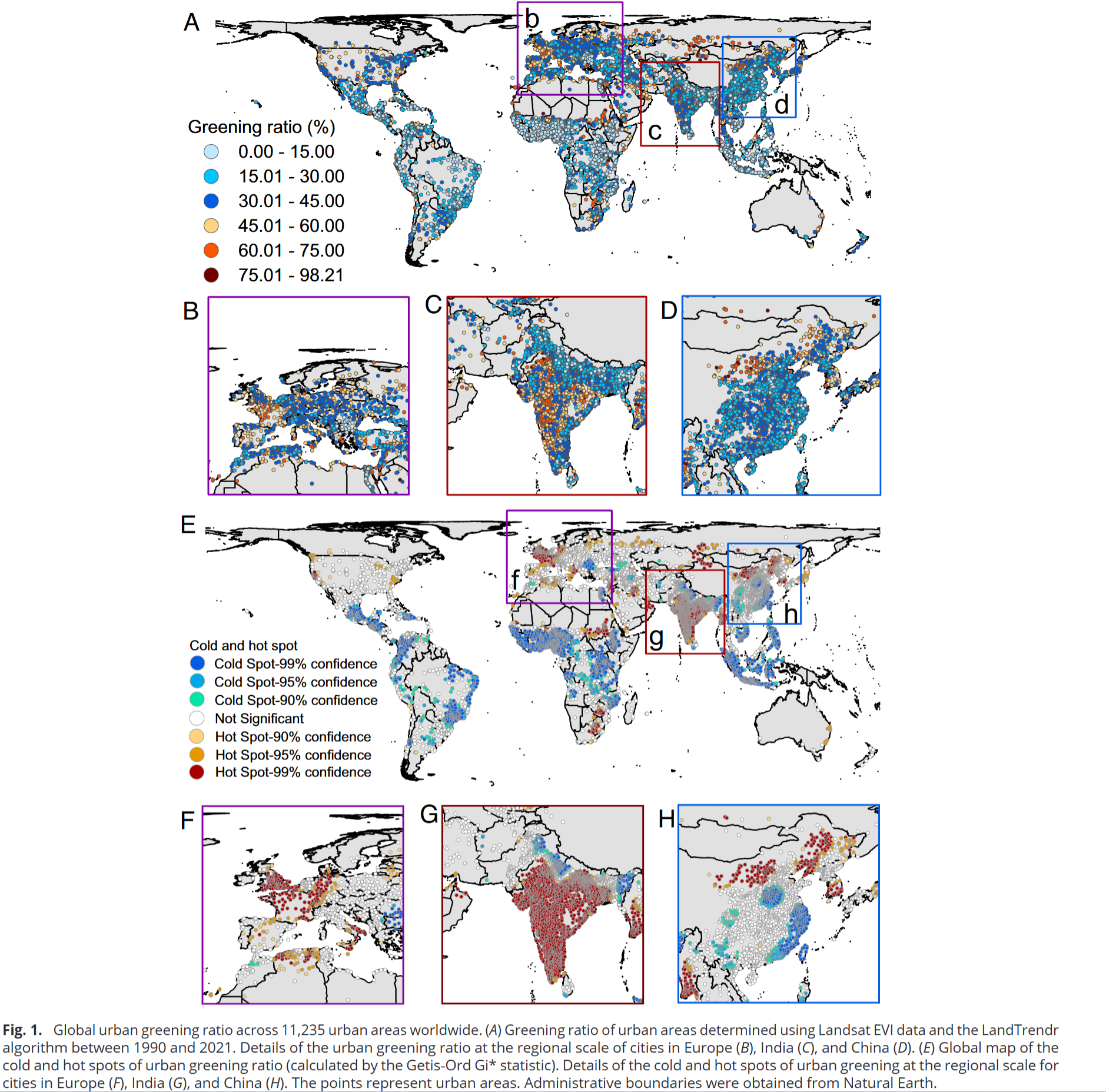
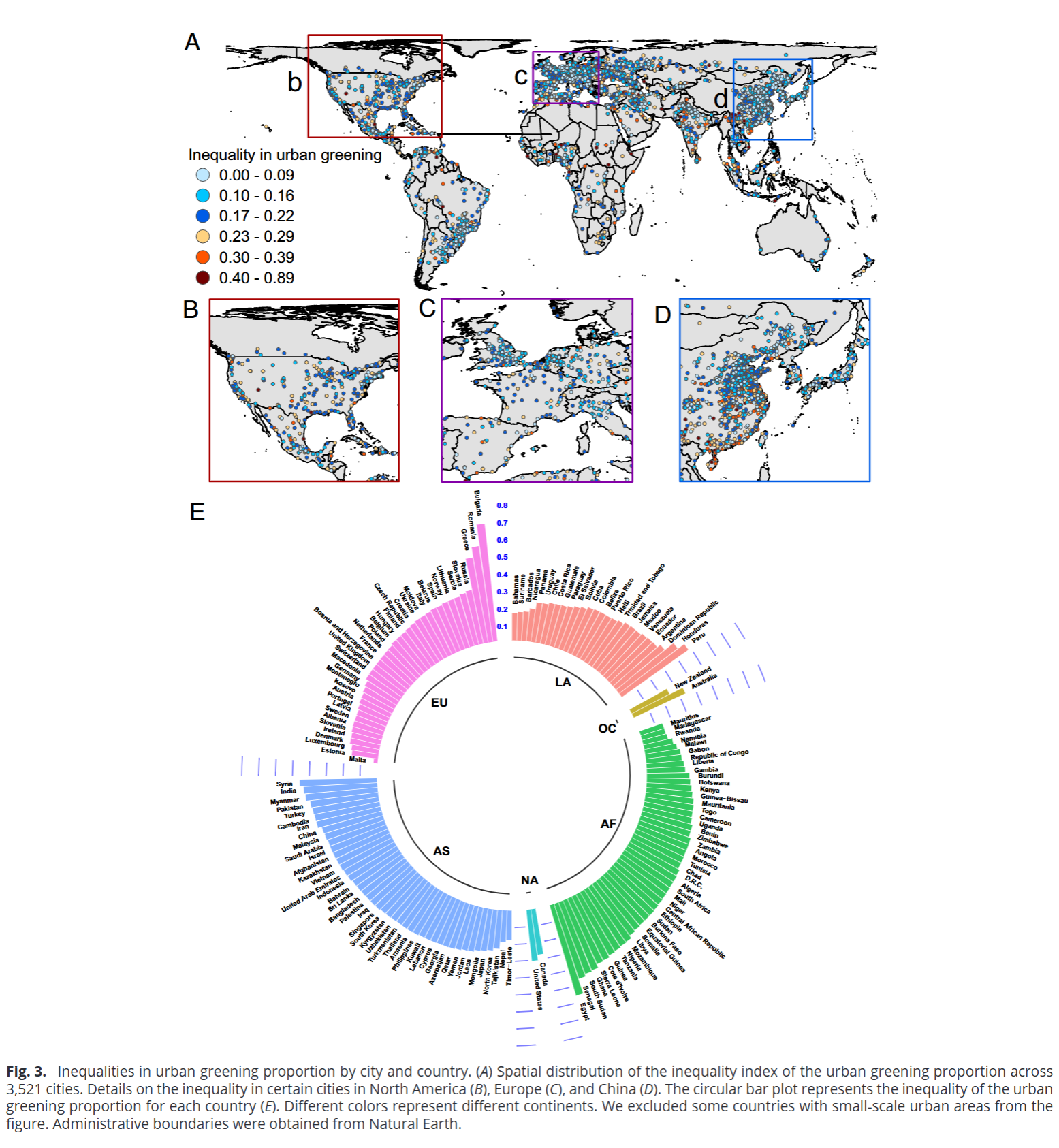
- Urban vegetation greening showed large inequalities across different spatial scales
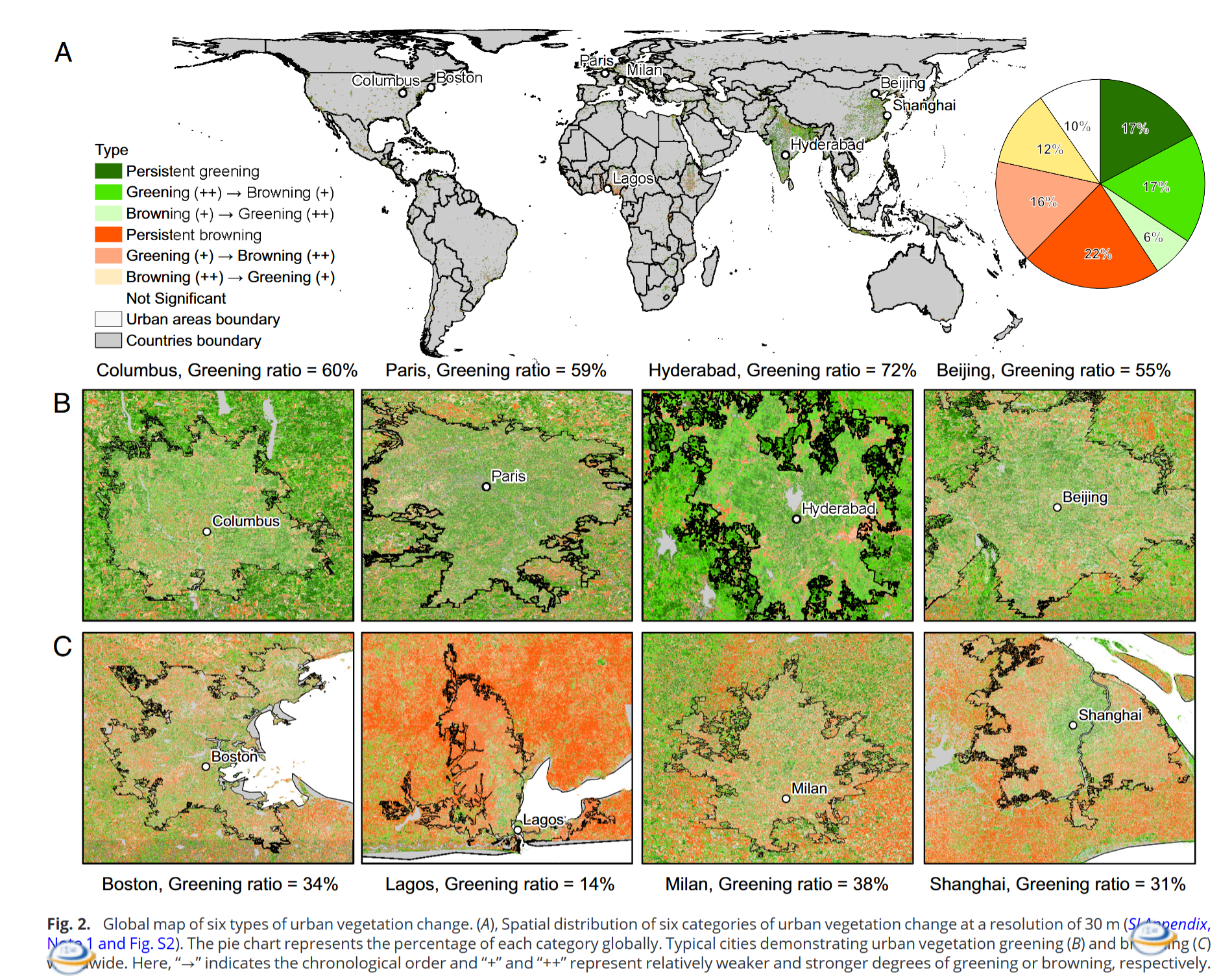
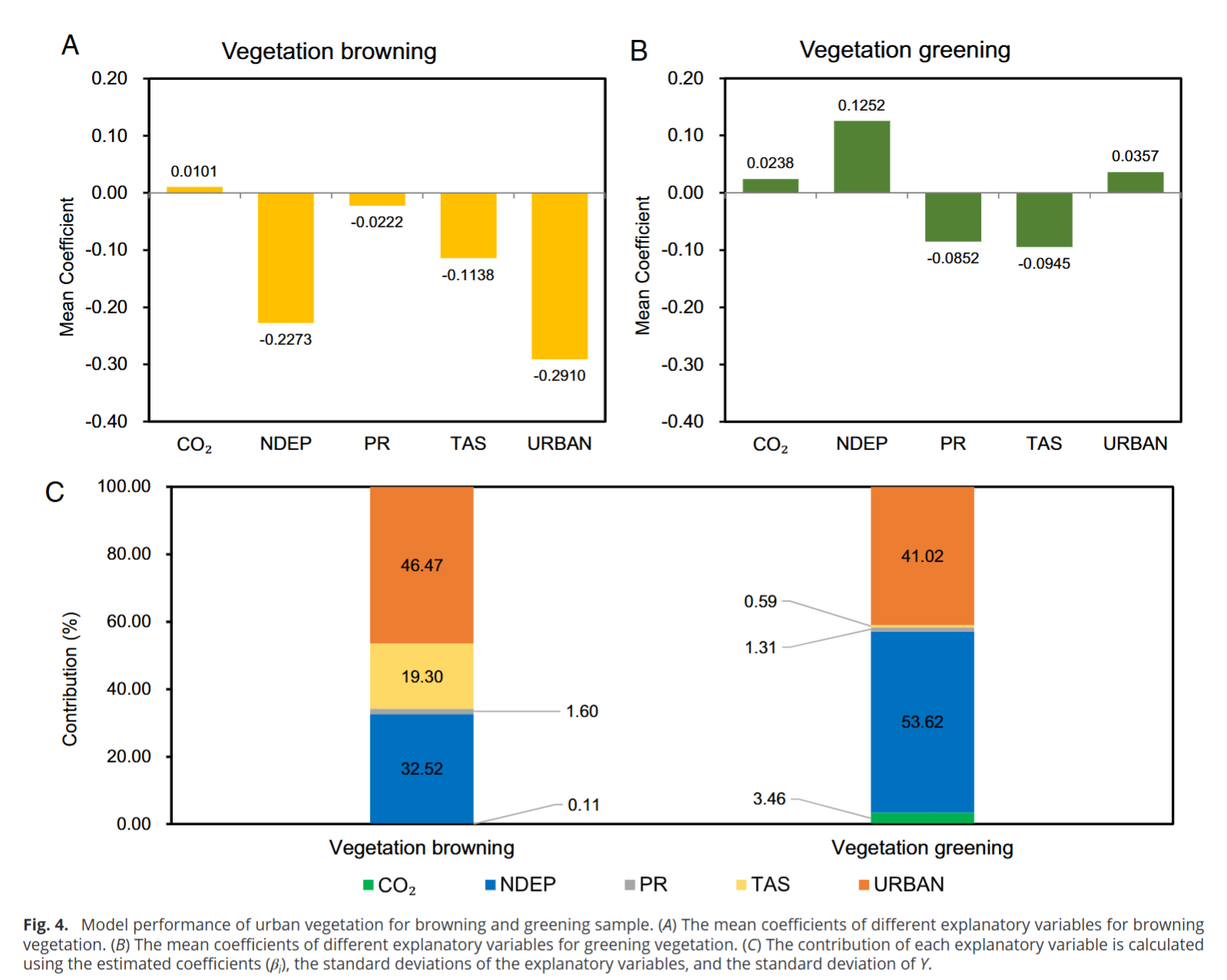
- Urbanization intensity played the dominant role in driving the vegetation borrowing trend; this phenomenon is more prevalent in urban fringe areas or regions with low urbanization intensity and rapid urbanization rate
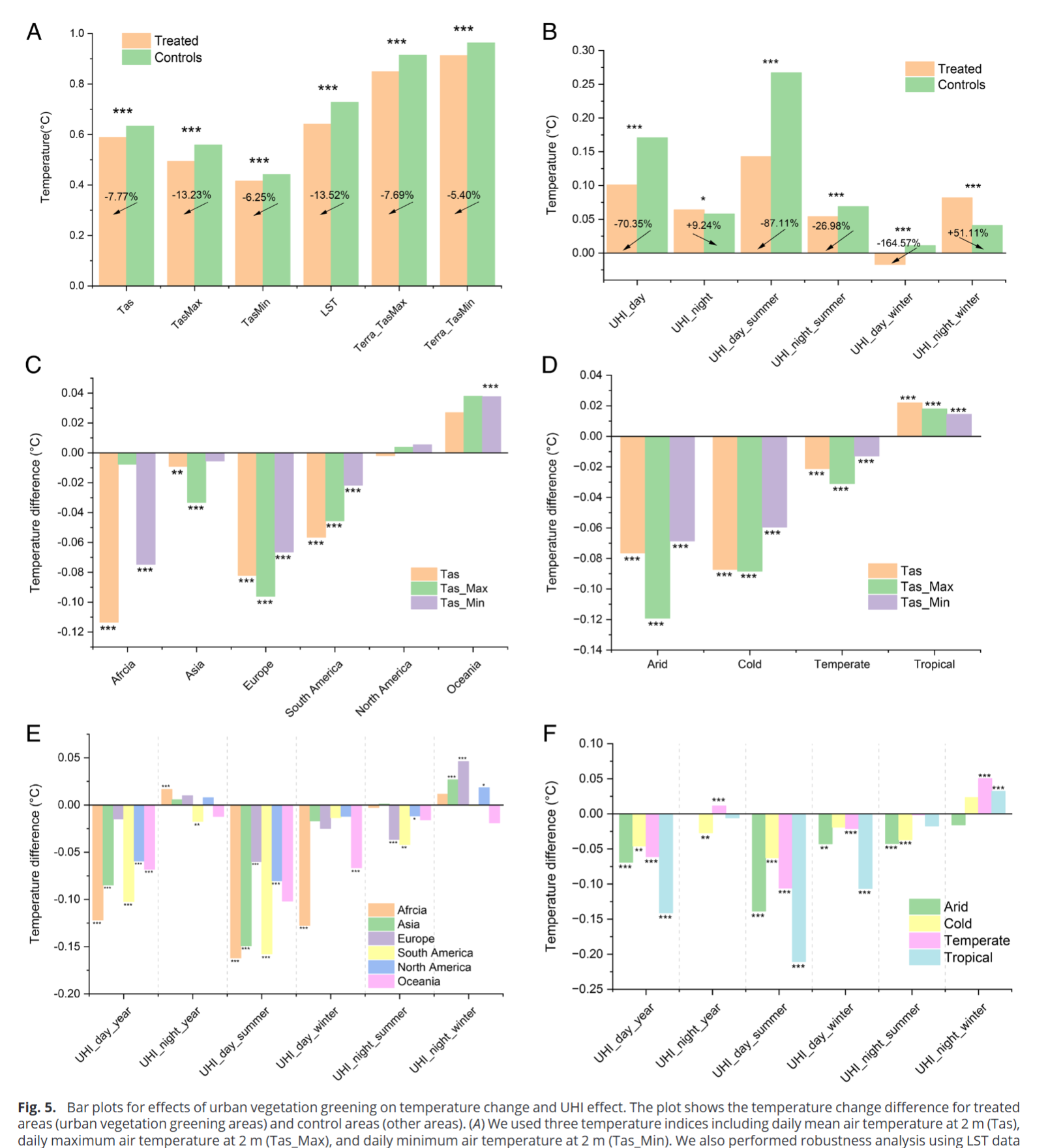
- Areas with urban vegetation greening had larger mitigation effects on climate change than other areas
Coding Reference:





