Objective:
- A clear understanding of the emissions of GHG and air pollutants from the Indian grid at a subnational scale has not existed before now.
Case:
Methodology:
- Reduced-order dispatch model
Data Source
Findings:
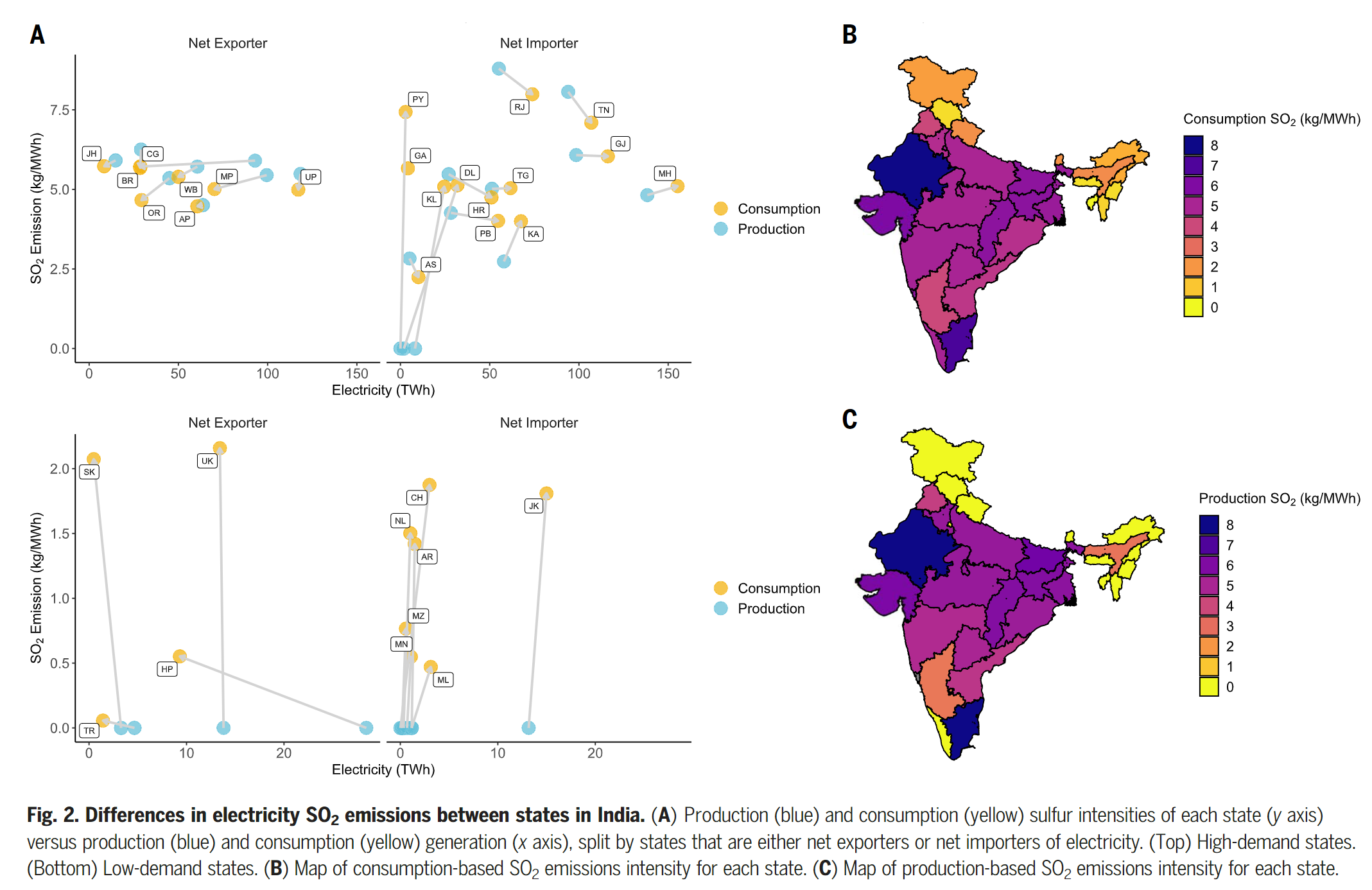
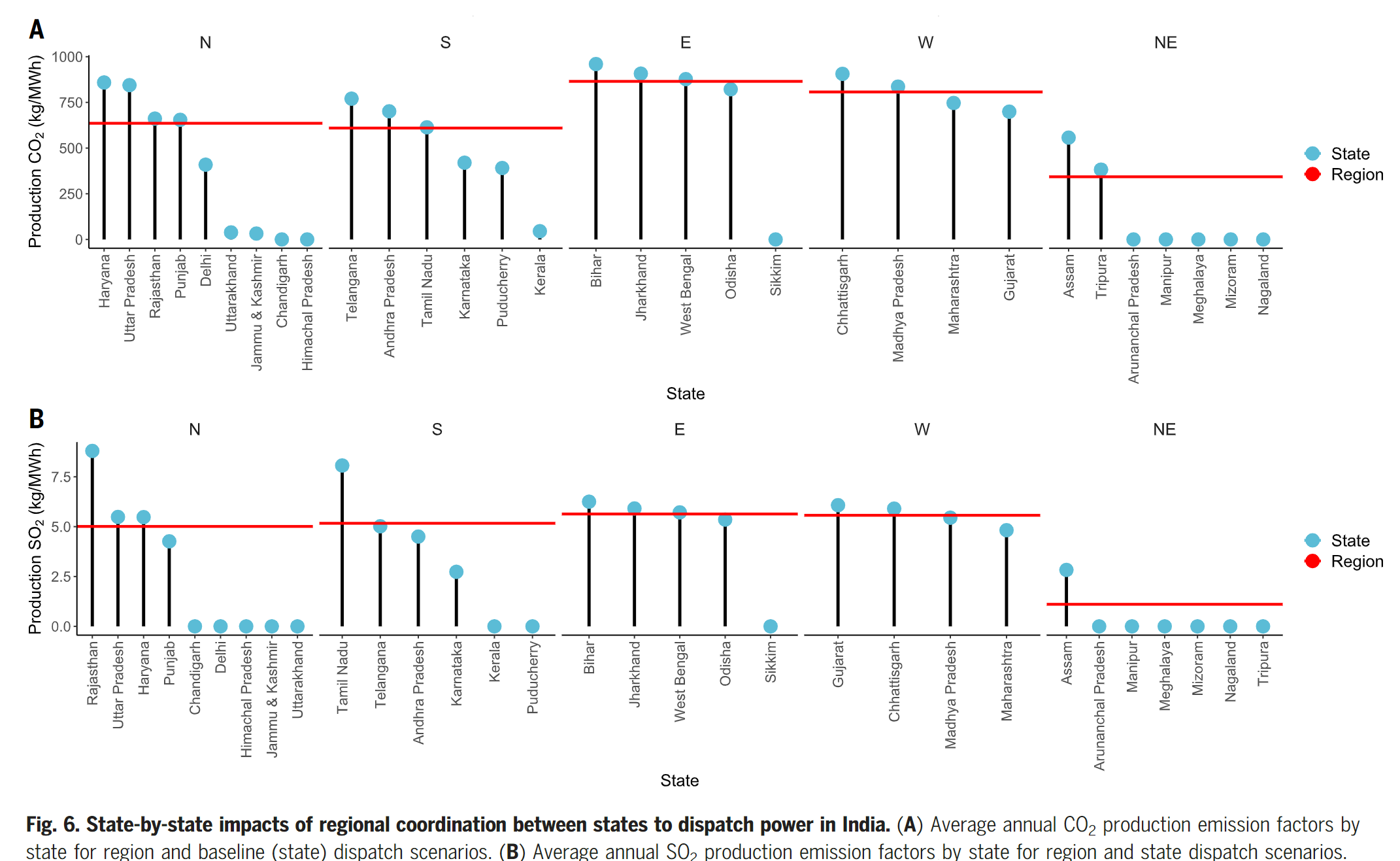
- Average nationawide CO2 and SO2 emissions intensities for electricity in India fail to capture the heterogeneity between states
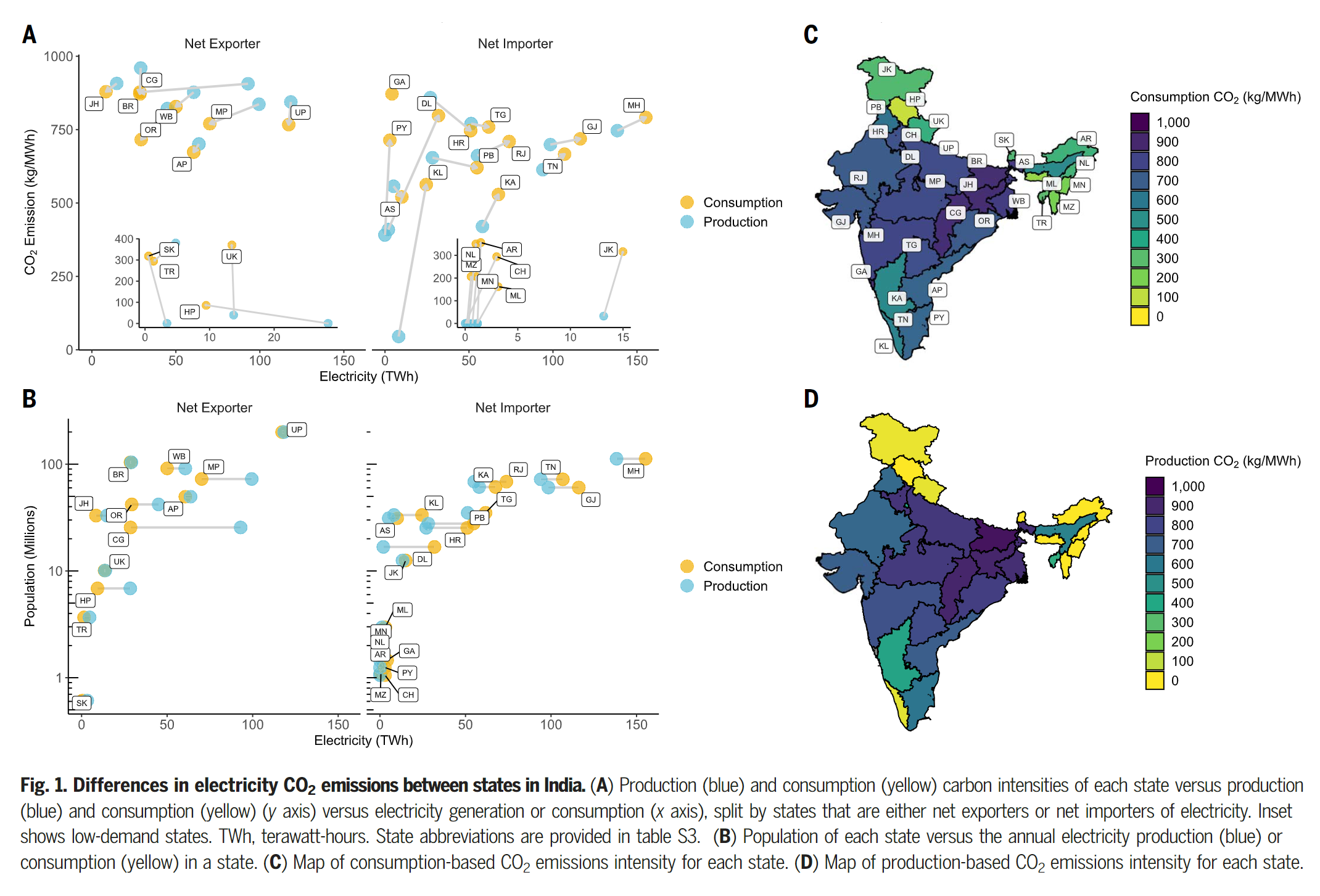
- The dominant global feature of embodied land-use emissions are large exports of emissiosn from countries such as Brazil, Indonesia, Argentina, Austrilia and Canada to consumers in developed regions such as the US, Europe and Japan
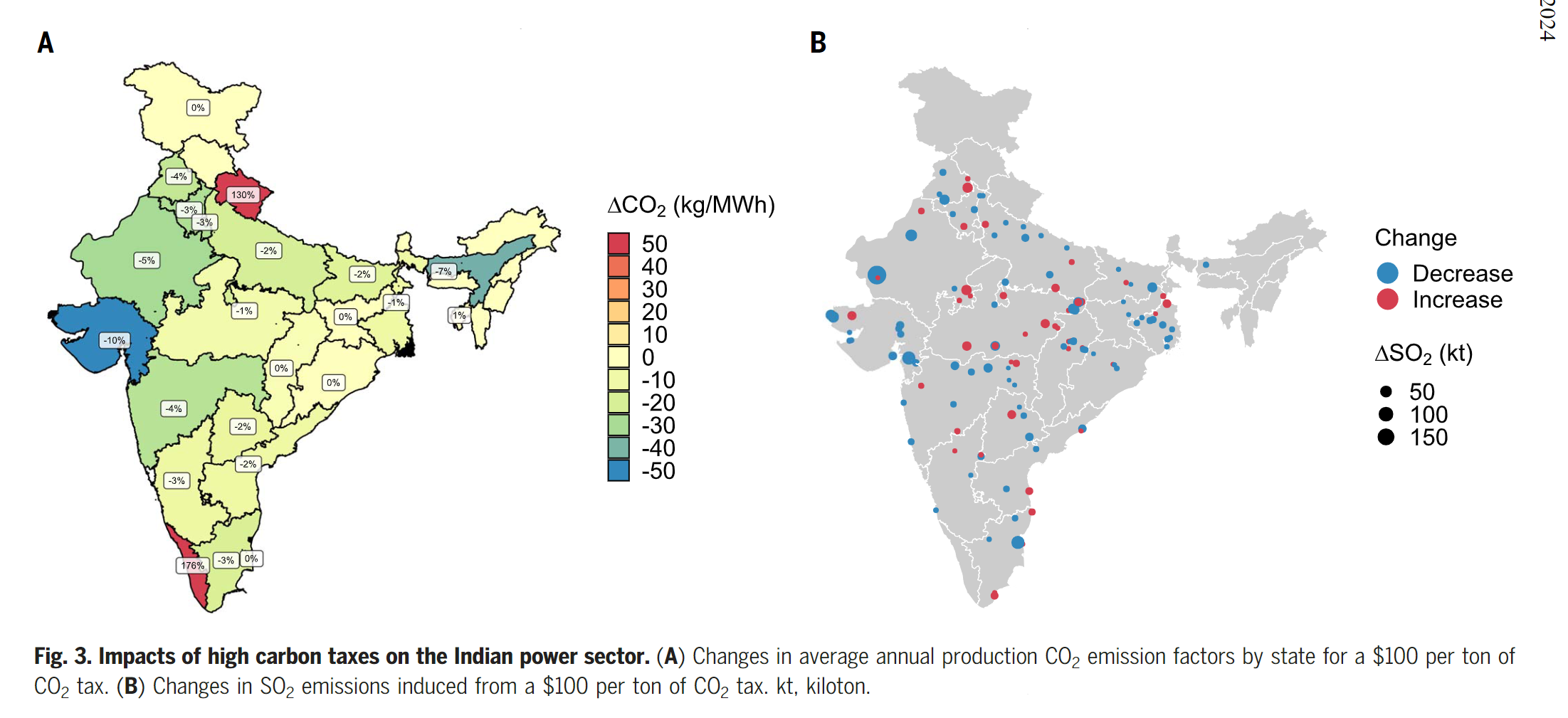
- A carbon tax results in a little short-term emissions reductions because there is not enough dispatchable lower emission spare capacity to substitute coal
- The implementation of sulfur controls will likely result in large reductions of SO2 emissions
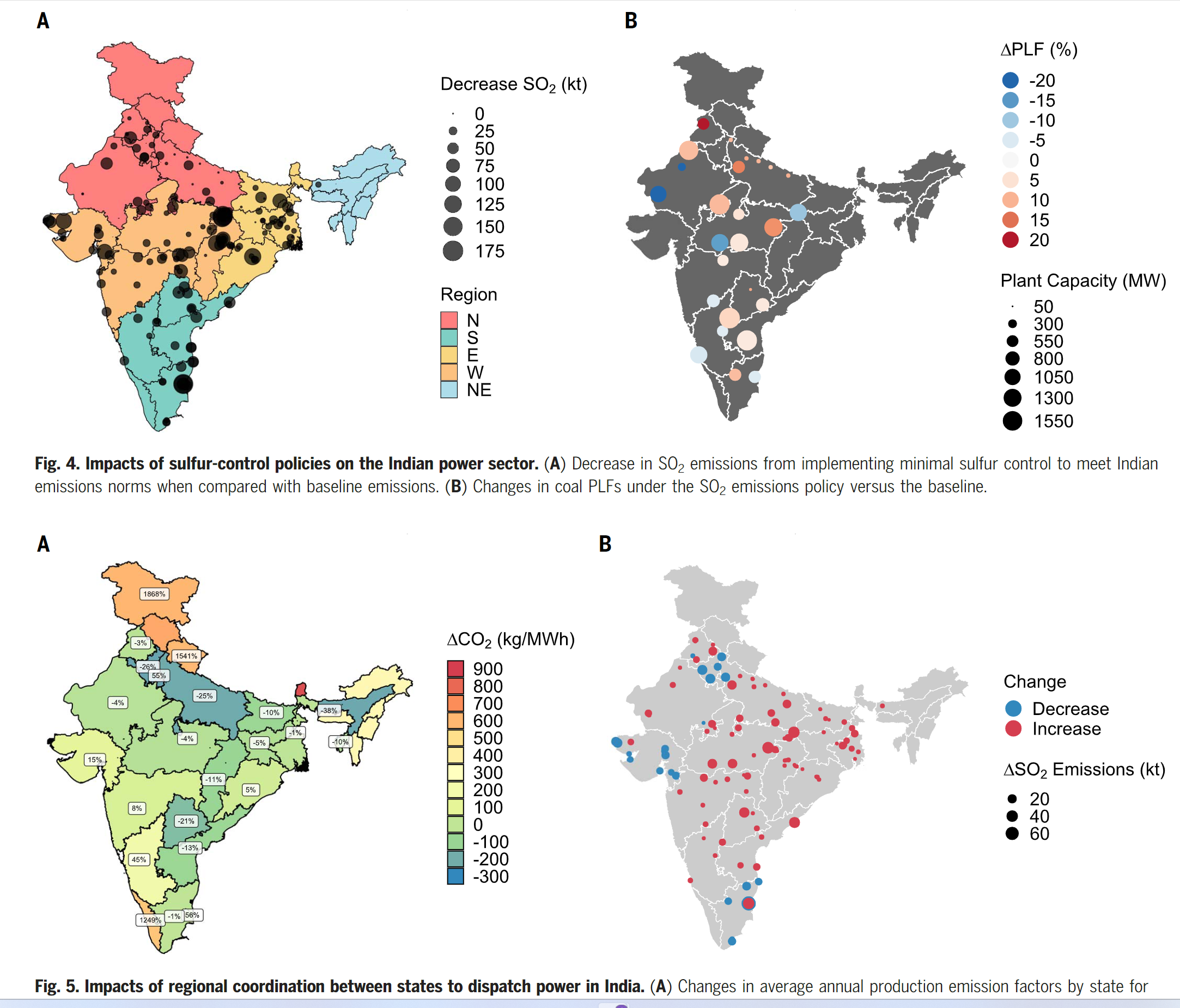
- The dispatching plants at the regional level would lead to a small increase in both SO2 and CO2 emissions with heterogeous cost effects on states.
Coding Reference:





